Top 6 Solar Panels Made In The Usa List and Guide: How To Solve S…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for solar panels made in the usa
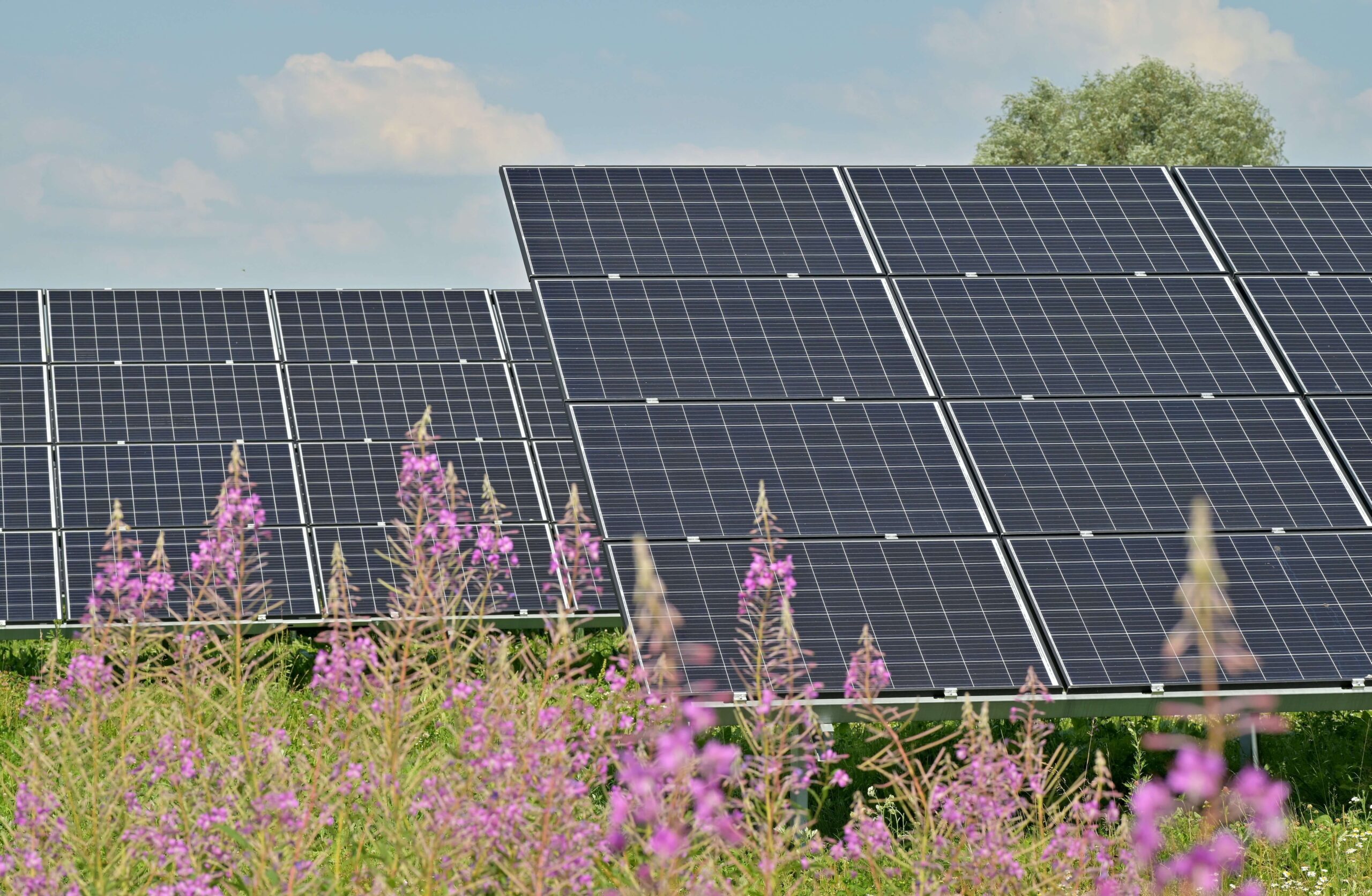
In today’s rapidly evolving energy landscape, sourcing high-quality solar panels made in the USA presents both an opportunity and a challenge for international B2B buyers. With increasing demand for renewable energy solutions, businesses from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are seeking reliable partners to navigate the complexities of the U.S. solar market. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the types of American-made solar panels available, their applications across various sectors, and insights into supplier vetting processes.
By delving into critical factors such as cost, performance metrics, and warranty offerings, this resource empowers decision-makers to make informed purchasing choices that align with their business objectives. Whether you’re looking to invest in solar technology for residential, commercial, or utility-scale projects, understanding the nuances of U.S. manufacturing standards can provide a competitive edge in your market.
Furthermore, as U.S. manufacturers increasingly innovate and adapt to global standards, this guide highlights the potential for long-term partnerships that not only support American jobs but also contribute to energy independence. Equip yourself with the knowledge needed to confidently engage with suppliers and optimize your procurement strategy in the dynamic world of solar energy.
