Top 6 Solar Energy Manufacturers Usa List and Guide: How To Solve…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for solar energy manufacturers usa
In the rapidly evolving landscape of renewable energy, sourcing solar energy manufacturers in the USA presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers. With a growing demand for reliable and efficient solar solutions, businesses in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly turning to American manufacturers to meet their energy needs. This guide serves as a vital resource, equipping buyers with comprehensive insights into the diverse types of solar products available, their various applications, and the essential criteria for vetting suppliers effectively.
Throughout this guide, we delve into the intricacies of the U.S. solar manufacturing sector, highlighting key players, production capacities, and technological advancements. We also explore cost considerations, ensuring that buyers can make informed decisions that align with their budgetary constraints and operational requirements. By understanding the dynamics of the solar energy market in the USA, international buyers can identify the most suitable partnerships that not only enhance their sustainability goals but also contribute to long-term economic benefits.
Empowered by this information, businesses can navigate the complexities of sourcing solar energy solutions, fostering connections with manufacturers that prioritize quality, innovation, and sustainability. This guide ultimately aims to facilitate smarter purchasing decisions, enabling companies to harness the full potential of solar energy in their respective markets.
Top 10 Solar Energy Manufacturers Usa Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. First Solar – Commercial Solar Solutions
Domain: energysage.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
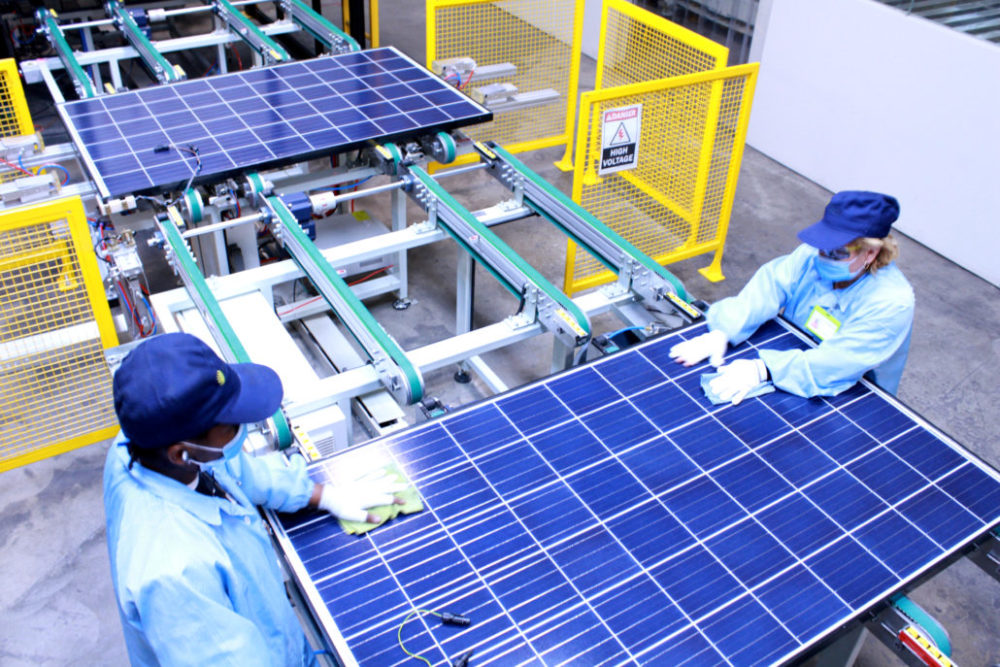
Introduction: First Solar: Largest manufacturer in the U.S., producing 6,300 MW, mainly for commercial/industrial installations. Qcells: Second-largest manufacturer, popular for residential panels, recently opened a plant in Georgia. Other notable manufacturers include Solar4America, Silfab Solar, Heliene, Jinko Solar, and Mission Solar. Annual capacities for other manufacturers: Auxin Solar (150 MW), Canadian …
2. Illuminate USA – Bifacial Solar Panels
Domain: illuminateusa.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Illuminate USA produces bifacial solar panels using advanced and efficient panel assembly technology. These panels are designed for two domestic solar markets: rooftop (residential) and utility-scale. The manufacturing facility is located in Pataskala, Ohio, and aims to expand the U.S. solar supply chain.
