Top 8 Apple Moving To Usa List and Guide: How To Solve Scenario 1…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for apple moving to usa
In today’s rapidly evolving landscape, international B2B buyers face the significant challenge of navigating the complexities associated with sourcing and moving apple products to the USA. As Apple commits to investing over $500 billion in the U.S. over the next four years, understanding the implications of this shift is essential for businesses looking to capitalize on new opportunities. This comprehensive guide serves as a roadmap for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, detailing the types of apples available for import, their various applications in industries ranging from food service to retail, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
Our guide empowers decision-makers by providing actionable insights into the sourcing process, including cost considerations, regulatory requirements, and logistics management. We delve into the nuances of supplier relationships, ensuring that buyers can identify trustworthy partners capable of meeting quality and compliance standards. Additionally, we explore the implications of local production shifts, such as Apple’s new manufacturing initiatives, and how these may affect pricing and availability in the market.
By equipping B2B buyers with the knowledge and strategies needed to make informed purchasing decisions, this guide aims to streamline the process of moving apple products to the U.S., ultimately facilitating successful business operations in a competitive global market.
Top 10 Apple Moving To Usa Manufacturers & Suppliers List
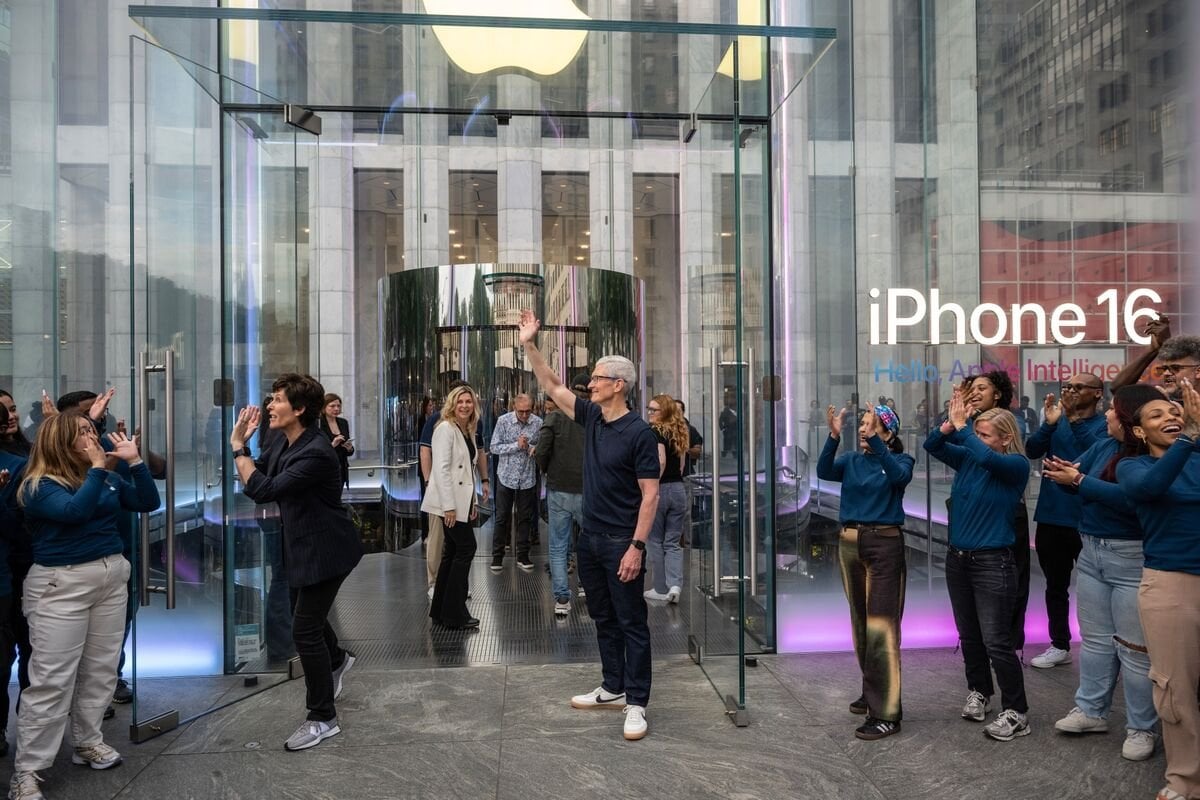
1. Apple – iPhone 16e
Domain: apple.com
Registered: 1987 (38 years)
Introduction: Apple plans to introduce the iPhone 16e, featuring the A18 chip and the new Apple C1 cellular modem, which is the most power-efficient modem ever on an iPhone.
2. Apple – iPhone Production Insights
Domain: fortune.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Apple iPhone production is primarily based in China, with a current price tag of approximately $1,000. If production were to shift to the U.S., costs could potentially rise to over $3,000 due to tariffs and manufacturing expenses. Apple has not publicly committed to manufacturing iPhones in the U.S. and has built a complex supply chain in China since the 1990s. The company continues to generate si…
3. Apple – iPhone Production Insights
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Apple iPhone production involves over 2,700 parts sourced from 187 suppliers across 28 countries. Notably, only 30 Apple suppliers operate entirely outside of China.