Top 10 Solar Panels Made In The Usa Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. First Solar – Commercial/Industrial Panels
Domain: energysage.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: First Solar: Largest manufacturer in the U.S., producing panels mainly for commercial/industrial installations. Qcells: Second-largest manufacturer, popular for residential panels, has a manufacturing plant in Georgia. Other notable manufacturers include Solar4America, Silfab Solar, Heliene, Jinko Solar, and Mission Solar. Annual capacities of various manufacturers include: Auxin Solar (California…
2. Jinko – JKM425N-54HL4-B Solar Panel
Domain: sunwatts.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: [{‘brand’: ‘Jinko’, ‘model’: ‘JKM425N-54HL4-B’, ‘type’: ‘Mono All-Black Solar Panel’, ‘wattage’: 425, ‘msrp’: 250.0, ‘sale_price’: 220.0, ‘description’: ‘The Jinko Solar 425 watt monocrystalline all black module is the best in terms of power output and long-term reliability. Features 108 half-cell monocrystalline solar cells on a black backsheet.’}, {‘brand’: ‘Hyundai’, ‘model’: ‘HiN-T435NF(BK)’, …
3. A1 SolarStore – American Made Solar Panels
Domain: a1solarstore.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: American made solar panels for sale | Buy online for home, boat and RV – A1 SolarStore. Available wattages: 640W, 615W, 600W, 595W, 590W, 585W, 580W, 555W, 550W, 545W, 540W, 535W, 500W, 480W, 460W, 450W, 440W, 435W, 430W, 425W, 420W, 415W, 410W, 405W, 400W, 395W, 385W, 380W, 365W. Brands include Axitec, Canadian Solar, Hanwha Q CELLS, JA Solar, and more. Features include bifacial panels, EcoFlow c…
4. Qcells – Solar Manufacturing
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Panels advertised as made in the USA often use imported cells. Most solar cells are manufactured overseas, primarily in China, Malaysia, or Cambodia. Qcells is noted for being close to manufacturing its own ingots/wafers/cells and has a source of polysilicon in the U.S. Silfab planned to start making cells in South Carolina, but faced zoning changes due to community concerns.
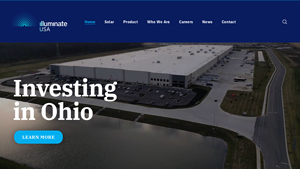
5. Illuminate USA – Bifacial Solar Panels
Domain: illuminateusa.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Illuminate USA produces bifacial solar panels using advanced and efficient panel assembly technology. The panels are designed for two domestic solar markets: rooftop (residential) and utility-scale. The manufacturing facility is located in Pataskala, Ohio, and aims to expand the U.S. solar supply chain.
6. MarketWatch – Solar Panel Manufacturers
Understanding solar panels made in the usa Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monocrystalline Solar Panels | High efficiency, sleek design, and space-efficient | Commercial rooftops, large installations | Pros: High power output; Cons: Higher cost |
| Polycrystalline Solar Panels | Cost-effective, slightly lower efficiency | Residential projects, small businesses | Pros: Affordable; Cons: Larger space requirement |
| Bifacial Solar Panels | Dual-sided energy generation, high efficiency | Utility-scale projects, large rooftops | Pros: Increased energy yield; Cons: Installation complexity |
| Thin-Film Solar Panels | Lightweight, flexible, and versatile | Unconventional surfaces, portable solutions | Pros: Easy to install; Cons: Lower efficiency |
| Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) | Integrated into building materials, aesthetic appeal | New constructions, renovations | Pros: Space-saving; Cons: Higher upfront costs |
What Are Monocrystalline Solar Panels and Their B2B Suitability?
Monocrystalline solar panels are known for their high efficiency and sleek aesthetics, making them an excellent choice for businesses with limited rooftop space. These panels are made from a single crystal structure, which allows them to achieve efficiencies of 20% or more. B2B buyers should consider these panels for commercial rooftops and large-scale installations where maximizing power output is critical. However, they come at a higher price point, which may impact budget considerations.
How Do Polycrystalline Solar Panels Compare for Business Use?
Polycrystalline solar panels are a cost-effective option for B2B buyers looking to invest in solar energy without breaking the bank. They are made from multiple crystal structures, resulting in slightly lower efficiency (typically around 15-17%) compared to monocrystalline panels. These panels are well-suited for residential projects and small businesses with ample installation space. While they offer affordability, their larger size may require more extensive installation areas, which can be a consideration for space-constrained projects.
What Are the Advantages of Bifacial Solar Panels for Utility Projects?
Bifacial solar panels are designed to capture sunlight from both sides, enhancing energy generation, especially in reflective environments. With efficiencies reaching up to 23%, they are ideal for utility-scale projects and large rooftops. B2B buyers should note that while these panels can increase overall energy yield, their installation can be more complex due to the need for specialized mounting systems. This complexity may lead to higher upfront costs but can result in significant long-term savings through increased energy production.
Why Consider Thin-Film Solar Panels for Unique Applications?
Thin-film solar panels are lightweight and flexible, making them suitable for unconventional surfaces and portable solutions. They are often used in applications where traditional panels cannot be installed, such as on curved surfaces or in mobile installations. While they offer ease of installation and versatility, their efficiency is generally lower (around 10-12%) compared to crystalline options. B2B buyers should consider these panels for niche applications where standard panels are impractical, but be mindful of their lower energy output.
What Are the Benefits of Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)?
Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) are designed to seamlessly integrate solar technology into building materials, such as windows and roofs. This approach not only generates energy but also maintains the aesthetic appeal of the building. B2B buyers looking at new constructions or renovations may find BIPV attractive for their space-saving qualities. However, the initial investment can be higher compared to traditional systems, requiring careful financial consideration. The potential for energy savings and enhanced property value can justify the costs in the long run.