3. MarketWatch – Leading Solar Panel Manufacturers
4. NextEra Energy – Solar Projects and Capacity
Domain: investopedia.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: NextEra Energy operates 33 solar projects with 37,000 MW generating capacity. First Solar provides solar panels, photovoltaic power plants, and related services, utilizing thin film semiconductor technology. Enphase Energy offers modularized smart technology integrating energy storage systems for homes and businesses. Nextracker provides solar software and tracking solutions for utility-scale sola…
5. Top Solar Manufacturers – Leading Brands in 2024
Domain: sunsave.energy
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: The 9 largest solar panel manufacturers in the world as of 2024 are: 1. Trina Solar Co. Ltd. (China, founded 1997, 34GWp), 2. LONGi Green Energy Technology Co. Ltd. (China, founded 2000, 31.3GWp), 3. Tongwei Solar (China, founded 2009, 18.7GWp), 4. Astronergy (Chint New Energy Technology Co. Ltd., China, founded 2006, 18.7GWp), 5. Canadian Solar Inc. (Canada, founded 2001, 14.5GWp), 6. GCL-SI (Chi…
6. NextEra Energy – Solar Power Solutions
Domain: climateinsider.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: NextEra Energy: Founded 1984, 16,800 employees, $6.4 billion adjusted earnings for 2023, 5 GW installed solar capacity. First Solar: Founded 1999, 6,700 employees, $830.8 million profit for 2023, plans for 25 GW capacity by 2026. Cypress Creek Renewables: Founded 2014, 380 employees, $200 million raised, owns 2 GW solar capacity. Recurrent Energy: Founded 2006, unclear employees, at least $904 mil…
Understanding solar energy manufacturers usa Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Large-Scale Manufacturers | High production capacity, often targeting commercial and utility markets. | Utility-scale solar farms, large commercial installations. | Pros: Economies of scale, lower per-watt costs. Cons: Less focus on residential applications, potential longer lead times. |
| Residential Panel Manufacturers | Focus on smaller-scale, high-efficiency panels for homes. | Residential solar installations. | Pros: Tailored solutions, higher efficiency. Cons: Higher costs per watt compared to large-scale. |
| Integrated Solar Solutions | Offer complete solar systems including panels, inverters, and mounting systems. | Turnkey solar projects, commercial and residential sectors. | Pros: Simplifies procurement, cohesive system performance. Cons: May limit options for specific components. |
| Polysilicon Manufacturers | Specialize in producing the raw material for solar panels. | Supply chain for solar panel production. | Pros: Essential for panel production, potential for long-term partnerships. Cons: Limited direct application for end-users. |
| OEM Manufacturers | Produce solar panels under private labels for various brands. | Private label solar products, niche markets. | Pros: Flexibility in branding, often cost-effective. Cons: Potential variability in quality and performance. |
What are the Characteristics of Large-Scale Manufacturers?
Large-scale manufacturers dominate the solar market by producing vast quantities of solar panels, primarily aimed at utility-scale solar farms and large commercial installations. Companies like First Solar exemplify this category, offering solutions that prioritize cost-effectiveness and reliability. B2B buyers should consider the economies of scale these manufacturers provide, which often translates to lower per-watt costs. However, these companies may not cater to residential applications, leading to potential longer lead times for specific projects.
How Do Residential Panel Manufacturers Differ?
Residential panel manufacturers focus on high-efficiency solar solutions tailored for individual homes. These companies often prioritize performance and aesthetic appeal, making them suitable for residential installations. B2B buyers looking for residential solutions should evaluate the efficiency ratings and warranty offerings of these manufacturers. While these panels tend to have a higher cost per watt, their effectiveness in limited spaces can result in quicker payback periods for homeowners.
What are Integrated Solar Solutions and Their Benefits?
Integrated solar solution providers offer complete systems, including solar panels, inverters, and mounting systems, facilitating a seamless procurement process for B2B buyers. This approach simplifies project management and ensures that all components are compatible, enhancing overall system performance. Buyers should consider the convenience and reliability of sourcing from a single manufacturer, though they may encounter limited choices for individual components.
Why are Polysilicon Manufacturers Important in the Supply Chain?
Polysilicon manufacturers produce the raw material essential for the creation of solar panels. They play a crucial role in the supply chain, particularly as demand for solar energy continues to grow. B2B buyers looking to engage with polysilicon manufacturers should focus on establishing long-term partnerships to secure a stable supply of materials. However, these manufacturers do not directly serve end-users, so their relevance is primarily in the context of production and supply chain management.
What Role do OEM Manufacturers Play in the Solar Market?
Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) produce solar panels under private labels, allowing various brands to offer solar products without manufacturing them in-house. This flexibility can be advantageous for niche markets looking for customized solutions. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of cost-effectiveness against potential variability in quality and performance, as OEM products may not always meet the same standards as those from established manufacturers.
Key Industrial Applications of solar energy manufacturers usa
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of solar energy manufacturers usa | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Solar-powered irrigation systems | Reduces energy costs and enhances crop yields | Assess durability, efficiency in various climates, and compatibility with existing systems |
| Manufacturing | Solar energy for powering production facilities | Lowers operational costs and carbon footprint | Evaluate energy output, installation support, and local regulations on solar use |
| Commercial Real Estate | Rooftop solar installations for office buildings | Increases property value and reduces utility bills | Consider roof space, local incentives, and long-term maintenance services |
| Mining | Solar energy for remote site operations | Ensures energy supply in off-grid locations | Focus on system reliability, scalability, and integration with existing power sources |
| Transportation | Solar-powered electric vehicle (EV) charging stations | Expands infrastructure while promoting sustainability | Look for modular solutions, local energy policies, and ease of installation |
How Are Solar Energy Manufacturers in the USA Beneficial for Agriculture?