4. Apple – iPhone Manufacturing Shift
Domain: theguardian.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Apple aims to source all iPhones for the US market from India by the end of 2026, reducing reliance on Chinese manufacturing. The company plans to double iPhone assembly in India to meet the annual demand of over 60 million units sold in the US. Currently, about 90% of iPhones are assembled in China. Apple has three plants in India and has been ramping up production there, with suppliers like Foxc…
5. Wedbush – Trump’s Tariff Threat to Apple
6. Apple – $500 Billion Investment
Domain: cnn.com
Registered: 1993 (32 years)
Introduction: Apple will invest $500 billion in expanding US facilities over the next four years, creating 20,000 jobs. This includes a new 250,000-square-foot server manufacturing facility in Houston, set to open in 2026, which will support Apple Intelligence, the company’s brand of artificial intelligence products. The servers, previously manufactured outside the US, are essential to Apple’s AI efforts.
7. Apple – Supply Chain Relocation Challenges
Domain: elitetrader.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Apple would require approximately 3 years and $30 billion to move 10% of its supply chain from Asia to the US, according to Wedbush analyst Dan Ives. The discussion highlights the significant challenges and potential disruptions involved in relocating facilities, as well as the impact of tariffs on Apple’s earnings.
8. Apple – iPhone Manufacturing Shift
Understanding apple moving to usa Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Manufacturing Facilities | Large-scale facilities focusing on high-tech manufacturing processes. | Production of servers, chips, and components. | Pros: High-quality production, job creation. Cons: High initial investment, long lead times. |
| R&D Investment Initiatives | Focus on research and development to innovate new technologies. | Development of new products and technologies. | Pros: Access to cutting-edge innovations. Cons: Risk of R&D failures, uncertain timelines. |
| Supplier Partnerships | Collaborations with local suppliers to enhance supply chain resilience. | Sourcing materials and components locally. | Pros: Reduced shipping costs, shorter lead times. Cons: Limited supplier options, potential quality variability. |
| Workforce Development Programs | Training programs aimed at upskilling the local workforce. | Enhancing skills in manufacturing and tech. | Pros: Skilled labor availability, community support. Cons: Time-consuming training processes, initial costs. |
| Sustainability Initiatives | Investments in renewable energy and environmentally friendly practices. | Green technology and sustainable manufacturing. | Pros: Positive brand image, compliance with regulations. Cons: Higher upfront costs, ongoing maintenance requirements. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Advanced Manufacturing Facilities?
Advanced manufacturing facilities are characterized by their focus on high-tech production processes, often integrating automation and advanced robotics. These facilities are crucial for producing complex components such as servers and chips that support Apple’s extensive ecosystem. For B2B buyers, investing in such facilities can ensure access to high-quality products and contribute to local job creation. However, the initial investment and long setup times can be significant considerations.
How Do R&D Investment Initiatives Benefit B2B Buyers?
Research and Development (R&D) investment initiatives are vital for fostering innovation and developing new technologies. These initiatives enable companies to stay competitive by creating advanced products that meet evolving market demands. For B2B buyers, engaging with firms that prioritize R&D can lead to access to cutting-edge technologies and solutions. However, the risks associated with R&D, including potential project failures and uncertain timelines, must be weighed carefully.
What Are the Advantages of Supplier Partnerships?
Supplier partnerships are essential for enhancing supply chain resilience and efficiency. By collaborating with local suppliers, companies can reduce shipping costs and lead times, ensuring a more reliable supply of materials and components. For B2B buyers, this means better inventory management and potentially lower costs. However, the limited options available from local suppliers might pose challenges regarding quality and consistency.
How Do Workforce Development Programs Impact the Industry?
Workforce development programs aim to upskill the local workforce, addressing the skills gap in advanced manufacturing and technology sectors. These programs enhance the availability of skilled labor, which is crucial for maintaining high production standards. For B2B buyers, this translates to a more competent workforce capable of meeting complex production demands. However, the time and resources required to implement these training programs can be a drawback.
What Role Do Sustainability Initiatives Play in Manufacturing?
Sustainability initiatives focus on integrating renewable energy and environmentally friendly practices into manufacturing processes. This approach not only enhances a company’s brand image but also ensures compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations. For B2B buyers, engaging with companies that prioritize sustainability can lead to more responsible sourcing and improved corporate social responsibility. However, these initiatives often involve higher upfront costs and ongoing maintenance, which can impact short-term profitability.
Key Industrial Applications of apple moving to usa
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of apple moving to usa | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Manufacturing | Establishing a new server manufacturing facility in Texas | Enhanced production capabilities and job creation | Proximity to suppliers, skilled labor availability |
| Semiconductor Industry | Doubling the U.S. Advanced Manufacturing Fund | Increased innovation and local chip production | Access to technology, collaboration with local firms |
| AI and Data Infrastructure | Building data centers for Apple Intelligence | Improved data processing and security | Infrastructure readiness, energy efficiency standards |
| Education & Workforce Development | Creating a manufacturing academy in Michigan | Development of a skilled workforce | Curriculum relevance, partnerships with local businesses |
| Renewable Energy | Expanding renewable energy use in data centers | Cost savings and sustainability benefits | Compliance with regulations, sourcing renewable energy |
How is Advanced Manufacturing Benefiting from Apple’s Move to the USA?
