Top 8 Auto Plants In Usa List and Guide: How To Solve Scenario 1:…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for auto plants in usa
Navigating the complex landscape of auto plants in the USA can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers seeking reliable manufacturing partners. With the automotive industry contributing over $863 billion to the US economy in 2022, understanding the nuances of sourcing from this market is critical. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of automotive manufacturing plants, their applications, and key factors influencing supplier selection, such as costs and logistical considerations.
By equipping buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly Germany and Saudi Arabia—with actionable insights, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions. It covers everything from the strategic location of major manufacturing hubs like Michigan and Ohio, known for their skilled labor and robust supply chains, to the latest trends in electric vehicle production and sustainable practices.
Whether you are looking to establish partnerships, evaluate potential suppliers, or gain insights into industry standards, this guide serves as a vital resource. By understanding the landscape of auto plants in the USA, you can navigate the global market with confidence, ensuring that your sourcing aligns with both your operational needs and strategic goals.
Top 10 Auto Plants In Usa Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Car Assembly Plants – Production Capacity & EV Status
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
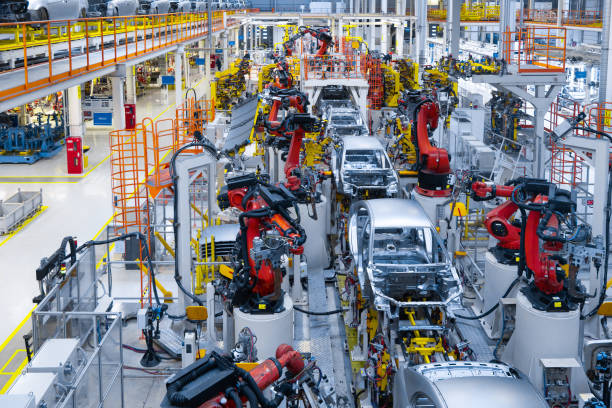
Introduction: Map of all car assembly plants in the US, their production capacity, and whether they produce electric vehicles.
2. OEM Plants – Key Locations
Domain: marklines.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: OEM Plants in the U.S.A. and Canada include various manufacturers such as GM, Ford, and Stellantis. Key locations for GM include Michigan (e.g., Bay City Powertrain, Flint Engine, and Lansing Delta Township), Indiana (e.g., Fort Wayne and Kokomo), and Texas (e.g., Arlington). Ford’s plants are located in Michigan (e.g., BlueOval Battery Park and Dearborn Truck), Ohio (e.g., Lima Engine), and Kentu…
3. Hyundai – Production Expansion and EV Investment
Domain: aljazeera.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Hyundai: Increasing production capacity at Metaplant in Georgia from 300,000 to 500,000 vehicles per year, including electric vehicles and hybrids. Planned investment of roughly $21bn in the US, including a $5.8bn steel plant in Louisiana for EV materials. Honda: Manufacturing next-generation Civic hybrid in Indiana instead of Mexico, with expected annual production of 210,000 starting May 2028. S…
4. Volkswagen – Wolfsburg Plant
Domain: manufacturingdigital.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Volkswagen’s Wolfsburg Plant: Size: 1,606 acres, Annual Production: 815,000+, Established: 1938. Hyundai’s Ulsan Plant: Size: 1,225 acres, Annual Production Capacity: 1.6 million+, Established: 1968. Tesla Gigafactory Shanghai: Size: 324 acres, Annual Production Capacity: 950,000+, Established: 2019. Ford River Rouge Complex: Size: 600 acres, Annual Production Capacity: 150,000+, Established: 1917…
5. Honda – Diverse Manufacturing
Domain: hondainamerica.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Honda manufactures a variety of products in the U.S., including: Honda and Acura vehicles (e.g., Honda Accord, CR-V, Acura Integra, TLX), aircraft (HondaJet Elite II), engines (L4, V6, Twin Turbo V6), transmissions, power equipment (e.g., ATVs, mini-tillers, snow blowers), and powersports products. Key manufacturing plants include Marysville, East Liberty, Alabama, Indiana, Timmonsville, Swepsonvi…
6. Automakers – Tariff Challenges
Domain: cnn.com
Registered: 1993 (32 years)
Introduction: American automakers face a variety of tariffs affecting the auto industry, including 25% duties on steel and aluminum imports, and upcoming levies on cars from Asia and Europe. Import taxes on goods, including cars and parts from Canada and Mexico, have been announced and are set to be implemented in April.