In the agricultural sector, solar energy manufacturers in the USA provide critical solutions through solar-powered irrigation systems. These systems help farmers reduce reliance on conventional energy sources, leading to significant cost savings. By harnessing solar energy, agricultural businesses can enhance crop yields, especially in regions with limited access to traditional power. International buyers must consider the durability of these systems in diverse climates, efficiency ratings, and compatibility with existing irrigation setups to ensure optimal performance.
What Role Do Solar Energy Solutions Play in Manufacturing?
Manufacturers increasingly turn to solar energy to power their production facilities, significantly lowering operational costs while minimizing their carbon footprint. Implementing solar solutions allows businesses to stabilize energy expenses and contribute to sustainability efforts. For B2B buyers in this sector, evaluating the energy output of solar systems, the support provided during installation, and compliance with local regulations are essential to maximize investment and ensure seamless integration into existing operations.
Why Is Solar Energy Important for Commercial Real Estate?
In the commercial real estate sector, solar energy is often leveraged through rooftop installations on office buildings. This approach not only reduces utility bills but also enhances property value, making it an attractive proposition for investors and tenants alike. B2B buyers should consider factors such as available roof space, local incentives for solar adoption, and the long-term maintenance services offered by manufacturers to make informed purchasing decisions.
How Can Solar Energy Support Mining Operations?
Solar energy manufacturers provide tailored solutions for the mining industry, particularly for remote site operations where access to reliable power sources is challenging. Solar energy ensures a consistent power supply, reducing operational disruptions and enhancing productivity. Buyers in the mining sector should prioritize the reliability of solar systems, their scalability to meet varying energy demands, and the potential for integration with existing power infrastructures to optimize their energy strategy.
What Are the Benefits of Solar-Powered EV Charging Stations?
The transportation sector benefits from solar energy through the installation of solar-powered electric vehicle (EV) charging stations. This infrastructure expansion supports sustainability initiatives and meets the growing demand for EVs. For international B2B buyers, key considerations include modularity of the solar solutions, alignment with local energy policies, and the ease of installation to ensure effective deployment in various locations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘solar energy manufacturers usa’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Supply Chain Disruptions in Solar Manufacturing
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter significant supply chain disruptions when sourcing solar products from U.S. manufacturers. With fluctuating global demand and geopolitical tensions, delays in obtaining critical components like inverters or batteries can stall projects and inflate costs. Buyers may find themselves scrambling to meet deadlines, leading to potential financial losses and damaged relationships with clients. This unpredictability can be particularly challenging for companies in regions like Africa and South America, where timelines are crucial for project viability.
The Solution: To mitigate supply chain issues, B2B buyers should establish relationships with multiple manufacturers and diversify their supplier base. Conducting thorough market research to identify U.S. manufacturers that maintain robust inventories and have flexible production capabilities can help. It’s also beneficial to engage in proactive communication with suppliers about their stock levels and lead times. Buyers can further protect themselves by negotiating contracts that include clauses for rapid response and alternative sourcing options in case of disruptions. Additionally, leveraging technology such as supply chain management software can enhance visibility into the supply process and facilitate better decision-making.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Quality and Compliance in Solar Products
The Problem: Quality assurance and compliance with international standards pose significant challenges for B2B buyers. Many manufacturers claim to meet U.S. standards, but discrepancies can lead to subpar products that fail to perform as expected, resulting in costly rework or replacements. For companies operating in regions with strict regulatory frameworks, such as the European Union, ensuring that all solar products comply with local laws is not just a matter of cost but also of legal necessity.
The Solution: B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that provide comprehensive documentation of compliance with relevant standards, such as UL certification for safety and performance. Conducting due diligence through supplier audits and requesting product samples for independent testing can ensure quality before large-scale procurement. Establishing a clear set of criteria for evaluating manufacturers, including their quality control processes and past performance metrics, will help in selecting reliable partners. It’s also advisable to stay informed about regulatory changes in the target markets, ensuring that the chosen manufacturers can adapt to new compliance requirements swiftly.
Scenario 3: Managing Cost Variability in Solar Projects
The Problem: The cost of solar components can be highly variable, influenced by factors such as raw material prices, tariffs, and shipping costs. For B2B buyers, this variability complicates budgeting and financial forecasting, making it difficult to secure project financing and manage client expectations. The challenge is particularly acute for companies in emerging markets where funding may be limited and price stability is crucial for project feasibility.