Apple’s commitment to establishing a new server manufacturing facility in Texas exemplifies the potential of advanced manufacturing in the U.S. This facility aims to produce servers that are crucial for powering Apple Intelligence, thereby enhancing production capabilities and generating thousands of jobs. For international B2B buyers, understanding the local supply chain and labor market is essential, as proximity to suppliers and skilled labor availability can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost.
What Opportunities Does the Semiconductor Industry Hold?
The doubling of Apple’s U.S. Advanced Manufacturing Fund signifies a strong push towards semiconductor innovation. This investment will enhance local chip production, which is vital for various tech applications. B2B buyers in this sector must consider access to cutting-edge technology and the potential for collaboration with local firms, which can lead to improved product offerings and supply chain resilience.
How Are AI and Data Infrastructure Evolving?
The construction of data centers dedicated to Apple Intelligence represents a significant investment in AI and data infrastructure. These centers will improve data processing capabilities and enhance security measures for cloud computing. For businesses in this domain, it’s critical to evaluate infrastructure readiness and energy efficiency standards, as these factors will influence operational costs and sustainability goals.
What Role Does Education Play in Workforce Development?
Apple’s initiative to create a manufacturing academy in Michigan is pivotal for workforce development in advanced manufacturing. This academy will equip the next generation of workers with necessary skills, ensuring a steady supply of talent for local industries. For international B2B buyers, aligning with educational institutions and ensuring curriculum relevance can enhance workforce quality and foster innovation within their organizations.
How is Renewable Energy Integrated into Apple’s Operations?
Apple’s expansion of renewable energy initiatives in its data centers not only promotes sustainability but also offers significant cost savings. By running data centers on 100% renewable energy, Apple sets a benchmark for energy efficiency in tech manufacturing. Companies looking to partner with Apple or invest in similar initiatives must prioritize compliance with energy regulations and sourcing renewable energy options to align with global sustainability trends.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘apple moving to usa’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Supply Chain Complexity Amid Apple’s U.S. Expansion
The Problem: As Apple announces its ambitious plans to invest over $500 billion in U.S. manufacturing, B2B buyers face a daunting challenge: navigating a complex supply chain that has long relied on overseas production. Companies that depend on Apple’s supply chain for components or services may struggle with sourcing materials locally, especially if they have established relationships with suppliers in China or other countries. This transition could lead to delays, increased costs, and potential disruptions in product availability, creating uncertainty for businesses that rely on timely access to Apple products or components.
The Solution: To effectively address this supply chain challenge, B2B buyers should start by conducting a thorough supply chain audit to identify critical components sourced from overseas. Establishing relationships with new U.S.-based suppliers is crucial. This may involve leveraging Apple’s announced partnerships and investments in local manufacturing. Engage with local suppliers who are part of Apple’s Advanced Manufacturing Fund or other collaborative initiatives. Additionally, consider forming strategic alliances with logistics firms that specialize in U.S. domestic transportation to ensure timely delivery of components. By diversifying the supply chain and focusing on local resources, businesses can reduce dependence on foreign suppliers and mitigate risks associated with Apple’s transition.
Scenario 2: Adapting to Regulatory Changes and Compliance Requirements
The Problem: With Apple’s move to expand its manufacturing footprint in the U.S., B2B buyers may encounter a myriad of regulatory changes that could impact their operations. Different states may have varying regulations concerning labor laws, environmental compliance, and manufacturing standards. Companies must ensure that their processes align with these new regulations, which can be particularly challenging for businesses that have historically operated under different legal frameworks in other countries. Failure to comply could result in hefty fines, operational delays, and reputational damage.
The Solution: B2B buyers need to proactively engage in compliance training and regulatory updates. Partner with legal and compliance experts who can provide insights into the specific requirements of each state where Apple is investing. Regularly review and update compliance protocols to align with evolving regulations. Additionally, implementing a robust compliance management system can help track changes in legislation and ensure adherence to local laws. By staying informed and proactive, businesses can navigate the regulatory landscape effectively and maintain smooth operations as Apple transitions its manufacturing processes.
Scenario 3: Managing Talent Acquisition and Workforce Development
The Problem: Apple’s significant investment in U.S. manufacturing and technology development will create a high demand for skilled labor, intensifying competition among companies for qualified talent. B2B buyers, particularly those in related industries, may face challenges in attracting and retaining skilled workers, especially in technical fields like AI, silicon engineering, and advanced manufacturing. This scarcity of talent can lead to increased hiring costs and project delays, impacting a company’s ability to meet demand and innovate.
