Top 6 Car Manufacturing Plants In Usa List and Guide: How To Solv…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for car manufacturing plants in usa
In today’s dynamic global market, sourcing car manufacturing plants in the USA presents both opportunities and challenges for international B2B buyers. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, understanding the landscape of American manufacturing—particularly in key regions like the Midwest and South—can significantly impact your purchasing decisions. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the diverse types of manufacturing facilities, including assembly plants and component suppliers, and explores their applications across various automotive sectors.
Navigating the complexities of supplier vetting, production costs, and logistical considerations is crucial for businesses looking to invest in U.S. automotive manufacturing. With an industry that contributed an impressive $863 billion to the U.S. economy in 2022, understanding the intricacies of this market can empower you to make informed decisions that align with your strategic goals.
This guide is tailored specifically for international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Brazil and Saudi Arabia. By providing actionable insights into supplier capabilities, market trends, and regional advantages, we aim to equip you with the knowledge needed to leverage the U.S. automotive manufacturing landscape effectively. Whether you’re assessing potential partnerships or evaluating production feasibility, this resource serves as a vital tool in your strategic sourcing efforts.
Top 10 Car Manufacturing Plants In Usa Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Hyundai – Production Expansion; Honda – Next-Gen Civic Hybrid
Domain: aljazeera.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Hyundai: Increasing production capacity at Metaplant in Georgia from 300,000 to 500,000 vehicles per year; $21bn investment in the US including a $5.8bn steel plant in Louisiana for EV materials. Honda: Manufacturing next-generation Civic hybrid in Indiana instead of Mexico, starting May 2028 with an expected annual production of 210,000. Stellantis: $5bn investment in the US, reopening assembly p…
2. OEM Plants – EV/PHEV/HEV Production
Domain: marklines.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: OEM Plants in the U.S.A. and Canada include manufacturers such as GM, Ford, and Stellantis, with various plants dedicated to EV/PHEV/HEV/FCV production, battery manufacturing, and motor production. Key locations include:
– **GM Plants**:
– Michigan: Bay City Powertrain, Brownstown Battery Factory, Flint Engine, Lansing Delta Township, etc.
– Indiana: Bedford, Fort Wayne, Kokomo, etc.
– Mis…
3. Ford – River Rouge Complex
4. Honda & Acura – Vehicles and Powersports
Domain: hondainamerica.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Honda and Acura vehicles, aircraft and aircraft engines, power equipment, powersports products, including cars, light trucks, ATVs, side-by-sides, and the HondaJet Elite II. Specific models include Honda Accord, Honda Accord Hybrid, Acura Integra, Acura TLX, CR-V, CR-V Hybrid, Acura MDX, Acura RDX, Odyssey, Passport, Pilot, Ridgeline, TrailSport Models, Civic Hatchback, Side x Side Utility Vehicle…
5. Acea – European Automobile Manufacturing Overview
Domain: acea.auto
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: In 2024, there are 255 automobile assembly, engine, and battery production plants in Europe, including 98 car manufacturers, 44 bus manufacturers, 32 truck manufacturers, 30 van manufacturers, 56 engine manufacturers, and 65 battery manufacturers. Additionally, 121 of these plants assemble battery-electric vehicles.
6. Ford – Key Product
Understanding car manufacturing plants in usa Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assembly Plants | Large facilities focused on assembling vehicles | Vehicle production and supply chain management | Pros: High output; established logistics. Cons: High competition; potential labor issues. |
| Component Manufacturing Plants | Facilities dedicated to producing auto parts | Parts supply for OEMs and aftermarket | Pros: Specialized production; diverse offerings. Cons: Quality control challenges; reliance on OEM contracts. |
| Electric Vehicle (EV) Plants | Facilities specifically for EV production | Growing EV market; battery and component supply | Pros: Access to emerging market; innovative tech. Cons: Higher initial investment; evolving regulations. |
| Modular Assembly Plants | Flexible plants that can adapt to different models | Custom vehicle solutions; rapid prototyping | Pros: Versatility; reduced time to market. Cons: Higher operational complexity; potential inefficiencies. |
| Specialty Vehicle Plants | Focused on niche markets (e.g., luxury, commercial) | Targeted production for specific segments | Pros: High margins; less competition. Cons: Market volatility; limited scalability. |
What Are the Characteristics of Assembly Plants in the USA?