Key Industrial Applications of solar panels made in the usa
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of solar panels made in the usa | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Solar-powered irrigation systems | Reduces operational costs and reliance on fossil fuels | Need for robust panels to withstand environmental factors |
| Manufacturing | Energy supply for manufacturing facilities | Lowers energy costs, enhances sustainability, and boosts brand image | Compliance with local regulations and certifications |
| Commercial Real Estate | Rooftop solar installations for office buildings | Generates renewable energy, reduces utility costs | Aesthetic considerations and building structure compatibility |
| Mining | Off-grid solar power solutions for remote sites | Ensures continuous operations and reduces diesel dependency | Durability and capacity to handle extreme conditions |
| Data Centers | Powering server farms with solar energy | Enhances energy efficiency and reduces carbon footprint | High-efficiency panels to manage large energy demands |
How Are Solar Panels Made in the USA Beneficial for the Agriculture Sector?
In the agriculture industry, solar panels made in the USA are increasingly being utilized for solar-powered irrigation systems. These systems help farmers reduce their operational costs by harnessing renewable energy, which minimizes reliance on expensive fossil fuels. Additionally, U.S.-made solar panels are designed to endure harsh environmental conditions, a critical consideration for agricultural applications. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, must ensure that the panels meet local climate challenges and have a proven track record in similar environments.
What Role Do Solar Panels Play in Manufacturing Operations?
In manufacturing, solar panels made in the USA can serve as a reliable energy source for production facilities. By integrating solar energy into their operations, manufacturers can significantly lower their energy costs while enhancing their sustainability efforts. This not only improves their bottom line but also strengthens their brand reputation as environmentally conscious enterprises. When sourcing solar panels, businesses should consider compliance with local regulations and the ability of the panels to withstand the operational demands of manufacturing environments.
How Can Solar Panels Enhance Commercial Real Estate Value?
Commercial real estate developers are increasingly installing solar panels on rooftops to generate renewable energy for office buildings. This application not only helps reduce utility costs but also adds value to the property by promoting sustainability. Furthermore, the aesthetic integration of solar panels into building designs is crucial for attracting tenants and buyers. International B2B buyers should assess the compatibility of solar solutions with existing building structures and ensure compliance with local building codes.
What Are the Advantages of Solar Energy in the Mining Industry?
In the mining sector, solar panels made in the USA are vital for providing off-grid solar power solutions to remote sites. These installations ensure continuous operations by reducing dependency on diesel generators, which can be costly and environmentally damaging. When sourcing solar panels for mining applications, durability is key, as they must withstand extreme weather and operational conditions. Buyers from regions with harsh climates should prioritize panels that have demonstrated resilience in similar environments.
How Do Solar Panels Support Data Center Operations?
Data centers are heavy consumers of energy, making solar panels made in the USA an attractive option for powering these facilities. By utilizing solar energy, data centers can enhance their energy efficiency and significantly reduce their carbon footprint. High-efficiency panels are essential for meeting the substantial energy demands of server farms. International buyers must look for solar solutions that offer superior performance and reliability to ensure uninterrupted service in data-intensive operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘solar panels made in the usa’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Assurance in Solar Panel Procurement
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges in ensuring the quality and reliability of solar panels made in the USA. With various manufacturers claiming superior performance, differentiating between genuinely high-quality products and inferior alternatives can be daunting. This is particularly critical for international buyers who may not have the opportunity to physically inspect the panels before purchasing. Poor quality panels can lead to increased maintenance costs, inefficiencies in energy production, and ultimately, a negative impact on the company’s bottom line.
The Solution: To navigate this quality assurance challenge, buyers should implement a robust vetting process for potential suppliers. Start by researching manufacturers with a proven track record in the solar industry, focusing on those with ISO certifications and positive third-party reviews. Engage with manufacturers directly to inquire about their production processes, quality control measures, and warranty offerings. It’s also advisable to request performance data and case studies from previous clients to evaluate real-world performance. Establishing a partnership with a reputable distributor who specializes in American-made products can further ensure that you are sourcing high-quality solar panels that meet your specific needs.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Cost Concerns in Importing American-Made Solar Panels
The Problem: Cost is a significant barrier for many international B2B buyers considering solar panels made in the USA. While these panels often come with a premium price tag due to higher manufacturing standards and labor costs, the initial investment can be daunting, especially for businesses operating on tight budgets or in developing markets. This raises concerns about the return on investment (ROI) and the long-term viability of such purchases.
The Solution: To mitigate cost concerns, buyers should conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis that includes not only the upfront costs but also long-term savings through energy efficiency and potential tax incentives. Many regions offer financial incentives for solar installations, including rebates and tax credits. Buyers should consult local energy authorities to identify applicable programs. Additionally, consider bulk purchasing agreements or long-term contracts with manufacturers to negotiate better pricing. Exploring financing options, such as power purchase agreements (PPAs) or solar leases, can also alleviate upfront costs while ensuring access to high-quality, American-made solar panels.
Scenario 3: Addressing Supply Chain Reliability for Solar Projects
The Problem: Supply chain disruptions can pose a significant risk for B2B buyers of solar panels, particularly those sourced from American manufacturers. Delays in production, shipping issues, or unexpected policy changes can lead to project timelines being extended, which impacts overall operational efficiency and financial planning. For international buyers, these challenges can be exacerbated by varying trade regulations and tariffs that might affect delivery schedules.