The Solution: To combat talent shortages, B2B buyers should consider investing in workforce development programs and partnerships with local educational institutions. Collaborating with universities and vocational schools can create tailored training programs that equip students with the necessary skills for the evolving manufacturing landscape. Establishing internships or apprenticeship programs can also provide a pipeline for talent while enhancing a company’s visibility in the community. Furthermore, investing in employee retention strategies, such as competitive benefits and continuous learning opportunities, can help retain existing talent and reduce turnover. By taking a proactive approach to workforce development, businesses can position themselves favorably in a competitive market driven by Apple’s expansion.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for apple moving to usa
What Are the Key Materials for Apple Moving to the USA?
When considering the materials for Apple’s manufacturing operations moving to the USA, it is essential to analyze the common materials used in electronics and technology sectors. The following materials are critical in ensuring the performance, durability, and compliance of Apple’s products.
How Do Metals Like Aluminum and Steel Impact Apple’s Manufacturing?
Aluminum is widely used in Apple products due to its lightweight and high strength-to-weight ratio. Its excellent corrosion resistance makes it suitable for various environments, particularly in electronics where heat dissipation is crucial. However, the manufacturing complexity can be high due to the need for specialized machining and finishing processes. For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN is vital, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where environmental regulations are stringent.
Steel, particularly stainless steel, is another common material, known for its exceptional durability and strength. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it ideal for components that require robustness. However, steel can be heavier and more expensive than aluminum, which may impact shipping costs and logistics. Buyers from Africa and South America should consider the local availability of these materials to mitigate costs.
What Role Do Plastics Play in Apple’s Product Design?
Plastics, especially high-performance polymers, are integral to Apple’s product design. They offer versatility in shaping and can be engineered for various properties, including high impact resistance and thermal stability. While plastics are generally less expensive and easier to manufacture, they may have limitations in terms of heat resistance compared to metals. For international buyers, it is crucial to ensure that the plastics used comply with local regulations regarding environmental impact, especially in the EU where strict guidelines exist.
Why Is Silicon a Critical Material for Apple’s Technology?
Silicon is the backbone of Apple’s semiconductor technology. Its key properties include excellent electrical conductivity and thermal stability, which are essential for high-performance computing applications. The primary disadvantage is the high cost of advanced silicon processing and the complexity of manufacturing processes. For B2B buyers, understanding the supply chain for silicon, particularly in regions like Asia and North America, is critical for ensuring consistent quality and availability.
What Are the Considerations for International Buyers in Material Selection?
International B2B buyers must consider various factors when selecting materials for Apple’s manufacturing operations. Compliance with international standards (like ASTM, DIN, and JIS) is crucial to ensure product quality and safety. Additionally, regional preferences for materials can influence sourcing decisions. For example, buyers from the Middle East may prioritize materials that can withstand high temperatures and humidity, while those from Europe may focus on sustainability and recyclability.
Summary Table of Strategic Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for apple moving to usa | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Casings and structural components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | High manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Steel | Structural frames and internal supports | Exceptional durability | Heavier and potentially costlier | High |
| Plastics | Internal components and casings | Versatile and cost-effective | Limited heat resistance | Low |
| Silicon | Semiconductors and chips | Excellent electrical properties | High processing costs | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials crucial for Apple’s manufacturing operations in the USA, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material will facilitate better sourcing and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for apple moving to usa
What Are the Main Stages of Apple’s Manufacturing Process in the USA?
Apple’s manufacturing processes, particularly as they expand in the U.S., are designed to optimize efficiency and maintain high quality. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves sourcing raw materials such as metals, plastics, and silicon. Apple emphasizes sustainable sourcing, often opting for recycled materials wherever possible. For instance, the company is known to use recycled aluminum in its product casings, aligning with its environmental goals.
-
Forming: In this phase, raw materials are transformed into components. Techniques such as injection molding for plastic parts and precision machining for metal components are commonly employed. Apple invests in advanced manufacturing technologies that enhance precision and reduce waste, ensuring that components meet stringent specifications.
-
Assembly: The assembly stage is where individual components come together to form the final product. Apple utilizes automated assembly lines, which are complemented by skilled labor for tasks requiring fine motor skills. This hybrid approach allows for high-speed production while maintaining the quality that Apple is known for.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves quality checks, surface treatments, and packaging. Finishing processes ensure that products not only function properly but also meet Apple’s aesthetic standards. This stage is crucial for maintaining brand integrity and customer satisfaction.
What Quality Control Measures Does Apple Implement in Its U.S. Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a cornerstone of Apple’s manufacturing philosophy. The company adheres to several international and industry-specific standards to ensure product quality and safety.
-
Relevant International Standards: Apple complies with ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. This certification ensures that Apple consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements while enhancing customer satisfaction.
-
Industry-Specific Standards: Apple also adheres to CE marking, which indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area. For more specialized products, such as medical devices, Apple may comply with API (American Petroleum Institute) standards.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Apple’s QC process involves several checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection verifies that incoming materials and components meet specified standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process ensures that any deviations are detected and corrected in real-time.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products leave the facility, they undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet Apple’s quality benchmarks.
How Do Common Testing Methods Enhance Apple’s Quality Assurance?
Testing methods are essential in verifying the integrity and functionality of Apple products. Common methods include:
-
Functional Testing: This ensures that all features of a product operate as intended. For example, the performance of the A18 chip in an iPhone must be validated through extensive functional testing.