7. Assembly Magazine – Automotive Manufacturing Insights
Domain: assemblymag.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Automakers are constructing assembly plants and battery-making facilities in the Southern U.S., particularly in Georgia, Kentucky, and Tennessee. These facilities are significant in size, with some occupying areas equivalent to 60 football fields. The U.S. auto industry has announced over $110 billion in EV-related investments since 2018, with about half allocated to Southern states. Ford’s Tennes…
8. Ford – Automotive Innovation
Understanding auto plants in usa Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assembly Plants | Facilities where vehicles are assembled from various components. | Vehicle manufacturing, large-scale production | Pros: High production capacity; established supply chains. Cons: Initial setup costs can be high. |
| Parts Manufacturing Plants | Specialized in producing vehicle components and parts. | Supply of OEM parts, aftermarket parts | Pros: Focused expertise; lower production costs. Cons: Limited to specific parts; may require multiple suppliers. |
| Electric Vehicle (EV) Plants | Dedicated to producing electric vehicles and their components. | EV manufacturing, battery production | Pros: Growing market demand; innovative technologies. Cons: Higher initial investment; evolving regulations. |
| Research and Development (R&D) Facilities | Centers focused on automotive innovation and technology. | New model development, technology testing | Pros: Cutting-edge advancements; potential for partnerships. Cons: Long timelines; uncertain outcomes. |
| Re-manufacturing Plants | Facilities that refurbish used vehicles or parts for resale. | Circular economy, cost-effective parts supply | Pros: Sustainable practices; cost savings. Cons: Quality control challenges; limited scalability. |
What are the Characteristics of Assembly Plants in the U.S.?
Assembly plants are pivotal in the automotive manufacturing process, where various vehicle components come together to form a finished product. These facilities typically have high production capacities and are strategically located near suppliers to minimize logistics costs. Buyers should consider the plant’s production volume, lead times, and the flexibility to adapt to changing market demands when evaluating potential partnerships.
How Do Parts Manufacturing Plants Operate?
Parts manufacturing plants focus on creating specific vehicle components, such as engines, transmissions, and body parts. These plants are essential for both original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and aftermarket suppliers. When purchasing from these plants, B2B buyers should assess the quality of parts, consistency in supply, and the plant’s ability to meet regulatory standards, as these factors can significantly impact production efficiency.
What Makes Electric Vehicle Plants Unique?
Electric vehicle (EV) plants are specialized facilities that manufacture electric vehicles and their associated components, such as batteries and electric drivetrains. The rise in global demand for sustainable transportation has led to significant investment in EV plants. Buyers looking to source from these facilities should evaluate the plant’s technological capabilities, production scalability, and compliance with environmental regulations, as these aspects will influence the long-term viability of their investments.
Why are R&D Facilities Important for Automotive Innovation?
Research and development (R&D) facilities play a crucial role in advancing automotive technology and developing new vehicle models. These centers focus on innovation, testing new materials, and integrating cutting-edge technology. For B2B buyers, partnering with R&D facilities can provide access to groundbreaking technologies and potential collaborations. However, they should be prepared for longer timelines and the inherent risks associated with developing new products.
What are the Benefits of Re-manufacturing Plants?
Re-manufacturing plants focus on refurbishing used vehicles or parts to extend their lifecycle and reduce waste. This approach aligns with the growing trend toward sustainability in the automotive industry. B2B buyers can benefit from cost savings and a reliable supply of refurbished parts. However, they must also consider quality control measures and the scalability of re-manufactured products, as these factors can affect overall product reliability.
Key Industrial Applications of auto plants in usa
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of auto plants in usa | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Production of Electric Vehicles (EVs) | Access to advanced technologies and sustainable solutions, boosting market competitiveness. | Evaluation of local regulations for EV production and incentives for sustainable practices. |
| Supply Chain Logistics | Component Manufacturing and Assembly | Reduced lead times and costs through localized production, enhancing supply chain efficiency. | Proximity to major suppliers and transportation networks; quality assurance standards. |
| Aftermarket Services | Parts Production and Distribution | Opportunities for recurring revenue through aftermarket parts and services, increasing customer loyalty. | Understanding of warranty and service requirements; compliance with international standards. |
| Research and Development | Innovation in Automotive Technologies | Collaboration opportunities with leading manufacturers to drive innovation and product development. | Access to skilled labor and research institutions; intellectual property considerations. |
| Export and Trade | Vehicle Assembly for International Markets | Enhanced export capabilities, tapping into emerging markets with tailored products. | Compliance with international trade regulations and tariffs; understanding of local market demands. |
How Are Auto Plants in the USA Used in Electric Vehicle Production?
Auto plants in the USA play a crucial role in the production of electric vehicles (EVs), leveraging advanced manufacturing technologies to create sustainable transportation solutions. For international buyers, especially from regions like Europe and the Middle East, sourcing EVs from US plants can enhance their portfolios with cutting-edge technologies. Buyers must consider local regulations regarding EV production, including incentives for sustainable practices, to maximize value.
What is the Role of Auto Plants in Supply Chain Logistics?
In the realm of supply chain logistics, auto plants in the USA are vital for component manufacturing and assembly. By producing parts locally, businesses can significantly reduce lead times and transportation costs, enhancing overall supply chain efficiency. For international B2B buyers, key considerations include the proximity to major suppliers and transportation networks, as well as adherence to quality assurance standards to ensure reliability.
How Do Auto Plants Support Aftermarket Services?
Auto plants also contribute to the aftermarket services sector by producing and distributing vehicle parts. This creates opportunities for businesses to generate recurring revenue through aftermarket sales, fostering customer loyalty. International buyers must understand warranty and service requirements, as well as compliance with international standards, to effectively navigate the aftermarket landscape.