The Solution: To counter supply chain reliability issues, buyers should adopt a proactive approach by establishing strong relationships with multiple suppliers and manufacturers. Diversifying your supply chain can minimize risks associated with reliance on a single source. Additionally, it is wise to keep abreast of industry trends and geopolitical developments that may impact manufacturing and shipping. Implementing a just-in-time inventory system can help manage stock levels effectively while accommodating potential delays. Lastly, consider collaborating with local logistics providers who understand the nuances of international shipping and can provide timely updates on the status of shipments, helping to keep projects on track.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for solar panels made in the usa
What Are the Key Materials Used in American-Made Solar Panels?
When selecting solar panels made in the USA, understanding the materials involved is crucial for international B2B buyers. The choice of materials affects performance, durability, and compliance with regional standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in solar panel manufacturing, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international markets.
What Are the Key Properties of Silicon in Solar Panels?
Silicon is the most widely used material in solar panels, particularly in crystalline forms such as monocrystalline and polycrystalline.
Key Properties: Silicon exhibits excellent electrical conductivity, a high melting point (around 1,414°C), and good thermal stability. It is also resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of silicon is its efficiency in converting sunlight into electricity, with monocrystalline panels typically offering higher efficiency rates. However, silicon panels can be more expensive to manufacture, leading to higher upfront costs for buyers. Additionally, they can be sensitive to extreme temperatures, which may impact performance in very hot climates.
Impact on Application: Silicon’s compatibility with various media makes it suitable for residential, commercial, and utility-scale applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that the silicon panels comply with local standards, such as ASTM or IEC certifications, to guarantee performance and safety.
How Do Glass and Encapsulants Contribute to Solar Panel Durability?
Glass is used as a protective layer for solar panels, while encapsulants (often made from ethylene-vinyl acetate, EVA) secure the solar cells.
Key Properties: Tempered glass provides high impact resistance and can withstand significant pressure (up to 5400 Pa). EVA encapsulants offer excellent adhesion and UV resistance, enhancing the longevity of solar panels.
Pros & Cons: The use of glass increases durability and resistance to environmental factors, which is essential for long-term performance. However, glass adds weight to the panels, which can complicate installation. Encapsulants, while effective, can degrade over time if not properly formulated, potentially leading to reduced efficiency.
Impact on Application: The combination of glass and encapsulants ensures that solar panels can withstand harsh weather conditions, making them suitable for diverse environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards for glass quality and encapsulation is critical, especially in regions with extreme weather conditions.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Solar Panel Frameworks?
Aluminum is commonly used for the frames of solar panels, providing structural support.
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has a high strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand various environmental conditions without significant degradation.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum simplifies transportation and installation, reducing overall project costs. However, aluminum can be more expensive than other materials, which may affect the budget for large-scale projects.
Impact on Application: Aluminum frames are suitable for both rooftop and ground-mounted installations, providing versatility in application.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that aluminum frames meet local standards for strength and corrosion resistance, particularly in coastal regions where salt exposure is a concern.
How Do Bifacial Solar Cells Enhance Energy Collection?
Bifacial solar cells, which can capture sunlight from both sides, are becoming increasingly popular in solar panel designs.
Key Properties: Bifacial cells are typically made with transparent back sheets and utilize advanced materials that allow light to penetrate from both sides, improving energy collection efficiency.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of bifacial panels is their increased energy output, particularly in reflective environments. However, they require specific installation conditions to maximize their benefits, which can complicate deployment.
Impact on Application: Bifacial panels are particularly effective in utility-scale applications where space and efficiency are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should assess the installation requirements and ensure that local regulations support the use of bifacial technology.
Summary Table of Key Materials for Solar Panels Made in the USA
| Material | Typical Use Case for solar panels made in the usa | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon | Residential, commercial, and utility-scale panels | High efficiency in energy conversion | Higher manufacturing costs | High |
| Glass | Protective layer for solar panels | Durability and weather resistance | Adds weight, complicating installation | Medium |
| Aluminum | Structural framework for solar panels | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost compared to other materials | Medium |
| Bifacial Cells | Utility-scale applications | Increased energy output from dual sides | Requires specific installation conditions | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers looking to invest in solar panels made in the USA. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials can help in making informed purchasing decisions that align with regional standards and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for solar panels made in the usa
The manufacturing of solar panels in the USA is a multi-faceted process that combines advanced technology, rigorous quality assurance, and adherence to international standards. For B2B buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes and quality controls is essential for making informed procurement decisions.
What Are the Main Stages of Solar Panel Manufacturing in the USA?
The manufacturing process for solar panels generally consists of four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage incorporates specific techniques and technologies designed to optimize efficiency and reliability.
How Does Material Preparation Work in Solar Panel Manufacturing?
In the material preparation phase, raw materials such as silicon, glass, and metals are sourced and processed. Silicon, the primary material used in solar cells, undergoes purification to create high-purity polysilicon. This is followed by crystallization, where the silicon is melted and reformed into ingots, which are then sliced into thin wafers.
Advanced robotics and automation are increasingly utilized in this phase to minimize human error and enhance precision. For instance, manufacturers like Silfab employ robotic systems to ensure that the wafers are cut to exact specifications, thereby maximizing material yield and reducing waste.
What Techniques Are Used During the Forming Stage?