-
Environmental Testing: Products are subjected to various environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures and humidity, to assess their durability and performance under stress.
-
Safety Testing: Compliance with safety standards is verified through rigorous testing protocols. This includes electrical safety tests to prevent hazards like overheating.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures. Here are several actionable strategies:
-
Conducting Audits: Regular supplier audits can reveal the effectiveness of their quality control processes. Buyers should establish a schedule for on-site audits to assess compliance with international standards and best practices.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including test results and certifications. This transparency helps buyers evaluate the reliability of their suppliers.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices. This step is especially vital for buyers unfamiliar with local manufacturing standards.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control and certification nuances when sourcing products from U.S. manufacturers:
-
Understanding Regional Standards: Different regions have specific regulations and standards that products must meet. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these standards to ensure compliance, especially when exporting products to their home countries.
-
Language and Documentation Barriers: Language differences can complicate understanding quality reports and certifications. Buyers may need translation services or local representatives to facilitate clear communication.
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Expectations: Quality expectations can vary significantly across cultures. B2B buyers should engage in open discussions with suppliers to align on quality standards and expectations.
How Does Apple’s Commitment to Quality Impact Its Supply Chain?
Apple’s commitment to quality directly influences its supply chain dynamics. By enforcing strict quality control measures, Apple not only ensures product reliability but also strengthens relationships with suppliers. This commitment encourages suppliers to adopt similar quality standards, creating a ripple effect that enhances overall supply chain integrity.
Moreover, Apple’s willingness to invest in local manufacturing—evidenced by its $500 billion commitment—fosters a robust ecosystem of suppliers and manufacturers in the U.S. This localized supply chain can lead to faster turnaround times and reduced shipping costs, benefiting international B2B buyers.
Conclusion
As Apple moves more manufacturing to the USA, understanding its manufacturing processes and quality control measures becomes essential for international B2B buyers. By familiarizing themselves with these processes, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they source high-quality products that meet their operational needs. Engaging in proactive verification practices, understanding regional nuances, and leveraging Apple’s commitment to quality can significantly enhance the purchasing experience for B2B buyers across the globe.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘apple moving to usa’
This guide provides a practical checklist for international B2B buyers interested in sourcing components or products related to Apple’s transition and investment in the U.S. market. With Apple’s commitment of over $500 billion to expand its operations in the U.S., there are significant opportunities for businesses to engage with new suppliers and partners in various sectors, from manufacturing to technology services.
Step 1: Understand Apple’s U.S. Investment Landscape
Familiarize yourself with the key areas where Apple is investing, such as Texas, Michigan, and Arizona. Understanding these regions helps identify potential suppliers and partners that could benefit from Apple’s expansion. Research local industry clusters that align with Apple’s focus on advanced manufacturing, artificial intelligence, and silicon engineering.
Step 2: Identify Relevant Suppliers
Once you understand the investment landscape, identify suppliers that align with Apple’s strategic priorities. Look for companies specializing in advanced manufacturing, semiconductor production, and AI technologies. Focus on suppliers that have a proven track record in these areas and are located within or near Apple’s investment zones.
- Research Supplier Capabilities: Evaluate their production capacities, technology capabilities, and past performance.
- Check Industry Certifications: Ensure they hold relevant certifications that demonstrate quality and compliance with industry standards.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; conduct interviews or site visits when possible to assess their operational capabilities.
- Review Financial Stability: Analyze their financial health to ensure they can meet your supply needs over time.
- Assess Production Flexibility: Determine if they can scale production based on your business demands.
Step 4: Engage in Due Diligence
Conduct thorough due diligence on shortlisted suppliers. This step is essential to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions or quality issues. Review their compliance with labor laws, environmental standards, and any other regulatory requirements pertinent to your industry.
- Request Documentation: Ask for proof of compliance and any relevant audit reports.
- Check References: Speak with other clients to gauge their satisfaction and reliability.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve identified a suitable supplier, negotiate favorable terms and conditions. This includes pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and quality assurance protocols. Clear agreements can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth partnership.
- Include Performance Metrics: Establish KPIs to measure supplier performance and accountability.
- Clarify Intellectual Property Rights: Ensure that IP rights are explicitly defined in the contract, especially when dealing with technological products.
Step 6: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is vital for the success of your partnership. Develop a communication plan that outlines how often and through what channels you will interact with your suppliers. Clear communication helps to address issues proactively and fosters a collaborative relationship.
- Set Regular Check-ins: Schedule regular updates to discuss performance and any potential challenges.
- Utilize Technology: Leverage collaboration tools to facilitate real-time communication and document sharing.
Step 7: Monitor and Evaluate Performance
After establishing the partnership, continuously monitor and evaluate supplier performance against the agreed-upon metrics. Regular assessments help identify areas for improvement and ensure alignment with your business goals.
- Provide Feedback: Offer constructive feedback to suppliers to foster improvement and innovation.
- Adjust Contracts as Necessary: Be prepared to renegotiate terms if your business needs change or if supplier performance varies significantly.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can strategically position themselves to take advantage of Apple’s substantial investments in the U.S., ensuring they partner with the right suppliers to meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for apple moving to usa Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Apple Moving to U.S. Sourcing?