What Innovations Can Be Expected from Research and Development at Auto Plants?
Research and development in automotive technologies is another significant application of auto plants in the USA. These facilities often collaborate with leading manufacturers to innovate and develop new automotive solutions. For international buyers, access to skilled labor and research institutions is crucial, as well as considerations related to intellectual property to protect innovations.
How Do Auto Plants Facilitate Export and Trade?
Finally, auto plants in the USA enhance export capabilities by assembling vehicles tailored for international markets. This allows businesses to tap into emerging markets, particularly in Africa and South America, where demand for vehicles is growing. Buyers must be aware of international trade regulations and tariffs, as well as local market demands, to successfully navigate the complexities of exporting vehicles.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘auto plants in usa’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex Supply Chains for Automotive Components
The Problem: B2B buyers in the automotive sector often face challenges in managing complex supply chains, particularly when sourcing components from multiple auto plants across the USA. Delays in parts delivery can lead to production halts, increased costs, and ultimately, missed deadlines. Buyers may struggle with inconsistent quality, varying lead times, and the reliability of suppliers, especially when coordinating with plants located in different states.
The Solution: To overcome these challenges, buyers should invest in robust supply chain management systems that allow for real-time tracking of parts and components. Establishing strong relationships with local Tier 1 and Tier 2 suppliers within the Midwest and South can also enhance reliability. Utilize data analytics to monitor supplier performance and predict potential disruptions. When sourcing components, leverage platforms that provide transparency into supplier capabilities and production timelines. Additionally, consider implementing just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices to reduce holding costs while ensuring that essential components are available when needed. Engaging in regular communication with suppliers can further foster trust and facilitate quicker resolutions to any issues that arise.
Scenario 2: Addressing Labor Shortages and Skill Gaps in Auto Manufacturing
The Problem: The U.S. automotive industry is currently facing significant labor shortages, exacerbated by a skills gap among potential workers. B2B buyers may find it increasingly difficult to source skilled labor for assembly lines and specialized manufacturing roles, which can impact production efficiency and product quality. This shortage is particularly pronounced in regions with a high concentration of auto plants, such as Michigan and Ohio, where competition for skilled workers is fierce.
The Solution: Buyers should proactively collaborate with educational institutions and vocational training programs to develop a pipeline of skilled labor. Partnering with local community colleges and universities can facilitate internships and apprenticeships, giving students hands-on experience in automotive manufacturing. Additionally, companies can invest in training programs for current employees to upskill their workforce, thereby improving retention rates and productivity. Offering competitive wages and benefits can also attract top talent. To streamline recruitment, consider utilizing specialized job boards and recruitment agencies that focus on the automotive sector, ensuring that you reach candidates with the right skill sets and experience.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with Regulatory Standards in Auto Manufacturing
The Problem: Navigating the complex regulatory environment in the U.S. automotive industry can be a daunting task for B2B buyers. Compliance with federal and state regulations, including safety, emissions, and labor laws, can lead to significant operational challenges. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, production delays, and damage to a company’s reputation, creating substantial risks for international buyers unfamiliar with U.S. regulations.
The Solution: To mitigate compliance risks, buyers should invest in legal counsel and compliance experts who specialize in the automotive sector. Conducting thorough due diligence on potential auto plants before entering into partnerships is crucial. Buyers should also establish a compliance management system that monitors changes in regulations and ensures that all operational practices align with current laws. Regular training sessions for employees on compliance issues can help cultivate a culture of adherence to regulations. Additionally, consider joining industry associations that provide resources and updates on regulatory changes, allowing buyers to stay informed and prepared for any shifts in compliance requirements. By proactively managing compliance, buyers can protect their investments and foster sustainable operations in the U.S. automotive market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for auto plants in usa
What Are the Key Materials Used in Automotive Manufacturing in the USA?
In the automotive manufacturing landscape of the USA, selecting the right materials is crucial for optimizing product performance, cost efficiency, and regulatory compliance. Below are four common materials utilized in auto plants, analyzed from a B2B perspective.
How Does Steel Contribute to Automotive Manufacturing?
Steel is the backbone of the automotive industry, primarily used for structural components, body panels, and frames. Its key properties include high tensile strength, excellent formability, and good weldability, making it ideal for various automotive applications. Steel can withstand high temperatures and pressures, which is vital for safety and durability.
Pros: Steel is relatively low-cost and widely available, which contributes to its popularity in automotive manufacturing. It also offers excellent impact resistance and can be recycled, aligning with sustainability goals.
Cons: Steel is susceptible to corrosion, which can lead to long-term durability issues if not properly treated. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex and energy-intensive, potentially increasing overall production costs.
For international buyers, understanding the compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 (for structural steel) is essential, as these standards ensure quality and safety.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Vehicle Production?