The forming stage involves converting the silicon wafers into functional solar cells. This is typically achieved through a series of doping processes, where impurities are introduced to create positive and negative layers within the silicon. The resulting solar cells are then treated with anti-reflective coatings to increase their efficiency by reducing light loss.
Manufacturers often leverage cutting-edge technologies, such as back-contact cell designs, which allow for more efficient light absorption. These designs are engineered specifically for the North American market, ensuring optimal performance in varied environmental conditions.
How is Assembly Conducted in the Solar Panel Manufacturing Process?
In the assembly stage, solar cells are arranged into modules. This involves the use of automated assembly lines where cells are interconnected through soldering. Quality control measures are critical during this phase to ensure that connections are secure and that the modules can withstand operational stresses.
Additionally, components such as glass covers and back sheets are integrated into the modules. The choice of materials at this stage is essential, as they must offer durability and protection against environmental factors, contributing to the panel’s overall lifespan.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied Before Solar Panels Are Deployed?
The finishing stage encompasses several important processes, including lamination, which seals the solar cells between protective layers. This is followed by electrical testing to ensure that the panels meet specified performance standards. Manufacturers often conduct visual inspections to identify any defects or irregularities before the panels are packaged for shipment.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Essential for Solar Panels Made in the USA?
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of solar panels is governed by various international and industry-specific standards. ISO 9001:2015 is one of the most recognized certifications, indicating that a manufacturer adheres to a quality management system that focuses on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
Which Quality Control Checkpoints Are Critical in Solar Panel Manufacturing?
The quality control process typically includes several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet predefined specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor the quality of production. This includes testing at various stages, such as during the forming and assembly processes.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, solar panels undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet performance and safety standards. This includes electrical testing, thermal cycling tests, and exposure to environmental conditions.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used to Ensure Quality?
Common testing methods include:
- Performance Testing: Panels are subjected to simulated sunlight to measure their energy output.
- Mechanical Testing: This assesses the structural integrity of the panels, including resistance to wind and hail.
- Environmental Testing: Panels are exposed to extreme temperatures and humidity to evaluate their long-term durability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is crucial. Here are several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the manufacturing and quality control processes. This allows buyers to assess compliance with international standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help buyers understand the testing methods used and the results achieved.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing facility and its adherence to quality standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances when dealing with U.S. manufacturers. Import regulations may require compliance with local standards, and understanding these can prevent potential issues during customs clearance. Additionally, knowing the specific certifications recognized in their home countries can aid in selecting the right supplier.
For example, while CE marking is crucial for products sold in Europe, B2B buyers from Brazil may need to ensure compliance with local regulatory standards such as ANATEL. Thus, it is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough due diligence on the certifications and quality practices of potential suppliers.
Conclusion
The manufacturing and quality assurance processes of solar panels made in the USA are characterized by meticulous attention to detail and adherence to international standards. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they procure high-quality, reliable solar panels that meet their specific needs. Whether navigating the complexities of international regulations or verifying supplier quality, the insights outlined here can serve as a valuable guide in the procurement journey.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘solar panels made in the usa’
To aid international B2B buyers in the procurement of solar panels made in the USA, this guide offers a comprehensive checklist. It emphasizes the importance of quality, compliance, and supplier reliability in ensuring a successful purchase that meets both operational and sustainability goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your project’s requirements is essential. Begin by identifying the specific needs of your installation, such as energy output, panel size, and efficiency ratings. Consider factors like the climate of the installation site and any specific certifications required in your region.
- Key Specifications: Look for efficiency ratings (e.g., above 18%), power output (measured in watts), and warranty offerings (at least 25 years).
- Performance Metrics: Analyze performance under various environmental conditions, such as low-light performance and temperature coefficients.
Step 2: Research Available Manufacturers
Compile a list of U.S.-based solar panel manufacturers. Focus on companies known for their high-quality products and reliable service. Assess their market reputation and the range of products they offer.
- Top Manufacturers: Notable names include First Solar, Qcells, and Silfab Solar. Each has unique strengths, such as efficiency, warranty terms, or technology.
- Market Presence: Verify their distribution capabilities and whether they have experience serving your specific geographical market.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure compliance with industry standards and certifications. Check for certifications such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) or IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) that indicate product quality and safety.
- Importance of Certifications: These certifications assure that the panels meet rigorous performance and safety standards, which is crucial for long-term reliability.
- Additional Compliance: Look for adherence to local regulations and any specific certifications required by your region, such as those related to sustainability.
Step 4: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough due diligence on potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, customer testimonials, and case studies relevant to your industry or similar projects.
- Supplier Background: Assess their experience in manufacturing and supplying solar panels, particularly focusing on their track record in international markets.
- Customer References: Contact past clients to gauge satisfaction levels and reliability in fulfilling orders.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Compare pricing structures and payment options. Request quotes from multiple suppliers and ensure that you understand what is included in the pricing—such as shipping, installation, and warranties.
- Transparent Pricing: Look for suppliers that provide clear breakdowns of costs to avoid hidden fees.
- Payment Flexibility: Consider suppliers that offer favorable payment terms, which can be critical for managing cash flow.
Step 6: Review Warranty and Support Services
Examine the warranty terms and post-purchase support offered by suppliers. A robust warranty indicates confidence in product quality and can protect your investment in the long run.
- Warranty Coverage: Aim for at least a 25-year warranty on performance, with clear terms on what is covered.
- Support Availability: Investigate the level of technical support available post-purchase and whether they provide maintenance services.