When analyzing the cost structure associated with Apple’s move to U.S. sourcing, several components play a critical role. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials varies depending on the sourcing strategy. As Apple expands its supply chain within the U.S., it may face higher material costs due to local sourcing. Materials used in high-tech manufacturing, such as silicon, can be significantly impacted by domestic supply chain dynamics.
-
Labor: Labor costs in the U.S. are generally higher compared to regions like Asia, where Apple has traditionally sourced its production. Skilled labor is essential for advanced manufacturing roles, and this can lead to increased operational costs. However, investments in training and development, such as the manufacturing academy planned in Michigan, could help mitigate some of these costs over time.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. With new facilities being established, such as the one in Texas, initial overhead might be high but could stabilize as production scales.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for U.S. manufacturing can be substantial. This encompasses the machinery and equipment needed to produce Apple products. The transition from overseas production to domestic manufacturing will require significant capital expenditure.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is paramount, especially for a brand like Apple. Implementing rigorous QC processes can add to the cost structure, but it is essential for maintaining brand reputation.
-
Logistics: Shipping and transportation costs could change as Apple shifts more of its supply chain to the U.S. Proximity to suppliers and customers might reduce some logistics costs, but the overall expense related to distribution and warehousing needs to be factored in.
-
Margin: Profit margins will be influenced by the above costs. With higher production costs in the U.S., Apple may need to adjust pricing strategies to maintain profitability.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Sourcing Decisions for Apple in the U.S.?
Several factors influence the pricing of Apple products sourced in the U.S., including volume, specifications, materials, quality certifications, supplier factors, and Incoterms.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders typically lead to reduced per-unit costs. However, Apple’s commitment to quality means they may not compromise on specifications even for larger quantities.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom products or components can drive up costs. Apple’s focus on premium quality and innovative features often requires unique specifications, which can affect overall pricing.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts production costs. High-quality materials are essential for Apple’s products, but they can also increase the cost significantly.
-
Quality/Certifications: Meeting industry standards and obtaining certifications can incur additional costs but are necessary for ensuring safety and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can affect costs. Apple’s partnerships with established suppliers can lead to more predictable pricing, but they may also come with premium costs.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers as they dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping. This can significantly affect total costs, especially for international transactions.
What Buyer Tips Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Sourcing from Apple?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are several strategies to consider when negotiating with Apple or its suppliers:
-
Negotiation: Leverage your position as a buyer. Understanding the market dynamics and being prepared to negotiate can lead to favorable pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront price. Consider long-term costs associated with maintenance, warranties, and potential tariffs.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware that pricing may fluctuate based on geopolitical factors, tariffs, and trade agreements. Staying informed about these variables can aid in strategic sourcing decisions.
-
Supplier Relationships: Build strong relationships with suppliers to negotiate better terms and ensure reliability in sourcing.
-
Customization and Specifications: Clearly define your requirements to avoid unexpected costs associated with last-minute changes or customizations.
Disclaimer
Prices and cost structures are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, negotiation outcomes, and specific sourcing agreements. International buyers should conduct thorough due diligence and market analysis before finalizing sourcing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing apple moving to usa With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Apple’s Move to the USA
As businesses consider the implications of Apple’s significant investment in U.S. manufacturing, it is crucial to explore alternatives that could achieve similar goals without the complexities and potential downsides associated with relocating production. This analysis compares the strategy of “Apple moving to the USA” with other viable solutions: Outsourcing to Low-Cost Countries and Investing in Automation and AI Technologies.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Apple Moving To USA | Outsourcing to Low-Cost Countries | Investing in Automation and AI Technologies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-quality manufacturing with advanced tech | Variable quality, dependent on local capabilities | Consistent quality, rapid production speeds |
| Cost | Extremely high initial investment and operating costs | Lower labor costs, but hidden costs may arise | High initial investment but reduced long-term costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex setup, long timelines for new facilities | Relatively quick setup with existing infrastructure | Requires skilled workforce, ongoing training necessary |
| Maintenance | High maintenance costs associated with advanced tech | Variable maintenance based on location and standards | Lower maintenance with smart technologies |
| Best Use Case | High-value, innovative products needing skilled labor | Cost-sensitive products where margins are critical | High-volume production with a focus on efficiency |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Outsourcing to Low-Cost Countries
Outsourcing remains a popular alternative for companies looking to reduce production costs. By leveraging labor in countries where wages are significantly lower, businesses can achieve substantial savings. However, the quality of products can be inconsistent, and there are risks related to supply chain disruptions, geopolitical factors, and compliance with international standards. Additionally, cultural and communication barriers can complicate operations.