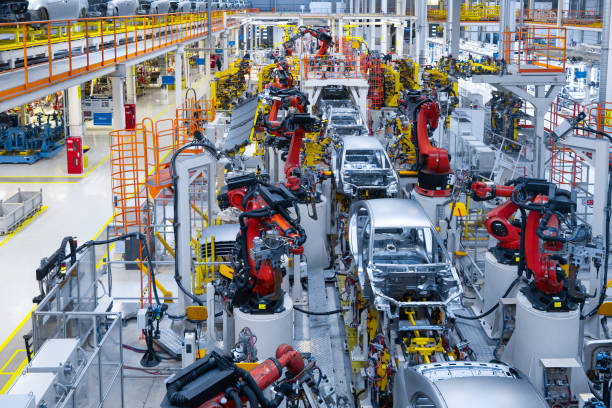
Assembly plants are large-scale manufacturing facilities where vehicles are assembled from various components. They are strategically located, often in regions with a strong automotive history, such as Michigan and Ohio. These plants have significant output capabilities, making them essential for meeting the high demand for vehicles. For B2B buyers, engaging with these plants means leveraging established logistics and supply chains, though they must also navigate a competitive landscape and potential labor-related disruptions.
How Do Component Manufacturing Plants Operate?
Component manufacturing plants focus on producing specific auto parts, such as engines, transmissions, or electronic systems. These facilities often specialize in particular components, allowing for streamlined production processes and high-quality outputs. For B2B buyers, these plants are crucial for sourcing parts for original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) or the aftermarket. However, buyers should consider the challenges of quality control and the reliance on contracts with larger automotive companies, which can affect pricing and availability.
What Sets Electric Vehicle (EV) Plants Apart?
Electric vehicle plants are increasingly prevalent due to the growing demand for sustainable transportation solutions. These facilities are equipped with advanced technologies for producing EVs and their components, such as batteries and electric drivetrains. B2B buyers interested in the EV market can benefit from forming partnerships with these manufacturers, gaining access to innovative technologies. However, the initial investment costs and the rapidly changing regulatory landscape can pose challenges for buyers looking to enter this market.
What Are the Advantages of Modular Assembly Plants?
Modular assembly plants offer flexibility by allowing manufacturers to produce various vehicle models on the same assembly line. This adaptability helps companies respond quickly to market demands and reduce time to market for new models. For B2B buyers, this means the potential for customized vehicle solutions tailored to specific needs. However, the complexity of operations can lead to inefficiencies, and buyers must weigh the benefits against potential operational challenges.
How Do Specialty Vehicle Plants Cater to Niche Markets?
Specialty vehicle plants focus on producing vehicles for niche markets, such as luxury cars, commercial vehicles, or specific utility applications. These plants often command higher margins due to the unique nature of their products and less competition in specialized segments. B2B buyers can benefit from these plants by accessing high-quality, tailored vehicles that meet specific industry needs. However, market volatility and scalability issues are important considerations, as demand can fluctuate significantly in niche markets.
Key Industrial Applications of car manufacturing plants in usa
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of car manufacturing plants in usa | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Parts Manufacturing | Sourcing components for vehicle assembly | Access to high-quality parts reduces production delays. | Supplier reliability, quality certifications, lead times. |
| Electric Vehicle Production | Manufacturing electric vehicles and components | Aligns with global sustainability trends and demand. | Technology compatibility, workforce skill sets, R&D support. |
| Supply Chain Logistics | Integrating logistics for just-in-time delivery | Minimizes inventory costs and enhances operational efficiency. | Proximity to suppliers, transportation infrastructure, and customs regulations. |
| Research and Development | Collaborating on vehicle innovation and design | Enhances competitive advantage through technological advances. | Intellectual property rights, partnership agreements, and local regulations. |
| Aftermarket Services | Providing parts and maintenance services | Increases revenue streams and customer loyalty. | Quality assurance, warranty management, and service networks. |
How Are Car Manufacturing Plants in the USA Used in Automotive Parts Manufacturing?