The Solution: To effectively manage cost variability, buyers should adopt a strategic procurement approach. This includes locking in prices with manufacturers through long-term contracts, which can provide price stability and predictability. Engaging in forward buying—purchasing in advance when prices are favorable—can also be an effective strategy. Additionally, buyers should explore bulk purchasing options or cooperative buying groups to leverage economies of scale. Staying informed about market trends and participating in industry forums can help buyers anticipate price changes and adjust their procurement strategies accordingly. Finally, establishing strong relationships with manufacturers can facilitate negotiations that account for potential cost fluctuations, allowing for more predictable project budgeting.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for solar energy manufacturers usa
What Are the Key Materials Used in Solar Energy Manufacturing in the USA?
When selecting materials for solar energy manufacturing, several key options stand out due to their specific properties and applications. Understanding these materials can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
What Are the Key Properties of Silicon in Solar Panels?
Silicon is the most widely used material in solar panels, particularly in crystalline forms. It boasts excellent electrical properties, high thermal resistance, and a temperature rating that can exceed 100°C. Its corrosion resistance is moderate, making it suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros: Silicon is durable and has a long lifespan, often exceeding 25 years in solar applications. It is relatively cost-effective, especially with advancements in manufacturing processes that have reduced costs over the years.
Cons: The manufacturing process can be complex and energy-intensive, which may lead to higher initial costs. Additionally, while silicon panels are efficient, they are not as efficient as some alternative materials like gallium arsenide.
Impact on Application: Silicon’s compatibility with various media makes it a versatile choice for different climates and installations. However, international buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM E1036 for silicon solar cells.
How Does Glass Contribute to the Durability of Solar Panels?
Glass is used extensively in solar panel manufacturing, primarily as a protective layer for solar cells. High-transmission, low-iron glass is often preferred due to its excellent light transmission properties and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and is resistant to UV radiation and corrosion.
Pros: Glass enhances the overall durability and efficiency of solar panels. It is also recyclable, which aligns with sustainability goals.
Cons: While glass is durable, it can be heavy, which may complicate installation and increase shipping costs. Breakage during transport or installation is also a concern.
Impact on Application: The choice of glass affects the panel’s efficiency and longevity. International buyers should consider compliance with standards such as IEC 61215, which governs the performance of solar panels.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Solar Panel Frames?
Aluminum is commonly used for the framing of solar panels due to its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. It can withstand various environmental conditions, making it suitable for both residential and commercial applications.
Pros: Aluminum is easy to fabricate and install, reducing labor costs. Its resistance to corrosion ensures longevity, especially in harsh environments.
Cons: While aluminum is cost-effective, fluctuations in market prices can affect overall project budgets. Additionally, it may not offer the same structural strength as steel in certain applications.
Impact on Application: The use of aluminum frames can enhance the overall performance of solar installations. Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions.
How Does Copper Influence Electrical Conductivity in Solar Applications?
Copper is often used in the wiring and connections of solar panels due to its excellent electrical conductivity. Its high-temperature rating and resistance to corrosion make it ideal for outdoor applications.
Pros: Copper’s superior conductivity ensures efficient energy transfer, which is crucial for maximizing the performance of solar systems. It is also highly durable and can withstand various environmental factors.
Cons: The cost of copper can be high, and its market volatility may impact project costs. Additionally, copper is heavier than alternatives like aluminum, which could complicate installation.
Impact on Application: Copper’s compatibility with various electrical systems makes it a preferred choice for international buyers. Compliance with standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire is essential for ensuring quality.
Summary Table of Strategic Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for solar energy manufacturers usa | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon | Solar cells in photovoltaic panels | Durable with a long lifespan | Complex manufacturing process | Medium |
| Glass | Protective layer for solar panels | Enhances durability and efficiency | Heavy and prone to breakage | Medium |
| Aluminum | Framing for solar panels | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Price fluctuations can impact costs | Low |
| Copper | Wiring and connections in solar systems | Excellent electrical conductivity | High cost and market volatility | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in solar energy manufacturing in the USA, offering valuable insights for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their procurement strategies.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for solar energy manufacturers usa
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Solar Panels?
The manufacturing process for solar panels involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the quality and efficiency of the final product. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: The journey begins with the procurement of high-purity polysilicon, which is the core material for silicon-based solar cells. Manufacturers often produce polysilicon through chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or Siemens processes, where silicon is purified and formed into ingots. This stage is crucial, as the quality of polysilicon directly influences the efficiency of the solar cells.
-
Forming: Once the polysilicon is prepared, it is shaped into silicon ingots, which are then sliced into thin wafers. These wafers undergo various processes, including doping, where materials like phosphorus or boron are added to create a p-n junction, essential for photovoltaic action. Advanced techniques like laser scribing and texturing are employed to enhance the surface area of the wafers, improving light absorption.