Investing in Automation and AI Technologies
Investing in automation and AI technologies offers a pathway to enhance productivity and reduce labor costs over time. Automated production lines can operate continuously, leading to increased output and consistent quality. However, the initial investment is substantial, and companies must also invest in training their workforce to work alongside these technologies. While this approach can ultimately lead to lower operational costs, it requires a long-term commitment to maintain and upgrade the technology.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
For B2B buyers considering their options, the decision ultimately hinges on specific business needs and strategic objectives. If the priority is to maintain high-quality production with innovation at the forefront, then investing in U.S. manufacturing may be justified, despite the higher costs. Conversely, if cost-efficiency is the primary concern, outsourcing to low-cost countries could be more appealing, though buyers should remain vigilant about quality and reliability. Lastly, for those looking to future-proof their operations, investing in automation and AI technologies may yield significant long-term benefits, although it requires a willingness to invest upfront and adapt to new processes. Each solution has its merits and drawbacks, making it essential for buyers to carefully assess their operational goals and market dynamics before making a decision.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for apple moving to usa
What Are the Critical Technical Properties for Apple Moving to the USA?
When it comes to the relocation and establishment of manufacturing facilities in the USA, several key technical properties are essential for ensuring quality, efficiency, and compliance. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and specifications of the materials used in production. For Apple, this could involve the types of metals and plastics used in devices. Choosing the right material grade is crucial for product durability and performance, impacting everything from manufacturing costs to customer satisfaction. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance levels define the acceptable limits of variation in physical dimensions of components. For example, if a component has a tolerance of ±0.01 mm, it must fit within this range to ensure the product functions as intended. Precision in tolerances is critical in electronics, where even minor deviations can lead to malfunctions, impacting reliability and safety. -
Energy Efficiency Standards
As Apple moves to increase its manufacturing footprint in the USA, energy efficiency becomes a priority. Products must comply with regulations such as ENERGY STAR, which sets benchmarks for energy consumption. Meeting these standards not only helps reduce operational costs but also aligns with sustainability goals, appealing to environmentally-conscious consumers and investors. -
Supply Chain Integration
Effective supply chain integration involves the seamless coordination of all components, from raw material sourcing to final assembly. For Apple, this means establishing a reliable network of suppliers in the USA to minimize delays and reduce costs. A well-integrated supply chain enhances operational efficiency and responsiveness to market demands. -
Manufacturing Scalability
Scalability refers to the ability to increase production capacity without compromising quality or efficiency. As Apple aims to ramp up manufacturing in the USA, understanding the scalability of their processes will be vital. This ensures that production can meet fluctuating market demands while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Which Trade Terms Are Important for Apple Moving to the USA?
Understanding industry-specific terminology is crucial for navigating the complexities of manufacturing and trade. Here are some common terms relevant to Apple’s operations:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In Apple’s context, this could involve partnering with other firms to produce components that meet Apple’s specifications. Understanding OEM relationships is essential for managing quality and supply chain dynamics. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. For Apple, negotiating MOQs with suppliers can impact inventory management and cost structures. A well-defined MOQ can help maintain favorable pricing while ensuring that production runs smoothly. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. For Apple, issuing RFQs allows for competitive bidding and helps in selecting the best suppliers based on cost, quality, and delivery timelines, which is crucial for keeping production on schedule. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. For Apple, understanding these terms is crucial for logistics and shipping, as they determine who bears the costs and risks associated with transportation. This knowledge is essential for negotiating contracts and managing supply chain logistics effectively. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time that elapses between the initiation of a process and its completion. In manufacturing, this includes the time taken for production, shipping, and delivery. For Apple, reducing lead time is essential for maintaining competitiveness and meeting consumer demand, particularly in a fast-paced tech market.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions regarding their partnership and procurement strategies as Apple expands its operations in the USA.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the apple moving to usa Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting the Apple Moving to USA Sector?
The landscape for the apple moving to the USA sector is evolving rapidly, driven by a mix of geopolitical, economic, and technological factors. A significant driver is Apple’s commitment to invest over $500 billion in the U.S. over the next four years, focusing on advanced manufacturing and R&D. This commitment signifies a shift towards localized production, which is increasingly attractive to international B2B buyers seeking to partner with U.S.-based suppliers.
Key trends include a heightened emphasis on supply chain resilience, particularly in light of recent disruptions caused by tariffs and global events. International buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are keenly observing how Apple’s investments may create new opportunities for local suppliers and manufacturers. Furthermore, the push for sustainable practices is influencing sourcing decisions, as buyers prioritize partners who align with environmental standards and ethical sourcing.
The integration of advanced technologies such as AI and silicon engineering is also pivotal. Companies that adopt innovative manufacturing processes will likely gain a competitive edge, making it essential for B2B buyers to seek out suppliers who are at the forefront of technological advancements. As the U.S. expands its manufacturing capabilities, the potential for collaboration increases, offering a fertile ground for international buyers to explore new partnerships.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Apple Moving to USA Sector?
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it is a critical component of the apple moving to USA sector. As Apple expands its footprint in the U.S., the environmental impact of its operations is under scrutiny. International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes the use of ‘green’ certifications and materials that minimize environmental harm.
Apple’s focus on renewable energy in its data centers and manufacturing facilities is a testament to its commitment to sustainability. Buyers looking to engage with Apple or its suppliers should assess their adherence to sustainability standards and certifications, such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) or ISO 14001, which signify a commitment to environmental management.