Car manufacturing plants in the USA serve as critical hubs for sourcing high-quality automotive components. These facilities not only assemble vehicles but also produce various parts that are essential for vehicle functionality. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa and South America, benefit from the advanced manufacturing technologies and stringent quality controls that American plants offer. This ensures that the components sourced can meet rigorous safety and performance standards, addressing issues like production delays due to inferior parts.
What Role Do Car Manufacturing Plants Play in Electric Vehicle Production?
With the global shift toward sustainability, car manufacturing plants in the USA are increasingly focused on electric vehicle (EV) production. These plants are equipped to manufacture not only the vehicles but also key components such as batteries and electric drivetrains. For international buyers from the Middle East and Europe, sourcing from these plants provides access to cutting-edge technology and innovation, meeting the rising consumer demand for eco-friendly vehicles. Buyers must consider technology compatibility and the availability of skilled labor when engaging with these manufacturers.
How Do Car Manufacturing Plants Enhance Supply Chain Logistics?
Car manufacturing plants in the USA are strategically located to optimize supply chain logistics. By integrating just-in-time delivery systems, these plants help businesses minimize inventory costs and enhance operational efficiency. For B2B buyers from regions like Brazil and Saudi Arabia, understanding the logistical advantages, such as proximity to suppliers and established transportation networks, is vital. Additionally, familiarity with local customs regulations can facilitate smoother import processes, ensuring timely delivery of parts and finished vehicles.
In What Ways Do Car Manufacturing Plants Contribute to Research and Development?
Collaboration in research and development is another significant application of car manufacturing plants in the USA. These facilities often partner with universities and tech firms to drive innovation in vehicle design and technology. For international buyers, particularly in Europe, engaging with these plants can lead to enhanced competitive advantages through access to the latest automotive technologies. Buyers should be aware of intellectual property rights and local regulations that may affect R&D collaborations.
How Are Aftermarket Services Supported by Car Manufacturing Plants?
Finally, car manufacturing plants in the USA play a crucial role in supporting aftermarket services. They provide high-quality parts and maintenance solutions that keep vehicles running smoothly. For B2B buyers, this means not only a potential increase in revenue streams but also improved customer loyalty through reliable service. Key considerations include warranty management and the establishment of service networks, which are essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘car manufacturing plants in usa’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Supply Chain Disruptions in U.S. Automotive Manufacturing
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges due to supply chain disruptions, especially when sourcing components for automotive manufacturing. Factors like geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or global pandemics can lead to delays in receiving essential parts. For international buyers, this can result in production standstills, increased costs, and ultimately, missed deadlines. The complexity of the U.S. supply chain, with its reliance on just-in-time delivery models, exacerbates these issues, leaving buyers feeling frustrated and anxious about maintaining production schedules.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, B2B buyers should prioritize building strong relationships with multiple suppliers across different regions. This diversification strategy can safeguard against localized disruptions. Additionally, leveraging advanced supply chain management software can enhance visibility into inventory levels and lead times, enabling buyers to make informed decisions. Engaging in proactive communication with U.S. manufacturing plants about potential supply issues can also lead to collaborative solutions, such as finding alternative parts or adjusting production schedules to accommodate delays. Regularly reviewing and updating contingency plans based on evolving market conditions will further strengthen resilience against supply chain disruptions.
Scenario 2: Addressing Labor Shortages in U.S. Automotive Manufacturing Plants
The Problem: Labor shortages are a pressing concern for automotive manufacturing plants in the U.S., particularly in regions heavily reliant on the industry. B2B buyers may find it challenging to secure timely production and quality standards due to a lack of skilled workers. This issue is compounded by an aging workforce and increased competition for talent from other sectors. As a result, buyers may experience delays in production, increased costs, and inconsistent quality in the vehicles they source.