Aluminum is increasingly favored in the automotive industry due to its lightweight nature, which contributes to fuel efficiency and performance. With properties such as high corrosion resistance and good thermal conductivity, aluminum is particularly useful in engine components and body structures.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its weight reduction capability, which can lead to significant improvements in fuel economy. Its resistance to corrosion extends the lifespan of components, making it a durable choice.
Cons: Aluminum can be more expensive than steel, and its manufacturing processes, such as extrusion and die-casting, can be complex and require specialized equipment.
International buyers should consider compliance with standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions, which ensures material quality and performance.
Why Is Plastic Becoming More Prominent in Automotive Applications?
Plastics are increasingly utilized in automotive manufacturing for components such as dashboards, bumpers, and interior fittings. Key properties include lightweight, corrosion resistance, and the ability to be molded into complex shapes.
Pros: The lightweight nature of plastics contributes to overall vehicle weight reduction, enhancing fuel efficiency. They also offer design flexibility and can be produced at a lower cost compared to metals.
Cons: Plastics may not offer the same level of durability as metals in high-stress applications. They can also degrade under UV exposure unless treated, which may limit their use in exterior components.
For international buyers, ensuring compliance with standards like ISO 9001 for quality management systems is critical when sourcing plastic materials, as it affects product reliability.
How Does Composite Material Enhance Vehicle Performance?
Composite materials, often a blend of fibers and resins, are gaining traction in automotive manufacturing, particularly for high-performance vehicles. Their key properties include high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent fatigue resistance.
Pros: Composites offer significant weight savings, which can lead to improved performance and fuel efficiency. They are also highly resistant to corrosion and can be tailored for specific applications.
Cons: The cost of composites can be high, and the manufacturing processes are often more complex, requiring specialized knowledge and equipment.
For international buyers, understanding compliance with standards such as ASTM D3039 for composite materials is essential to ensure product quality and safety.
Summary of Material Selection for Automotive Manufacturing
| Material | Typical Use Case for auto plants in usa | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components, body panels | Low cost, high strength | Corrosion susceptibility | Low |
| Aluminum | Engine components, body structures | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Plastic | Dashboards, bumpers, interior fittings | Design flexibility, low cost | Less durable, UV degradation | Low |
| Composite | High-performance vehicle components | High strength-to-weight ratio | High cost, complex processes | High |
This guide provides international B2B buyers with essential insights into material selection for automotive manufacturing in the USA, emphasizing compliance, performance, and cost considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for auto plants in usa
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process in U.S. Auto Plants?
The manufacturing process in U.S. automotive plants is a complex and highly coordinated series of stages that ensure the production of vehicles meets both quality standards and market demands. Here’s a breakdown of the main stages involved:
Material Preparation: What Happens Before Production Begins?
The first stage, material preparation, involves sourcing and preparing raw materials. This includes metals, plastics, and composites that will be used in various vehicle components. Suppliers are often selected based on their ability to meet stringent quality standards, ensuring that only the best materials are used. Advanced technologies like laser cutting and CNC machining are employed to shape these materials accurately before they proceed to the next stage.
Forming: How Are Components Shaped for Assembly?
The forming stage transforms raw materials into specific shapes required for vehicle components. Techniques such as stamping, forging, and casting are commonly used. Stamping, for example, involves using hydraulic presses to shape metal sheets into parts like doors and hoods. This stage requires precision machinery and highly skilled operators to ensure that components meet exact specifications, which is critical for later assembly.
Assembly: What Techniques Ensure Efficient Vehicle Construction?
In the assembly stage, the various components come together. This process often employs a mix of manual labor and automated systems, including robotics. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and assembly lines streamline the process, allowing for high efficiency and reduced labor costs. Techniques such as lean manufacturing are implemented to minimize waste and optimize workflow, ensuring that the assembly is both fast and effective.
Finishing: How Is the Final Product Prepared for Market?
The finishing stage includes painting, coating, and quality checks. Advanced painting technologies, such as electrocoating and robotic painting, ensure a uniform finish while also providing protection against corrosion. Following this, vehicles undergo comprehensive inspections to verify that they meet all design and safety standards. This is a critical step, as any defects at this stage can affect the vehicle’s performance and safety.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are in Place in U.S. Auto Plants?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the automotive industry, given the safety and reliability standards required for vehicles. U.S. auto plants adhere to various international and industry-specific standards to ensure quality throughout the manufacturing process.
Which International Standards Are Essential for Automotive Manufacturing?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international standards that guide quality management systems across industries, including automotive manufacturing. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that processes are standardized and continually improved. Furthermore, automotive-specific standards like IATF 16949 are vital as they focus on the quality management system specifically for automotive production and service parts organizations.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Production Process?
Quality control (QC) is integrated into various stages of the manufacturing process through different checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint assesses the quality of incoming materials and components. Suppliers must meet predefined specifications to pass this stage.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, IPQC ensures that processes are being followed correctly. This involves regular inspections and testing of components at various points in the production line.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the finished vehicles undergo thorough inspections and testing to ensure they meet all safety and performance standards before they are released to the market.
How Are Common Testing Methods Utilized in Quality Assurance?