Step 7: Finalize Logistics and Installation Plans
Plan for logistics and installation to ensure a smooth procurement process. Confirm shipping times, installation timelines, and the availability of necessary installation support.
- Logistics Coordination: Work closely with suppliers to align delivery schedules with your project timelines.
- Installation Partnerships: Consider local installers with experience in handling U.S.-made solar panels to ensure adherence to best practices and local regulations.
This checklist serves as a practical roadmap to navigating the complex process of sourcing solar panels made in the USA, ensuring that your investments align with your energy goals and operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for solar panels made in the usa Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Solar Panels Made in the USA?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing solar panels manufactured in the USA, several key components come into play. Understanding these elements can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, including silicon, glass, and metals, constitutes a significant portion of the overall price. American manufacturers often source high-quality materials to ensure durability and efficiency, which can lead to higher initial costs but lower maintenance expenses over time.
-
Labor: Labor costs in the USA are typically higher than in many other countries. Skilled labor is necessary for the manufacturing of solar panels, especially those that incorporate advanced technologies. This can increase the cost per unit but often results in a higher quality product with better long-term performance.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. U.S. manufacturers may have higher overhead due to stricter regulations and standards, which can impact pricing.
-
Tooling and Equipment: Investment in cutting-edge machinery and technology is crucial for producing efficient solar panels. The costs associated with tooling can be significant, especially for companies aiming to innovate and improve product quality.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the panels meet high performance and safety standards. While this adds to the cost, it significantly reduces the risk of defects and enhances customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Transportation and distribution costs can vary depending on the destination. For international buyers, understanding shipping costs and potential tariffs is essential for budget planning.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a profit margin to cover their expenses and ensure sustainability. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of U.S.-Made Solar Panels?
Several factors can influence the pricing of solar panels sourced from the USA, making it essential for buyers to understand their implications.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchases often result in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate to secure better pricing based on their anticipated volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized panels tailored to specific project requirements can increase costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization with the potential for added expense.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (such as ISO or UL) can increase costs but also enhance reliability and performance, making them a worthwhile investment.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established manufacturers may command higher prices due to their quality assurances and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of trade (Incoterms) is crucial for international buyers. These terms dictate responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect total costs.
What Are the Best Tips for Negotiating Solar Panel Prices as an International Buyer?
International B2B buyers should adopt strategic approaches to ensure cost-effectiveness when sourcing solar panels.
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage in discussions about pricing and terms with multiple suppliers to leverage competitive offers. Highlighting potential for volume purchases can lead to better deals.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term savings and efficiency of the solar panels rather than focusing solely on the upfront price. High-quality panels may have a higher initial cost but offer lower maintenance and energy costs over their lifespan.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Familiarize yourself with market trends and pricing dynamics within the solar industry. Prices can fluctuate based on demand, government incentives, and raw material costs.
-
Be Aware of International Trade Factors: Tariffs, import duties, and currency fluctuations can impact the final cost of solar panels. Engaging with local experts can provide insights into these variables.
Conclusion
When sourcing solar panels made in the USA, understanding the cost structure, pricing influencers, and negotiation strategies is vital for international buyers. By considering these aspects, businesses can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their project goals and budgets. As always, indicative prices should be used cautiously, as they may vary based on the factors discussed.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing solar panels made in the usa With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Solar Panels Made in the USA
As the global energy landscape evolves, B2B buyers face an array of choices when it comes to sustainable energy solutions. While solar panels made in the USA offer numerous advantages, it is crucial to explore alternative technologies that can also meet energy needs effectively. This comparison will delve into two viable alternatives: wind energy systems and energy storage solutions.
Comparison of Solar Panels Made in the USA with Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Solar Panels Made In The USA | Wind Energy Systems | Energy Storage Solutions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency; reliable power output, especially in sunny regions | Variable output; dependent on wind conditions, but can produce substantial energy | Enhances grid reliability; stores excess energy for later use |
| Cost | Initial costs are moderate; long-term savings due to tax incentives | Higher upfront costs; potential for lower operating costs depending on location | Costs vary widely; investment in batteries can be significant but offers long-term savings |
| Ease of Implementation | Generally straightforward with local installers; various financing options available | Requires specific site assessments; more complex installation | Can be integrated with existing systems but requires upfront planning |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; occasional cleaning required | Moderate maintenance; turbine inspections needed periodically | Maintenance varies; battery systems require monitoring and replacement over time |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for residential and commercial applications in sunny areas | Suited for areas with consistent wind; best for larger-scale applications | Useful for balancing supply and demand; enhances solar or wind systems |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Wind Energy Systems
Wind energy systems capture kinetic energy from wind and convert it into electricity. They can be highly efficient in regions with consistent wind patterns. However, their effectiveness varies based on geographical location, making them less reliable in areas with low wind speeds. Additionally, the initial investment can be substantial, including costs for site assessments and turbine installations. Despite these challenges, wind energy can provide a renewable solution that, when combined with other technologies, contributes to a resilient energy strategy.
Energy Storage Solutions
Energy storage systems, primarily lithium-ion batteries, store excess energy produced during peak generation times for later use. This technology is particularly advantageous for integrating renewable sources like solar and wind, providing stability to the energy supply. However, the initial costs can be significant, and the longevity of batteries varies, requiring regular monitoring and eventual replacement. Energy storage can be especially beneficial for businesses looking to manage energy costs and enhance operational efficiency, making it a strong complement to solar panel systems.