The Solution: To overcome labor shortages, B2B buyers should consider partnering with U.S. manufacturing plants that have robust workforce development programs. These initiatives often include training and apprenticeship programs aimed at upskilling the existing workforce. Additionally, buyers can support their partners by investing in technology that automates repetitive tasks, thus reducing the reliance on manual labor. Collaborating with local educational institutions to create tailored training programs can also foster a new generation of skilled workers. By actively engaging in workforce development, buyers can help ensure a steady supply of skilled labor, thereby enhancing production efficiency and quality.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with U.S. Regulations in Automotive Manufacturing
The Problem: Compliance with U.S. regulations can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers looking to source from American automotive manufacturing plants. The automotive industry is subject to a myriad of regulations covering safety, emissions, and labor standards. Failure to comply can lead to significant penalties, production delays, and damage to brand reputation. For buyers unfamiliar with the regulatory landscape, navigating these requirements can be overwhelming and fraught with risk.
The Solution: To effectively manage compliance issues, B2B buyers should invest in a comprehensive understanding of U.S. automotive regulations. This can be achieved through consulting with legal experts or compliance specialists familiar with the industry. Additionally, engaging directly with manufacturing plants to discuss their compliance processes can provide invaluable insights. Buyers should also consider implementing a rigorous supplier evaluation process that includes compliance checks as a key criterion. Utilizing technology, such as compliance management systems, can streamline the monitoring of regulatory requirements, ensuring that all sourced components meet necessary standards. By prioritizing compliance, buyers can protect their investments and foster strong, trustworthy relationships with U.S. manufacturers.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for car manufacturing plants in usa
What Are the Key Materials Used in Car Manufacturing Plants in the USA?
In the automotive manufacturing sector, material selection is crucial for ensuring product performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four common materials used in car manufacturing plants in the USA: steel, aluminum, composites, and plastics. Each material has unique properties and implications for international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Does Steel Contribute to Automotive Manufacturing?
Steel is the backbone of the automotive industry, primarily used for the vehicle’s body and structural components. Its key properties include high tensile strength and excellent formability, making it suitable for various manufacturing processes. Steel exhibits good corrosion resistance when treated, and it can withstand high temperatures and pressures, essential for safety and performance.
Pros: Steel is durable, cost-effective, and widely available, making it an ideal choice for mass production. It also offers excellent crash safety performance due to its strength.
Cons: However, steel is heavier than other materials, which can affect fuel efficiency. The manufacturing process can be complex, requiring advanced techniques for shaping and welding.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various media, including oils and fuels, but it may corrode if exposed to moisture without proper treatment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel. Understanding local regulations regarding emissions and safety can also impact the choice of steel grades.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Vehicle Manufacturing?
Aluminum is increasingly favored in automotive applications due to its lightweight properties, which enhance fuel efficiency. Key properties include excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, making it suitable for components like engine blocks and heat exchangers.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which contributes to improved fuel economy and performance. It also has good recyclability, aligning with sustainability goals.
Cons: The main downside is its higher cost compared to steel and potential challenges in welding and joining techniques.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various fluids is generally good, but it can react with certain chemicals, necessitating careful selection in specific applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. Additionally, understanding local market conditions and preferences for lightweight vehicles can influence purchasing decisions.
How Do Composites Enhance Automotive Design?
Composites, particularly carbon fiber and fiberglass, are gaining traction in automotive manufacturing for their strength-to-weight ratio. Key properties include high tensile strength, low weight, and resistance to corrosion and fatigue.
Pros: Composites allow for innovative designs and can significantly reduce vehicle weight, enhancing performance and fuel efficiency. They also offer excellent aesthetic flexibility.
Cons: The primary limitations are higher costs and complex manufacturing processes, which can lead to longer production times.
Impact on Application: Composites are often used in high-performance vehicles and applications where weight savings are critical. They are generally resistant to various media but can be sensitive to UV exposure.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with standards like ASTM D7264 for composite materials. Awareness of local manufacturing capabilities for composites is also essential.
What Advantages Do Plastics Offer in Automotive Manufacturing?