-
Assembly: The sliced wafers are assembled into solar cells, which are then interconnected to form a solar panel. This process involves stringing the cells together using conductive ribbons and encapsulating them between protective layers of glass and polymer. Manufacturers utilize automated assembly lines to ensure precision and efficiency.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves testing and quality assurance. After assembly, the solar panels undergo rigorous tests for performance, durability, and weather resistance. This includes electroluminescence testing, thermal cycling, and mechanical load testing to ensure they can withstand environmental stresses.
What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented in Solar Panel Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is paramount in solar panel manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. The key components of QC include adherence to relevant international standards, established checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, and various testing methods.
What International Standards Guide Quality Assurance in Solar Manufacturing?
Solar energy manufacturers in the USA typically adhere to several international quality standards, such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS), ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
- IEC 61215 and IEC 61730: These standards specifically address the design qualification and type approval of solar modules, focusing on performance, reliability, and safety.
- CE Certification: This European standard indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Manufacturers may also comply with additional certifications relevant to specific markets, such as Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certification for safety and performance.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Structured?
Quality control is integrated at various stages of the manufacturing process through specific checkpoints, including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify defects early. This includes visual inspections, automated testing, and process audits.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before packaging, finished products undergo comprehensive testing to verify performance metrics such as efficiency, output, and durability.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Solar Panel Quality?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the reliability and efficiency of solar panels:
- Electroluminescence Testing: This method detects micro-cracks and defects within solar cells by applying an electric current and capturing the emitted light.
- Thermal Cycling Tests: Panels are subjected to extreme temperature variations to assess their thermal stability and durability.
- Mechanical Load Testing: This evaluates the panel’s ability to withstand wind and snow loads, simulating real-world environmental conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Quality Control Practices of Suppliers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control practices of solar panel suppliers is crucial. Here are several actionable steps:
-
Request Certification Documentation: Buyers should ask for copies of relevant certifications (ISO, IEC, etc.) to confirm compliance with industry standards.
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Engaging in on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and overall operational practices of the supplier.
-
Review Quality Control Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed reports on their QC processes, including testing results and any corrective actions taken for non-conformities.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices, ensuring that products meet the required standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must be aware of specific nuances that can affect the quality control of solar panels. These include:
- Regulatory Differences: Different countries have varying regulations regarding solar panel standards. Buyers should ensure that products comply with local regulations in their respective markets.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Understanding the supply chain is critical, as many components may come from different regions. Buyers should inquire about the sourcing of materials and components to assess potential risks.
- Cultural and Language Barriers: Communication can pose challenges in understanding quality standards and practices. Establishing clear communication channels and possibly involving local intermediaries can help mitigate misunderstandings.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting solar energy manufacturers in the USA, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs and expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘solar energy manufacturers usa’
Introduction
In the rapidly evolving solar energy market, identifying the right manufacturers in the USA is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking reliable solar solutions. This guide provides a structured checklist to streamline your sourcing process, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your project’s needs and sustainability goals.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating contact with manufacturers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes the type of solar panels (e.g., monocrystalline, polycrystalline), efficiency ratings, and any specific certifications (e.g., UL, IEC). Well-defined specifications not only facilitate better communication with suppliers but also help in evaluating their product offerings against your project needs.
2. Research Market Trends and Manufacturer Reputation
Conduct thorough market research to understand current trends in solar technology and the reputation of potential manufacturers. Focus on aspects like innovation, customer service, and market presence. Look for reviews, testimonials, and case studies to gauge customer satisfaction and reliability.
- Use resources like:
- Industry publications
- Online forums
- Social media platforms
3. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. This evaluation will provide insights into their operational capabilities and past performance.
- Key points to consider:
- Years in operation
- Production capacity
- Previous projects and client feedback
4. Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the manufacturers you consider hold relevant certifications that attest to their product quality and environmental compliance. Certifications from recognized bodies (e.g., ISO, IEC) are indicators of reliability and adherence to industry standards.
- Look for:
- Compliance with local regulations
- Environmental management systems
- Safety standards
5. Request Samples and Product Specifications
Before finalizing your order, request samples and detailed product specifications. This step allows you to evaluate the physical product quality and performance metrics firsthand. Assess factors such as durability, efficiency, and warranty terms to ensure alignment with your project requirements.
6. Analyze Pricing and Payment Terms
Pricing can vary significantly among manufacturers. Analyze quotes not just for the base price but also for any additional costs, such as shipping and installation. Ensure that you understand the payment terms, including deposit requirements and financing options, to avoid any financial surprises later.
7. Establish Communication Channels
Effective communication is key to a successful partnership. Establish clear lines of communication with your chosen manufacturer, including points of contact for technical support, order tracking, and issue resolution. This proactive approach can help mitigate misunderstandings and ensure smooth project execution.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing from solar energy manufacturers in the USA, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes and long-term partnerships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for solar energy manufacturers usa Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Solar Panels from U.S. Manufacturers?