Making the Right Choice: Factors for B2B Buyers
When considering energy solutions, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific energy needs, geographic location, and financial capabilities. Solar panels made in the USA stand out for their reliability and efficiency, particularly in sunny regions, while wind energy systems may be more appropriate for areas with consistent winds. Energy storage solutions can enhance any renewable energy strategy by providing flexibility and reliability. Ultimately, the decision should be guided by a thorough analysis of performance, cost, and the specific energy requirements of the business, ensuring a sustainable and economically viable energy strategy.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for solar panels made in the usa
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Solar Panels Made in the USA?
Understanding the technical specifications of solar panels is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing products from the USA. Here are some essential properties that impact performance, reliability, and overall value.
1. Efficiency Rating
Efficiency refers to the percentage of sunlight that a solar panel can convert into usable electricity. Higher efficiency ratings mean more power generation from the same amount of sunlight, which is vital for maximizing energy output, especially in areas with limited space. For example, panels with efficiency ratings of over 20% are considered high-performing, making them suitable for both residential and commercial applications.
2. Power Output (Wattage)
Power output, measured in watts, indicates the amount of energy a solar panel can produce under standard test conditions. This specification is critical for calculating the number of panels required to meet specific energy needs. For instance, a panel with a power output of 400 watts can generate more energy than one rated at 300 watts, impacting the overall system size and cost.
3. Temperature Coefficient
The temperature coefficient measures how much a solar panel’s output decreases as temperatures rise. A lower temperature coefficient indicates better performance in hot climates, which is essential for buyers in warmer regions. For example, a panel with a temperature coefficient of -0.3%/°C will lose less power in higher temperatures compared to one rated at -0.5%/°C, making it a more reliable choice for those areas.
4. Warranty Duration
The warranty duration for solar panels typically ranges from 25 to 30 years, covering performance and product defects. A robust warranty not only ensures quality but also reduces the long-term risk for buyers. It is essential for B2B buyers to consider the warranty terms when evaluating potential suppliers, as this reflects the manufacturer’s confidence in their product’s durability.
5. Material Grade
The grade of materials used in solar panels affects their longevity and performance. Common materials include monocrystalline silicon, polycrystalline silicon, and thin-film technologies. Monocrystalline panels, for instance, are known for their high efficiency and space-saving design, making them a popular choice for premium applications.
6. Certifications and Standards
Solar panels should meet various industry standards and certifications, such as IEC 61215 and UL 1703, which ensure safety and performance. These certifications are crucial for B2B buyers as they validate the product’s quality and compliance with regulatory requirements, which can influence project approvals and financing.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Solar Panel Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the solar market. Here are several key terms you should know.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces components or products that are sold by another company under its brand name. In the solar industry, working with an OEM can provide access to high-quality panels while allowing buyers to market them under their brand, enhancing their product offerings.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is crucial for international buyers, as it affects inventory management and pricing strategies. Suppliers with lower MOQs can be more appealing for smaller businesses or new entrants in the market.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing for specific products or services. It allows buyers to compare offers from multiple vendors efficiently. A well-structured RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms, essential for effective procurement.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps clarify shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery responsibilities, which can significantly affect the total cost of procurement.
5. LCOE (Levelized Cost of Energy)
LCOE is a measure of the average net cost of electricity generation for a project over its lifetime, considering all costs. This metric is vital for B2B buyers as it helps assess the financial viability of solar projects, allowing for better investment decisions.
6. PPA (Power Purchase Agreement)
A PPA is a long-term contract between a power producer and a buyer, typically for the sale of electricity generated by a solar power system. Understanding PPAs is essential for buyers looking to finance solar installations, as they can provide predictable pricing and revenue streams.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing solar panels made in the USA, ensuring they choose the right products for their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the solar panels made in the usa Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Affecting Solar Panels Made in the USA?
The solar panel market is experiencing a transformative shift driven by several global factors. The increasing urgency of climate change is propelling governments and businesses worldwide to adopt renewable energy solutions, with solar power at the forefront. In regions like Africa and South America, the demand for affordable, sustainable energy is escalating, while Europe, particularly Germany, is pushing for energy independence and carbon neutrality. The expiration of the 30% solar tax credit in the U.S. by January 1, 2026, adds a layer of urgency for international buyers to consider U.S.-made solar panels, as purchasing before the deadline could yield significant savings.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing trends, particularly in manufacturing processes and materials. Automation and advanced robotics in production are enhancing the efficiency and reliability of solar panels made in the USA. International buyers should also be aware of the competitive landscape, where manufacturers like First Solar and Qcells are leading the charge. The latter has recently expanded its U.S. operations, providing high-quality residential panels that cater to a growing market. Additionally, sustainability is becoming a purchasing criterion, with buyers increasingly favoring manufacturers that demonstrate a commitment to eco-friendly practices.
How Does Sustainability Influence Sourcing Decisions for Solar Panels?
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it’s a fundamental aspect of sourcing decisions in the solar panel sector. International buyers are increasingly prioritizing ethical supply chains that minimize environmental impact. U.S.-made solar panels often adhere to stringent regulations and certifications that ensure responsible sourcing of materials. These certifications not only validate the sustainability claims of manufacturers but also serve as a competitive advantage in a market where consumers are more eco-conscious.