Plastics are extensively used in automotive interiors, dashboards, and exterior trim due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. Key properties include low weight, good impact resistance, and ease of molding.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight and can be produced in various colors and finishes, enhancing design flexibility. They are also generally less expensive than metals.
Cons: However, plastics may have lower mechanical strength compared to metals and can degrade under UV exposure unless treated.
Impact on Application: Plastics are compatible with a wide range of automotive fluids, but their longevity can be affected by environmental factors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for tensile properties of plastics. Understanding local consumer preferences for materials can also guide purchasing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for car manufacturing plants in usa | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Vehicle body and structural components | Durable and cost-effective | Heavier than alternatives | Medium |
| Aluminum | Engine blocks and heat exchangers | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and welding challenges | High |
| Composites | High-performance vehicle parts | High strength-to-weight ratio | Complex manufacturing processes | High |
| Plastics | Interiors and exterior trim | Versatile and low weight | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with valuable insights into the materials commonly used in car manufacturing plants in the USA, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for car manufacturing plants in usa
What Are the Key Stages in Car Manufacturing Processes in the USA?
The car manufacturing process in the United States is a complex and meticulously organized operation that typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is crucial to ensuring that the final product meets the high standards expected by consumers and regulatory bodies.
How is Material Prepared for Automotive Manufacturing?
Material preparation begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials, primarily steel, aluminum, and various plastics. In many plants, advanced techniques such as laser cutting and CNC machining are employed to shape these materials into components that meet specific design requirements. This stage often includes quality checks to ensure that the materials are free from defects and conform to the required specifications.
Additionally, just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems are commonly used to minimize waste and ensure that materials arrive at the manufacturing plant exactly when needed, which enhances efficiency and reduces costs.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Car Manufacturing?
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes. This includes stamping, forging, and casting, which transform raw materials into usable parts. Stamping, for example, is widely used to create body panels, while forging is typically reserved for components requiring higher strength, such as crankshafts.
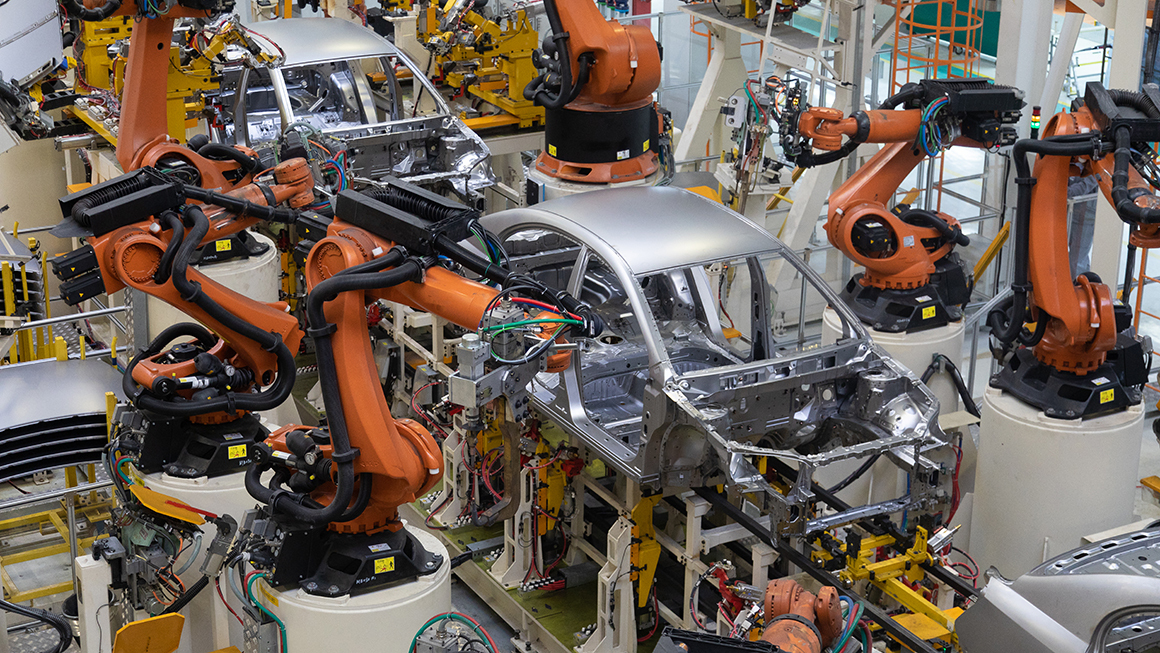
Modern car manufacturing plants often employ advanced robotics to perform these tasks, significantly increasing precision and reducing labor costs. Automation not only speeds up production but also ensures consistency across components, which is vital for assembly line operations.