Testing methods in automotive quality assurance include non-destructive testing (NDT), durability testing, and functional testing. NDT methods, such as ultrasonic and radiographic testing, help identify defects without damaging components. Durability testing simulates real-world conditions to assess vehicle performance over time, while functional testing evaluates specific systems, such as brakes and electronics, to ensure they operate as intended.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control processes is crucial. Here are some actionable steps:
What Audit Practices Should Buyers Implement?
Conducting audits is one of the most effective ways to verify a supplier’s quality control measures. Buyers should establish a schedule for regular audits to assess compliance with industry standards and internal protocols. This can include reviewing documentation, inspecting production facilities, and interviewing personnel involved in quality assurance.
How Can Buyers Utilize Reports and Third-Party Inspections?
Buyers should request quality assurance reports from their suppliers, detailing their compliance with relevant standards and highlighting any corrective actions taken. Additionally, engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s capabilities and adherence to quality standards. These inspections can help identify potential risks and ensure that the supplier meets the buyer’s expectations.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must be aware of specific nuances when dealing with U.S. automotive suppliers. Understanding local regulations, cultural differences, and logistical challenges is vital for establishing successful partnerships. For example, buyers from Europe may need to consider additional certifications required for vehicles sold in their markets, such as the CE marking, which indicates compliance with European safety standards.
Moreover, maintaining open communication with suppliers about quality expectations and timelines can help avoid misunderstandings and ensure that the final product meets the buyer’s needs. Leveraging technology, such as supply chain management software, can enhance visibility and collaboration throughout the manufacturing process, benefiting both parties.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures employed in U.S. automotive plants are designed to ensure high standards of safety, performance, and reliability. By understanding these processes, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions and establish strong partnerships with suppliers. Implementing robust verification practices and being aware of regional nuances will further enhance their success in sourcing automotive products from the U.S. market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘auto plants in usa’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of procuring automotive plants in the USA. With the US automotive industry being a significant player in the global market, understanding the key steps in sourcing can streamline your procurement process and enhance your operational efficiency.
Step 1: Identify Your Sourcing Needs
Begin by clearly defining what you need from the automotive plants. This includes understanding the types of vehicles you want to manufacture, the scale of production, and specific technologies (e.g., electric vehicles). A well-defined sourcing need will guide your selection process and ensure alignment with your business goals.
Step 2: Research Major Automotive Hubs
Focus your attention on the primary automotive manufacturing regions in the USA, particularly the Midwest and South, where most plants are located. Michigan, Ohio, and Kentucky are notable hubs, housing key players like Ford, General Motors, and Toyota. Understanding these regional dynamics will help you identify potential suppliers that match your requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making any commitments, conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Look for company profiles, financial health, production capabilities, and references from existing clients. This step is crucial to ensure that the suppliers can meet your quality standards and production timelines.
- Request Case Studies: Analyze past projects similar to your needs.
- Check Certifications: Ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Step 4: Assess Labor Market and Workforce Skills
Investigate the local labor market where the plants are situated. The automotive industry relies heavily on a skilled workforce, particularly in engineering, assembly, and machining. Regions like Michigan boast a rich talent pool due to their longstanding automotive history, which can be beneficial for your operations.
Step 5: Review Logistics and Supply Chain Accessibility
Consider the logistics involved in sourcing from specific plants. Proximity to suppliers and transportation networks can significantly impact your production efficiency. Evaluate the availability of major highways, railroads, and shipping routes that facilitate the movement of parts and finished products.
Step 6: Understand Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Familiarize yourself with the regulatory landscape governing automotive manufacturing in the USA. Compliance with local, state, and federal regulations is essential to avoid legal issues and ensure smooth operations. This includes environmental regulations, labor laws, and safety standards.
Step 7: Negotiate Contracts and Terms
Once you have selected your preferred suppliers, focus on negotiating favorable contract terms. Ensure that your agreements cover critical aspects such as pricing, delivery schedules, quality assurance measures, and penalties for non-compliance. Clear terms will protect your interests and foster a strong supplier relationship.
By following these steps, international B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing landscape of automotive plants in the USA, positioning their businesses for success in a competitive market.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for auto plants in usa Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing from Auto Plants in the USA?
When engaging in B2B sourcing from auto plants in the USA, understanding the cost structure is critical for negotiating favorable terms. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as steel, aluminum, and plastics, significantly impacts overall pricing. Fluctuations in global commodity prices can lead to variations in material costs. Buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers that offer competitive pricing or have long-term contracts to stabilize costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs in the automotive sector are a significant factor, particularly in regions like Michigan, where a highly skilled workforce is available. Hourly wages for skilled workers can vary based on location and union agreements. International buyers should factor in potential labor shortages and associated wage increases.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, maintenance, and facility operations. Auto plants in the Midwest often benefit from established infrastructures, which can lead to lower overhead costs compared to newer facilities in less developed areas.