When considering sourcing solar panels from U.S. manufacturers, it’s essential to understand the various cost components involved. These typically include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The primary material for solar panels is polysilicon, which has seen fluctuating prices due to global supply chain dynamics. Other materials include glass, aluminum for frames, and various electronic components for inverters. The choice of materials impacts both performance and cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly depending on the manufacturing location within the U.S. States with higher living costs, such as California, may have higher labor expenses. Conversely, manufacturers in regions with lower living costs may offer competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Manufacturers that have invested in automation may have lower overhead costs, which can translate into more competitive pricing for buyers.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for production can be substantial. Custom tooling for specialized products can lead to higher upfront costs, but these can be amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the reliability and efficiency of solar panels requires rigorous QC processes, which add to the overall cost. Manufacturers that prioritize quality will often have a higher price point but offer better long-term performance.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for shipping solar panels can vary based on distance and mode of transport. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is crucial, as they define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
-
Margin: Profit margins for manufacturers can vary widely. Established brands with a strong market presence may command higher prices, while newer entrants might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Solar Panels?
Several factors influence pricing for solar panels, particularly for B2B buyers sourcing from the U.S.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can impact pricing significantly. Larger orders typically qualify for bulk discounts, making it crucial for buyers to plan their procurement strategically.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to the need for specialized manufacturing processes. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential cost increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., UL, ISO) often command higher prices but can lead to better performance and longevity, enhancing the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established manufacturers may offer warranties and service agreements, providing added value despite a higher upfront cost.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly affect the final landed cost of solar panels.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Negotiating Solar Panel Prices?
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage in negotiations with manufacturers to explore pricing flexibility, especially for larger orders. Establishing a long-term relationship can also yield better pricing over time.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate the long-term savings from energy production against the upfront costs. Sometimes, investing in higher-quality panels can lead to greater returns.
-
Consider Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Import duties, taxes, and shipping costs can significantly impact the final price. Buyers from regions like Africa or South America should account for these factors when comparing U.S. manufacturers.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Gathering multiple quotes allows buyers to benchmark prices and negotiate better terms. This practice can reveal the competitive landscape and help identify the best value.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keeping abreast of market trends, such as changes in material costs or new technologies, can empower buyers to make timely purchasing decisions.
By understanding these components and influencers, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing solar panels from U.S. manufacturers, ensuring they make informed and strategic purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing solar energy manufacturers usa With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Solar Energy Manufacturers in the USA
When considering solar energy solutions, it is essential for international B2B buyers to explore various options available in the market. While American-made solar panels offer unique benefits, alternative energy solutions can also provide significant value depending on the specific needs of a business. This section compares solar energy manufacturers in the USA with other viable alternatives, including wind energy solutions and energy storage technologies.
| Comparison Aspect | Solar Energy Manufacturers USA | Wind Energy Solutions | Energy Storage Technologies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High efficiency, especially in residential and commercial applications; panels can last 25+ years. | Consistent energy generation in suitable locations; efficiency varies by wind conditions. | Enhances renewable energy use; efficiency depends on the technology (e.g., lithium-ion vs. flow batteries). |
| Cost | Initial investment can be high, but tax credits (30% until 2026) and long-term savings are attractive. | Generally lower upfront costs compared to solar; however, installation may require land and infrastructure investment. | Initial costs can be significant, but prices are declining; potential for savings through demand charge reduction. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires space for installation, permits, and grid connection; installation can be complex depending on location. | Requires suitable land with high wind potential; zoning and environmental impact assessments can be time-consuming. | Integration with existing systems is often straightforward; however, sizing and capacity planning are critical. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance needs; regular cleaning and occasional inspections recommended. | Moderate maintenance; turbines require regular checks and can be more complex to service. | Low maintenance, but battery lifespan and performance can degrade over time without proper management. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for regions with high solar insolation; suitable for both residential and commercial settings. | Best suited for areas with consistent high winds; effective for large-scale energy generation. | Excellent for balancing intermittent renewable energy sources; useful in both commercial and residential setups for backup power. |
Exploring Wind Energy Solutions
Wind energy presents a compelling alternative to solar energy manufacturers in the USA. Wind turbines harness kinetic energy from wind and convert it into electricity. This method is particularly advantageous in regions with consistent wind patterns, making it a practical solution for large-scale energy generation. However, the initial investment for land and infrastructure can be substantial. Additionally, wind energy’s performance is highly dependent on geographical conditions, which may limit its applicability in certain regions.