How is the Assembly Process Structured in Car Manufacturing?
The assembly stage is where the individual components come together to create the final vehicle. This stage is often performed on assembly lines, where vehicles move from station to station, and workers or robots add parts in a systematic manner.
American automotive plants utilize modular assembly techniques, which allow for flexibility in production. This means that different vehicle models can be produced on the same line with minimal downtime. Key components such as engines, transmissions, and electronics are often pre-assembled before being integrated into the vehicle, streamlining the overall assembly process.
What Finishing Techniques Are Utilized in Car Manufacturing?
Finishing involves several processes that enhance the vehicle’s aesthetic and functional qualities. This includes painting, which often employs advanced techniques like robotic spray painting to ensure an even coat and reduce waste.
Additionally, finishing processes can involve the application of protective coatings, interior assembly, and final inspections. Quality control teams are heavily involved in this stage to ensure that all vehicles meet the required standards before leaving the assembly line.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Critical for Car Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a cornerstone of the automotive manufacturing process, particularly in the United States. Adherence to international standards such as ISO 9001 ensures that companies maintain a consistent quality management system. This standard focuses on meeting customer expectations and delivering satisfaction.
Moreover, industry-specific certifications like ISO/TS 16949 (now IATF 16949) are crucial for automotive suppliers. This standard addresses quality management systems specifically for the automotive industry, emphasizing defect prevention and the reduction of variation and waste in the supply chain.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Car Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) in automotive manufacturing typically includes several critical checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials and components upon delivery to ensure they meet specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various checkpoints are established to monitor processes and components. This includes inspections at each stage of production to catch defects early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly is complete, the final product undergoes a comprehensive inspection to verify that it meets all design and performance specifications.
Common testing methods employed in automotive QC include dimensional inspections, functional tests, and endurance tests. These assessments help ensure that vehicles are safe and perform as expected.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier QC processes is vital. Here are several actionable strategies:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help assess their adherence to quality standards and operational practices. Buyers can request audit reports to gain insights into the supplier’s quality management systems.
-
Request Certifications: Buyers should verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949) and understand the implications of these certifications for product quality.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s production processes and product quality.
-
Review Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports, including defect rates, non-conformance issues, and corrective actions taken. These reports can be instrumental in assessing the reliability of a supplier.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must be aware of specific nuances related to quality control when dealing with suppliers from the U.S. For instance, understanding the differences in quality standards across countries can affect procurement decisions.
Buyers should also consider the logistics of transporting vehicles and parts internationally, as this can introduce additional quality risks. Ensuring that suppliers have robust packaging and shipping processes in place can mitigate these risks.
Furthermore, international buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulatory requirements in their respective markets. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for ensuring that imported vehicles meet local safety and environmental standards.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in U.S. automotive plants is essential for international B2B buyers. By leveraging this knowledge, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers that meet their quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘car manufacturing plants in usa’
The following guide serves as a practical checklist for international B2B buyers seeking to procure car manufacturing plants in the USA. This step-by-step approach will help you make informed decisions and maximize your investment in this crucial sector.
Step 1: Identify Your Business Needs
Understanding your specific requirements is the foundation of a successful procurement process. Consider factors such as production capacity, types of vehicles you intend to manufacture, and technological capabilities required. Align these needs with your market demand to ensure the plant you choose can meet your operational goals.
- Production Capacity: Determine the volume of vehicles you plan to produce annually.
- Technology Requirements: Identify whether you need advanced manufacturing technologies, such as automation or electric vehicle production lines.