-
Tooling: The expenses associated with tooling and machinery setup can be substantial. Custom tooling for specific vehicle parts can increase upfront costs but may lead to lower per-unit costs over time as production volume increases.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous QC processes incurs costs. Buyers should inquire about the certifications and standards adhered to by manufacturers to mitigate risks associated with product defects.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including transportation and warehousing, can vary greatly depending on the destination and the efficiency of the supply chain. Proximity to major transportation hubs in the Midwest can lower logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a margin to cover profit and reinvestment. Understanding the margin expectations of potential suppliers can help buyers negotiate more effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Decisions?
Several factors can influence the pricing structure when sourcing from US auto plants:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can affect pricing. Higher order volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs, making it essential for buyers to assess their needs and negotiate favorable terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products often incur higher costs due to the additional engineering and manufacturing processes involved. Buyers should clearly define specifications to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products with higher quality standards or specific certifications may command a premium. Buyers should evaluate whether these certifications are necessary for their target markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established manufacturers with a track record of delivering quality products may charge more but can offer peace of mind regarding product performance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery (Incoterms) can significantly impact total costs. Different Incoterms determine who bears the risk and cost at various points in the supply chain, which can affect pricing negotiations.
What Are the Best Practices for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigating the complexities of sourcing from US auto plants requires strategic considerations:
-
Negotiation: Engage in thorough negotiations to explore price flexibility based on volume and long-term commitments. Leverage market insights to propose competitive terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Calculate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) by considering not only the purchase price but also logistics, tariffs, and potential currency fluctuations. This comprehensive view can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of pricing fluctuations due to market conditions, seasonal demand, and geopolitical factors. Staying informed about these trends can help in timing purchases more effectively.
-
Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, focusing on their financial stability, operational capacity, and past performance. This diligence reduces risks and enhances the likelihood of successful transactions.
In conclusion, a well-rounded understanding of the cost structure, price influencers, and strategic negotiation practices is essential for international B2B buyers looking to source from auto plants in the USA. By applying these insights, buyers can optimize their sourcing strategies and achieve favorable outcomes.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing auto plants in usa With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives: How Do Auto Plants in the USA Compare to Other Solutions?
When evaluating the landscape of automotive manufacturing, it’s essential to consider various alternatives to traditional auto plants in the USA. The decision to invest in manufacturing capabilities can significantly affect operational efficiency, cost management, and overall product quality. Below, we compare auto plants in the USA against two viable alternatives: Contract Manufacturing and Automation Technologies.
| Comparison Aspect | Auto Plants In USA | Contract Manufacturing | Automation Technologies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-quality production; skilled labor | Variable quality; depends on the partner | Consistent output; reduced human error |
| Cost | High initial investment; ongoing expenses | Lower initial costs; variable pricing | Moderate initial costs; potential savings over time |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex setup; regulatory hurdles | Easier to implement; partner-dependent | Requires skilled implementation; training needed |
| Maintenance | Ongoing maintenance costs; skilled labor | Minimal; mostly managed by the partner | Requires regular updates and oversight |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale production; brand reputation | Rapid scaling; specialized products | High-volume, repetitive tasks |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Contract Manufacturing?
Contract manufacturing involves outsourcing production to third-party companies that specialize in manufacturing. This approach can be beneficial for companies looking to scale quickly without the heavy upfront investment associated with building and operating their own plants.
Pros:
– Cost-effective in the short term, as it reduces the need for heavy capital investment.
– Flexibility in scaling production up or down based on demand.
– Access to specialized expertise and advanced manufacturing technologies without direct investment.
Cons:
– Quality control can be an issue, as the manufacturer’s standards may not align with your brand.
– Dependency on third-party timelines and production capabilities.
– Potential supply chain risks if the contract manufacturer faces disruptions.
How Do Automation Technologies Stack Up Against Traditional Auto Plants?
Automation technologies, such as robotics and AI-driven manufacturing systems, are increasingly being adopted in automotive production. These solutions can enhance efficiency and consistency, particularly for repetitive tasks.
Pros:
– Consistent quality and reduced variability in production.
– Lower long-term labor costs and increased production speed.
– Ability to operate 24/7 without human fatigue, maximizing output.
Cons:
– Significant upfront investment in technology and infrastructure.
– Requires ongoing maintenance and updates, which can be costly.
– Dependence on technology can lead to vulnerabilities if systems fail.
Choosing the Right Solution: What Should B2B Buyers Consider?
When selecting the most suitable manufacturing solution, B2B buyers must assess their unique operational needs, budget constraints, and long-term goals. Auto plants in the USA offer robust performance and quality assurance, making them ideal for brands focused on reputation and high-volume production. However, businesses aiming for flexibility and cost-effectiveness may find contract manufacturing to be a more suitable option.
Conversely, companies looking to innovate and enhance operational efficiency may benefit from investing in automation technologies. Ultimately, the decision should align with your strategic vision, operational requirements, and market dynamics to ensure optimal outcomes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for auto plants in usa
What Are the Essential Technical Properties Relevant to Auto Plants in the USA?