Analyzing Energy Storage Technologies
Energy storage technologies, such as lithium-ion and flow batteries, are another viable alternative that complements renewable energy sources. These systems store excess energy generated from solar or wind sources and release it when demand is high or generation is low. They enhance energy reliability and can significantly reduce energy costs by managing demand charges. While the initial investment can be high, the declining costs of battery technologies make them increasingly accessible. However, proper sizing and capacity planning are critical to ensure optimal performance and lifespan.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Energy Solution
For B2B buyers, selecting the right energy solution hinges on understanding specific operational needs and regional resources. Solar energy manufacturers in the USA provide a reliable and efficient option, particularly in regions with abundant sunlight. However, wind energy solutions and energy storage technologies may offer better returns in specific contexts, such as areas with high wind potential or those requiring robust energy management systems. Conducting a thorough analysis of performance, cost, and implementation challenges will empower businesses to make informed decisions tailored to their unique requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for solar energy manufacturers usa
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Solar Panels for Manufacturers in the USA?
Understanding the technical specifications of solar panels is essential for B2B buyers looking to source quality products. Here are some critical properties that you should be aware of:
-
Efficiency Rating
The efficiency rating indicates how well a solar panel converts sunlight into usable electricity. This is expressed as a percentage, with higher percentages signifying better performance. For manufacturers, high-efficiency panels can lead to lower installation costs per watt, making them more appealing to potential buyers. Efficiency is particularly important in markets where space is limited. -
Power Output
Measured in watts (W), power output refers to the maximum electricity a solar panel can generate under standard test conditions. This specification helps buyers determine how many panels they need to meet their energy requirements. Manufacturers should provide clear power output ratings to facilitate informed purchasing decisions. -
Material Grade
The material grade of solar panels typically refers to the quality of silicon used in their construction. Higher-grade materials can enhance durability and energy production. For B2B buyers, selecting panels made from premium materials often translates to longer lifespans and better warranties, reducing long-term costs. -
Temperature Coefficient
This specification measures how much a panel’s output decreases as temperatures rise. A lower temperature coefficient indicates better performance in high-temperature environments, which is crucial for regions with hot climates. Understanding this property allows buyers to select panels suited for their local weather conditions. -
Warranty Period
Warranties usually cover both product defects and performance guarantees. A longer warranty period indicates a manufacturer’s confidence in their product. For B2B buyers, a solid warranty can significantly mitigate financial risk and ensure long-term reliability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Solar Energy Industry?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms you should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the solar industry, many brands rely on OEMs to produce solar panels or components under their label. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers navigate product availability and quality assurance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ specifies the smallest number of units a buyer must purchase from a supplier. This term is vital for B2B negotiations, as it influences pricing and inventory management. Buyers should be aware of MOQs to avoid overcommitting resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. Providing clear RFQs can streamline procurement and ensure competitive pricing. For manufacturers, responding to RFQs accurately can lead to successful business relationships. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms can help buyers and manufacturers navigate shipping costs, insurance, and delivery risks effectively. -
PPA (Power Purchase Agreement)
A PPA is a contract between a power producer and a buyer, often used in the solar industry to secure financing for solar projects. By understanding PPAs, buyers can engage more effectively with financing options and project developers. -
SREC (Solar Renewable Energy Certificate)
SRECs are tradable certificates that represent the environmental benefits of generating solar energy. For B2B buyers, SRECs can provide additional revenue streams and help meet regulatory requirements. Understanding SREC markets can enhance the financial viability of solar investments.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing solar energy products from manufacturers in the USA. This knowledge not only enhances negotiation capabilities but also ensures alignment with business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the solar energy manufacturers usa Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing Solar Energy Manufacturers in the USA?
The solar energy market in the USA is experiencing significant growth, driven by global demand for renewable energy solutions. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly interested in sourcing solar technologies from the U.S. due to the country’s robust manufacturing capabilities and innovations in solar technology. The impending expiration of the 30% solar tax credit in January 2026 is prompting businesses to accelerate their investments in solar energy to capitalize on current financial incentives. This creates an urgent opportunity for international buyers to secure favorable pricing before these incentives diminish.
Emerging trends include advancements in solar panel technology, such as bifacial panels and integrated energy storage solutions, which enhance efficiency and energy management. The rise of smart solar systems, incorporating IoT technologies for real-time monitoring and optimization, is also reshaping the landscape. Furthermore, the U.S. is witnessing a shift towards localized supply chains, reducing dependency on overseas manufacturing and ensuring more reliable sourcing for international buyers. This trend aligns with geopolitical considerations and supply chain resilience, making U.S. manufacturers attractive partners for businesses looking to mitigate risks associated with global sourcing.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Reshaping the Solar Energy Manufacturing Landscape?
Sustainability is at the forefront of solar energy manufacturing, driven by increasing environmental awareness and regulatory pressures. For international buyers, understanding the environmental impact of sourcing decisions is critical. U.S. manufacturers are increasingly adopting sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials in production and minimizing waste throughout the manufacturing process. This commitment not only reduces the carbon footprint of solar panels but also enhances their appeal in markets that prioritize green credentials.