Moreover, ethical sourcing is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of supplier selection. Buyers must ensure that their partners maintain transparent supply chains, avoid child labor, and promote fair labor practices. In a globalized market, where consumers are more aware and concerned about the origins of products, demonstrating a commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing can significantly enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to B2B buyers.
What Is the Historical Context of the Apple Moving to USA Sector?
Historically, Apple has built its manufacturing prowess primarily in Asia, particularly in China, where it developed a complex supply chain over decades. However, geopolitical tensions and trade tariffs have prompted a reevaluation of this strategy. Apple’s recent commitment to invest heavily in U.S. manufacturing marks a significant shift in its operational model, aiming to enhance resilience and meet growing demands for local production.
This transition not only reflects changing market dynamics but also highlights the evolving expectations of international buyers who are increasingly looking for reliable, ethically sourced products. The historical reliance on overseas manufacturing is giving way to a more localized approach, which is expected to redefine the sourcing landscape for B2B buyers in the apple moving to USA sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of apple moving to usa
-
How do I solve issues with sourcing Apple products from the USA?
To address sourcing challenges, establish clear communication channels with your suppliers. Research potential suppliers thoroughly, focusing on their reputation, reliability, and ability to meet your requirements. Utilize platforms that specialize in B2B transactions to access verified suppliers. Additionally, ensure that you have a comprehensive understanding of U.S. regulations, tariffs, and import/export laws that may impact your purchasing decisions. Engaging with a local trade consultant can also help navigate these complexities. -
What is the best approach for vetting suppliers of Apple products?
The best approach for vetting suppliers includes conducting thorough background checks, reviewing their business history, and assessing their financial stability. Request references and case studies from previous clients to gauge their reliability and quality. It’s also beneficial to visit suppliers in person if possible or utilize video conferencing tools for virtual inspections. Consider certifications related to quality standards, such as ISO, which can further validate a supplier’s capabilities in delivering high-quality Apple products. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) when sourcing Apple products?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly based on the supplier, type of product, and your specific requirements. For Apple products, MOQs are often set to ensure production efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Typically, larger orders may reduce the per-unit cost, so consider your inventory needs and cash flow when negotiating MOQs with suppliers. Always communicate your expectations upfront to find a mutually beneficial arrangement that aligns with your business goals. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing from the USA?
Payment terms in B2B transactions can vary by supplier and are often negotiable. Common terms include net 30, net 60, or upfront payment requirements. Credit terms may be offered based on your business relationship and creditworthiness. Always clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., wire transfer, credit card, letters of credit) and inquire about any associated fees. Establishing a clear agreement on payment terms can help avoid misunderstandings and strengthen supplier relationships. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when importing Apple products?
To ensure quality assurance, implement a rigorous QA process that includes setting clear specifications and performance standards for the products you source. Request samples before placing a bulk order to assess quality firsthand. Work with third-party inspection services to conduct quality checks at various stages of production and before shipping. Maintaining open communication with your supplier about quality expectations can also foster a collaborative approach to achieving your QA goals. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing from the USA?
When importing from the USA, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Evaluate the total landed cost, including shipping, tariffs, and insurance, to avoid unexpected expenses. Collaborate with a reliable freight forwarder who understands the intricacies of international shipping and can assist with documentation. Additionally, stay informed about potential delays due to customs regulations and plan your inventory accordingly to maintain a steady supply chain. -
What are the potential challenges when moving Apple production to the USA?
Challenges in moving Apple production to the USA include high labor costs, the complexity of the existing supply chain, and the need for significant investment in infrastructure. Transitioning production may also lead to increased product prices, affecting market competitiveness. Companies must carefully assess their operational capabilities and the long-term benefits versus short-term disruptions. Strategic planning and collaboration with local governments and organizations can help mitigate these challenges. -
How does trade policy impact sourcing Apple products from the USA?
Trade policies, including tariffs and import regulations, significantly impact the cost and feasibility of sourcing Apple products. Changes in trade agreements can lead to increased costs or restrictions on certain products. It is crucial to stay updated on current trade policies affecting your specific industry and region. Engaging with legal and trade experts can help you navigate these complexities and develop strategies to minimize risks associated with fluctuating trade environments.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for apple moving to usa
As Apple embarks on a transformative journey to strengthen its U.S. manufacturing capabilities, the implications for international B2B buyers are profound. The company’s commitment to investing over $500 billion in the U.S. not only underscores the importance of strategic sourcing but also signals a shift towards localized supply chains. This move is expected to enhance the reliability of product availability and foster innovation through advanced manufacturing techniques, particularly in artificial intelligence and silicon engineering.
For businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this presents a unique opportunity to engage with a robust ecosystem of suppliers and partners emerging from Apple’s expanded operations. Companies can leverage this investment to access cutting-edge technology and skilled labor, essential for driving competitive advantage in their respective markets.
Looking ahead, it is crucial for international buyers to explore collaborative ventures and supplier relationships that align with Apple’s evolving supply chain. By doing so, they can position themselves strategically within a rapidly changing landscape. Engage with this opportunity to not only source quality products but also to be part of a new era of innovation and manufacturing excellence.