Understanding the technical specifications of automotive manufacturing is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to establish partnerships with U.S. auto plants. Here are some key properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of materials used in manufacturing based on specific mechanical and chemical properties. In the automotive industry, common materials include steel, aluminum, and composites. The right material grade ensures durability, weight reduction, and compliance with safety standards. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade can significantly impact vehicle performance and longevity, influencing customer satisfaction and return on investment.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the acceptable limits of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. In automotive manufacturing, tight tolerances are essential for parts that need to fit together precisely. High tolerance levels ensure that components operate efficiently and safely, reducing the likelihood of failures. For buyers, understanding tolerance specifications is vital when sourcing parts, as it directly affects assembly processes and overall vehicle quality.
3. Annual Production Capacity
Annual production capacity indicates the maximum number of units a manufacturing plant can produce in a year. This metric is critical for B2B buyers as it helps gauge whether a supplier can meet their demand. Understanding a plant’s capacity can aid in planning inventory and production schedules, ensuring timely delivery and reducing the risk of stockouts.
4. Supply Chain Integration
Supply chain integration refers to the alignment and coordination of all partners involved in the manufacturing process, from raw material suppliers to logistics providers. Effective integration is essential for optimizing production efficiency and minimizing costs. For international buyers, evaluating a manufacturer’s supply chain capabilities can help ensure that components are sourced and delivered in a timely manner, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
5. Compliance Standards
Compliance standards are regulations that automotive manufacturers must adhere to, such as safety, environmental, and quality standards set by organizations like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). Understanding these standards is crucial for B2B buyers as it influences product design and marketability. Non-compliance can lead to costly recalls and brand damage, making it imperative for buyers to verify that their suppliers meet all necessary regulations.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the U.S. Automotive Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology can facilitate smoother negotiations and partnerships. Here are some common terms relevant to auto plants:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the automotive context, OEMs supply components that are used in the assembly of vehicles. For buyers, partnering with OEMs ensures that they receive high-quality parts that meet the original specifications and standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In automotive manufacturing, MOQs can vary significantly depending on the part and the supplier. Understanding MOQs is essential for buyers as it affects inventory management and cost-efficiency. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to avoid excess inventory.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. In the automotive sector, issuing an RFQ can help buyers compare costs and evaluate suppliers based on their offerings. This process is crucial for budget planning and ensuring competitive pricing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in a transaction. They clarify who pays for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. For international B2B buyers, understanding Incoterms is essential for managing logistics and ensuring compliance with trade regulations.
5. Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3 Suppliers
These terms classify suppliers based on their relationship with OEMs. Tier 1 suppliers directly supply parts to the OEM, while Tier 2 suppliers provide components to Tier 1 suppliers, and Tier 3 suppliers supply raw materials. For buyers, knowing the tier structure helps in assessing the supply chain’s complexity and reliability, which can influence production timelines and costs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can navigate the U.S. automotive manufacturing landscape more effectively, fostering successful partnerships that drive mutual growth.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the auto plants in usa Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the US Automotive Sector?
The US automotive manufacturing sector is experiencing significant transformations driven by global trends such as electrification, automation, and sustainability. As the second-largest automotive producer globally, the industry generated $863 billion in 2022, showcasing its resilience and importance to the US economy. International B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of several key trends shaping the market.
One prominent trend is the shift towards electric vehicles (EVs). Major automotive manufacturers in the US, including Ford, GM, and Tesla, are investing heavily in EV production and associated technologies. This transition is not only driven by consumer demand for greener alternatives but also by regulatory pressures aimed at reducing carbon emissions. Consequently, B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers and manufacturers that align with these sustainability goals, especially those involved in the production of EV components and batteries.
Additionally, the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies, including automation and artificial intelligence, is optimizing production processes. This trend enhances efficiency, reduces labor costs, and improves product quality, making it essential for international buyers to evaluate the technological capabilities of potential partners in the US.
Moreover, the supply chain dynamics are evolving, with a focus on localizing supply chains to mitigate risks associated with global disruptions. Buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers located within the US to ensure reliability and responsiveness, particularly in an era marked by geopolitical tensions and trade uncertainties.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting B2B Relationships in the Automotive Sector?
The environmental impact of automotive production has prompted a growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical sourcing. International buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as reducing waste and carbon footprints. This shift is particularly critical for companies looking to enhance their brand reputation and comply with stricter regulations in their home markets.
A significant aspect of this trend is the demand for ‘green’ certifications and materials. Manufacturers in the US are adopting eco-friendly practices by utilizing recyclable materials and seeking certifications like ISO 14001, which reflects a commitment to effective environmental management systems. B2B buyers should actively seek partnerships with companies that have demonstrated their commitment to sustainability through these certifications, as this can lead to better alignment with corporate social responsibility goals and consumer expectations.
Furthermore, the importance of transparency in supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are encouraged to inquire about the sourcing of materials and the ethical practices of their suppliers, including labor conditions and sourcing origins. Establishing relationships with manufacturers that prioritize ethical sourcing can enhance trust and mitigate risks related to reputational damage or regulatory penalties.
What Is the Historical Context of the US Automotive Industry Relevant to Current B2B Trends?