Ethical sourcing is becoming a vital consideration for B2B buyers. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and environmentally responsible production methods is essential for maintaining brand integrity and compliance with international regulations. Many U.S. solar manufacturers are obtaining certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade certifications, which can provide assurance to buyers seeking responsible sourcing options. By prioritizing suppliers with robust sustainability practices, international businesses can enhance their corporate social responsibility profiles while ensuring high-quality solar products.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the Growth of Solar Energy Manufacturers in the USA?
The evolution of solar energy manufacturing in the USA can be traced back to the 1970s when the first solar technologies emerged as a response to the oil crisis. This initial interest laid the groundwork for a burgeoning industry that has evolved significantly over the decades. By the early 2000s, technological advancements and government incentives spurred rapid growth, positioning the U.S. as a leader in solar research and development.
The recent push towards renewable energy, fueled by climate change concerns and energy independence goals, has further catalyzed the expansion of solar manufacturing. With the introduction of federal and state-level incentives, such as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), the U.S. solar market has matured, attracting significant investment and innovation. Today, American manufacturers are not only focused on producing high-quality solar panels but are also at the forefront of developing next-generation solar technologies, making them key players in the global renewable energy landscape.
As international B2B buyers look to invest in solar energy solutions, understanding this historical context can provide valuable insights into the reliability and technological prowess of U.S. manufacturers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of solar energy manufacturers usa
-
How do I identify reputable solar energy manufacturers in the USA?
To identify reputable solar energy manufacturers in the USA, start by researching industry certifications such as UL and IEC standards. Look for manufacturers with a proven track record, positive customer reviews, and transparent business practices. Utilize resources like the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA) or platforms like EnergySage to find manufacturer ratings and reviews. Additionally, attending trade shows and networking events can help you connect with established manufacturers and verify their credentials. -
What is the best type of solar panel for commercial applications?
For commercial applications, monocrystalline solar panels are often the best choice due to their high efficiency and space-saving qualities. They typically have a higher power output compared to polycrystalline panels, making them ideal for businesses with limited roof space. Additionally, consider factors such as warranty offerings and the manufacturer’s reputation for reliability, as these can significantly impact long-term performance and return on investment. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for solar panels from US manufacturers?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for solar panels can vary significantly between manufacturers, often ranging from a few hundred to several thousand units. It’s essential to inquire directly with manufacturers about their MOQ policies, as some may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or bulk orders. Additionally, consider negotiating terms that can benefit both parties, especially if you plan to establish a long-term partnership. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing solar panels from US manufacturers?
Payment terms vary by manufacturer, but common practices include upfront payments, deposits (typically 30-50%), and balance payments upon delivery. Some manufacturers may also offer financing options or extended payment plans for larger orders. Always clarify payment conditions upfront and ensure that terms are documented in the purchase agreement to avoid potential disputes. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing solar panels?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed information on the manufacturer’s quality control processes and certifications. Reputable manufacturers should provide documentation of their testing procedures and compliance with industry standards. Additionally, consider third-party inspections or audits before accepting deliveries to verify that the products meet your specifications and performance expectations. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing solar panels?
When importing solar panels, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may affect your costs. It’s crucial to work with logistics providers experienced in handling solar products to ensure safe transportation and compliance with international shipping laws. Additionally, evaluate the lead times for production and shipping to ensure timely delivery to your project sites. -
Are there customization options available for solar panels?
Many US manufacturers offer customization options for solar panels, including variations in size, efficiency ratings, and power outputs to meet specific project requirements. When discussing customization, be clear about your needs and project goals. This can include branded panels or unique configurations that enhance performance in your specific climate or application. -
What support services do US solar manufacturers provide to international buyers?
Most US solar manufacturers offer a range of support services for international buyers, including technical assistance, installation guidance, and warranty support. Some manufacturers may also provide training for local installation teams or assistance with local regulations and incentives. Establishing a strong communication channel with the manufacturer can help facilitate a smoother procurement process and ongoing support.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for solar energy manufacturers usa
In conclusion, the landscape of solar energy manufacturing in the USA is marked by a diverse range of options for international B2B buyers seeking reliable and efficient solar solutions. With leading manufacturers like First Solar and Qcells dominating the market, companies can benefit from high-quality American-made products that support local economies and energy independence. The impending expiration of the 30% solar tax credit by January 2026 serves as an urgent reminder for businesses to act now and secure significant savings.
Strategic sourcing in this sector enables companies to not only enhance their supply chain resilience but also gain access to innovative technologies and sustainable practices. As the U.S. continues to ramp up its domestic manufacturing capabilities, including advancements in polysilicon production, buyers can expect an increasingly robust supply of solar components.
For B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, now is the time to explore partnerships with American manufacturers. By tapping into this growing market, you can position your business at the forefront of the renewable energy revolution, ensuring a sustainable and profitable future. Take action today to leverage these opportunities and contribute to a greener tomorrow.