Manufacturers like Silfab Solar emphasize their commitment to sustainable practices, utilizing advanced technologies that reduce waste and enhance the lifecycle of their products. Moreover, companies are increasingly focusing on recycling solutions for end-of-life solar panels, further mitigating environmental impacts. Buyers looking for sustainable options should inquire about the certifications held by manufacturers, such as ISO 9001:2015, and any green certifications that demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing.
How Has the Solar Panel Manufacturing Sector Evolved Over Time?
The solar panel manufacturing sector has undergone significant changes over the past few decades, evolving from nascent technologies to a robust industry that plays a crucial role in the global energy landscape. Initially dominated by a few key players, the market has expanded considerably, driven by technological advancements and increased demand for renewable energy solutions. The establishment of U.S. manufacturing plants by international companies like Qcells and Jinko Solar marks a pivotal shift, highlighting the strategic importance of local production in meeting domestic and international demand.
Furthermore, the rise of automation and innovative manufacturing techniques has enabled U.S. manufacturers to improve product quality and efficiency, thereby enhancing their competitive edge. As international buyers increasingly recognize the value of U.S.-made solar panels, the sector is poised for continued growth, supported by favorable policies and a global commitment to sustainability. This evolution not only reflects technological advancements but also signifies a broader societal shift toward renewable energy solutions that prioritize both economic and environmental well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of solar panels made in the usa
-
How do I ensure the quality of solar panels made in the USA?
To ensure the quality of solar panels made in the USA, prioritize suppliers that adhere to strict manufacturing standards, such as ISO 9001:2015 certification. Request product specifications, performance warranties, and independent testing certifications. Additionally, consider panels that have been rated highly in performance indexes, which often include metrics on efficiency, durability, and defect rates. Engaging in direct communication with manufacturers can also provide insights into their quality control processes and any recent advancements in technology. -
What is the best way to evaluate solar panel suppliers in the USA?
When evaluating solar panel suppliers in the USA, look for established manufacturers with a proven track record in the industry. Assess their production capacity, range of products, and compliance with international standards. Reading customer reviews and case studies can provide insight into their reliability. Additionally, verify their financial stability and ability to support long-term contracts, which is essential for B2B partnerships. Engaging in industry networking events can also yield valuable recommendations and insights. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for solar panels made in the USA?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for solar panels can vary significantly by manufacturer and the specific product lines. Generally, MOQs for commercial orders can range from a few hundred to several thousand panels, depending on the scale of the order and the manufacturer’s production capabilities. It’s advisable to discuss your project requirements directly with suppliers to understand their MOQ policies and explore potential flexibility based on your business needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing solar panels from USA manufacturers?
Payment terms when purchasing solar panels from USA manufacturers typically vary but may include options like upfront payment, net 30 or net 60 days, or installment plans. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring the supplier’s security. Additionally, consider establishing a letter of credit for larger transactions, which can offer protection for both parties. Always clarify these terms in the contract to avoid misunderstandings. -
What customization options are available for solar panels made in the USA?
Customization options for solar panels can include variations in size, wattage, and aesthetic features, such as color and design. Some manufacturers also offer tailored solutions for specific applications, like commercial or residential installations. When seeking customization, it’s important to discuss your specific requirements with the manufacturer early in the negotiation process, as this may influence lead times and pricing. -
How can I manage logistics when importing solar panels from the USA?
Managing logistics for importing solar panels from the USA involves coordinating shipping, customs clearance, and local transportation. Work closely with your supplier to understand their shipping options and ensure compliance with export regulations. Consider partnering with a logistics provider experienced in solar equipment to facilitate customs documentation and reduce transit times. Additionally, factor in lead times for production and shipping to align with your project timelines. -
What are the regulatory considerations for importing solar panels into my country?
Regulatory considerations for importing solar panels vary by country and may include tariffs, import duties, and compliance with local standards. It’s essential to research your country’s import regulations and any specific requirements related to solar technology. Engaging with a local customs broker can provide insights into necessary documentation and help navigate potential hurdles. Additionally, ensure that the panels meet your country’s quality and safety standards to avoid complications upon arrival. -
How do I verify the sustainability practices of solar panel manufacturers in the USA?
To verify the sustainability practices of solar panel manufacturers, review their environmental certifications, such as ISO 14001, which demonstrates commitment to effective environmental management. Investigate their supply chain practices, including the sourcing of raw materials and waste management strategies. Manufacturers that publish sustainability reports or participate in industry sustainability initiatives are often more transparent about their practices. Engaging in direct discussions with suppliers can also clarify their commitment to sustainability and corporate social responsibility.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for solar panels made in the usa
As the demand for sustainable energy solutions grows, the strategic sourcing of solar panels made in the USA presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers. U.S. manufacturers, including First Solar and Qcells, are leading the charge in quality and innovation, offering panels that meet rigorous performance standards while supporting American jobs and energy independence. The impending expiration of the 30% solar tax credit in 2026 further emphasizes the urgency for stakeholders to act now, potentially saving substantial costs in the process.
Emphasizing strategic sourcing allows businesses to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and fluctuating international prices. By investing in American-made solar panels, companies not only ensure compliance with stringent quality standards but also align with growing consumer preferences for domestic products.
Looking ahead, international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are encouraged to explore partnerships with U.S. manufacturers. This approach not only fosters resilience and sustainability but also positions businesses favorably in a competitive global market. Seize the moment to enhance your energy portfolio with reliable, high-quality solar solutions that promise long-term benefits.