The US automotive industry has a storied history, rooted in the early 20th century with the rise of iconic companies like Ford and General Motors. This legacy has shaped a robust manufacturing ecosystem, particularly in the Midwest, where expertise and infrastructure have flourished over decades. The industry’s evolution from mass production to incorporating advanced technologies and sustainable practices is crucial for B2B buyers to understand.
As the sector adapts to changing consumer preferences and global pressures, recognizing this historical context allows international buyers to appreciate the depth of innovation and resilience within US automotive manufacturing. Engaging with suppliers who understand this evolution can facilitate better strategic partnerships, enabling businesses to leverage historical insights while navigating the complexities of modern market dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of auto plants in usa
-
How do I solve issues related to sourcing automotive plants in the USA?
To effectively address sourcing issues, begin by conducting comprehensive market research to identify reputable automotive plants that align with your business needs. Utilize industry reports, trade shows, and networking within automotive associations to gather insights. Establish clear criteria for selection, including production capabilities, quality standards, and supplier reliability. Additionally, consider engaging local consultants or trade experts who can facilitate introductions and provide insights into the regulatory landscape, ensuring a smoother sourcing process. -
What is the best approach for vetting suppliers of automotive manufacturing plants?
The best approach for vetting suppliers involves a multi-step evaluation process. Start with a preliminary assessment of their financial stability, production capacity, and previous client testimonials. Request references and case studies to gauge their reliability and performance history. Conduct site visits to observe their operations firsthand, ensuring they meet quality and safety standards. Lastly, assess their compliance with international regulations, such as ISO certifications, to ensure they adhere to best practices in the automotive sector. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for automotive parts from US plants?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the type of automotive parts required. Generally, MOQs range from a few hundred to several thousand units, particularly for custom or specialized components. It’s crucial to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your production schedule and budget constraints. Additionally, some manufacturers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or smaller projects to foster long-term partnerships. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing from US automotive plants?
Payment terms can vary among suppliers, but many automotive plants typically require a deposit upfront, followed by balance payments upon delivery or after meeting certain milestones. Common terms include net 30, net 60, or even net 90 days for larger orders. It is advisable to establish clear payment terms during negotiations to avoid misunderstandings. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing automotive parts from the USA?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing automotive parts, implement a robust QA process that includes pre-production inspections, in-process quality checks, and final product evaluations. Collaborate with suppliers to understand their quality control protocols, and request documentation such as certificates of compliance and testing reports. Additionally, consider third-party quality audits or certifications to validate the supplier’s adherence to industry standards. Establishing clear communication about quality expectations will also help maintain high standards throughout the production process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing automotive parts from the USA?
When importing automotive parts from the USA, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Evaluate the most efficient shipping options—air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness. Be aware of import duties and taxes in your country, and ensure compliance with local regulations to avoid delays. Collaborating with experienced logistics partners can streamline the shipping process, providing end-to-end visibility and support for customs clearance. -
What are the key benefits of sourcing automotive manufacturing from the USA?
Sourcing automotive manufacturing from the USA offers several advantages, including access to advanced technology, skilled labor, and high-quality standards. US manufacturers often invest in cutting-edge production techniques and automation, enhancing efficiency and product quality. Additionally, the robust infrastructure and supply chain networks in the US facilitate timely deliveries. Sourcing from reputable US plants also helps mitigate risks associated with geopolitical factors, ensuring a more stable supply chain for your business. -
How do regulations impact international buyers of automotive plants in the USA?
Regulations play a critical role in the international sourcing of automotive plants. Buyers must navigate various federal and state regulations concerning safety, emissions, and labor standards. Compliance with the U.S. Department of Commerce and trade regulations, including tariffs and trade agreements, is essential. It is advisable to consult with legal and trade experts familiar with both US and international laws to ensure adherence and to avoid potential fines or disruptions in supply chains. Understanding these regulations will help you make informed decisions and foster successful partnerships.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for auto plants in usa
Why is Strategic Sourcing Critical for International Buyers in the U.S. Automotive Market?
In conclusion, the U.S. automotive industry, with its robust manufacturing capabilities and strategic locations, offers immense opportunities for international B2B buyers. The concentration of over 90% of automotive plants in the Midwest and South, particularly in states like Michigan and Ohio, underscores the importance of these regions in facilitating efficient supply chains. Strategic sourcing not only enhances procurement efficiency but also mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions, enabling companies to capitalize on the U.S. market’s advanced technologies and skilled labor force.
As global markets evolve, the demand for innovative automotive solutions, including electric and autonomous vehicles, is on the rise. International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can leverage this trend by establishing strategic partnerships with U.S. manufacturers. Engaging with these established plants can unlock access to cutting-edge technologies and a diverse supplier network that is crucial for staying competitive.
Moving forward, we encourage international buyers to explore collaboration opportunities with U.S. auto manufacturers, ensuring they are well-positioned to meet the future demands of the automotive landscape. Embrace the potential that strategic sourcing presents, and take actionable steps to enhance your supply chain resilience and market reach.