Step 2: Research Potential Locations
The geographical location of a manufacturing plant can significantly impact logistics and operational efficiency. The Midwest and South are key hubs for automotive manufacturing in the USA, with states like Michigan, Ohio, and Kentucky hosting numerous plants.
- Logistical Advantages: Assess proximity to suppliers and distribution networks to minimize shipping times and costs.
- Labor Market: Evaluate the availability of skilled labor in the region to ensure you can recruit qualified employees.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to thoroughly vet their capabilities. Request detailed company profiles, including their manufacturing history, technology used, and current production outputs.
- Case Studies: Look for evidence of successful projects similar to your needs.
- References: Obtain testimonials from other B2B buyers in your industry to gauge reliability and performance.
Step 4: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers comply with industry regulations and possess the necessary certifications. This step is vital for maintaining quality standards and avoiding legal complications.
- Quality Management Systems: Check for certifications such as ISO 9001 or IATF 16949, which indicate a commitment to quality.
- Safety Standards: Verify compliance with OSHA regulations and other safety standards relevant to automotive manufacturing.
Step 5: Assess Financial Stability
A supplier’s financial health can impact their ability to deliver on commitments. Review financial statements and market position to ensure long-term viability.
- Credit Reports: Obtain credit ratings from reliable agencies to evaluate financial risk.
- Market Trends: Analyze the supplier’s market presence and growth potential in the automotive sector.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, engage in negotiations to establish favorable terms. This includes pricing, delivery timelines, warranties, and after-sales support.
- Pricing Structure: Ensure transparency in pricing to avoid hidden costs.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Define expectations regarding production timelines and quality benchmarks.
Step 7: Finalize Contracts and Initiate Partnership
After reaching an agreement, finalize contracts to formalize the partnership. Ensure that all terms are clearly outlined and that both parties understand their responsibilities.
- Legal Review: Have legal counsel review the contract to protect your interests.
- Kick-off Meeting: Organize an initial meeting to align on objectives and expectations, setting the stage for a successful collaboration.
By following this checklist, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of procuring car manufacturing plants in the USA effectively. Each step is designed to ensure a thorough evaluation process, leading to informed decisions that support long-term success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for car manufacturing plants in usa Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Car Manufacturing in the USA?
When sourcing from car manufacturing plants in the USA, understanding the cost structure is paramount. The primary components influencing the cost include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as steel, aluminum, plastics, and electronics, significantly impacts overall production costs. Fluctuations in commodity prices can lead to variations in the final pricing of vehicles.
-
Labor: Labor costs in the U.S. automotive industry are among the highest globally, driven by the need for skilled workers. States like Michigan boast a highly trained workforce, but this comes at a premium. Salary rates, benefits, and union negotiations can all affect labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and other operational expenses. Efficient plant operations can help mitigate overhead costs, but this requires investment in technology and training.
-
Tooling: The setup costs for specialized equipment and tools are significant, especially for unique vehicle designs or large-scale production runs. These costs are amortized over the production volume, making them critical for pricing strategies.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with safety and quality standards involves additional costs. American manufacturers often invest heavily in QC processes to meet stringent regulations and maintain customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Distribution costs are influenced by the plant’s location, transportation methods, and supply chain efficiency. Proximity to suppliers and markets can help lower logistics costs.
-
Margin: Finally, manufacturers will factor in their desired profit margin, which varies based on competition, market demand, and financial health.
How Do Volume and Specifications Affect Pricing?
Volume and minimum order quantities (MOQ) play a crucial role in determining the pricing structure. Higher production volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. This is particularly relevant for international buyers looking to import vehicles or components in bulk.
Customization can also impact pricing significantly. Tailored specifications, such as unique designs or features, may incur additional tooling and labor costs, leading to higher prices. Buyers should be prepared for these potential increases when negotiating contracts.
What Are the Influencing Factors on Price for International Buyers?
When sourcing from U.S. car manufacturing plants, several factors can influence pricing for international buyers, including:
-
Materials: The choice of materials can greatly affect cost and quality. Buyers should consider the specifications required for their markets and how these influence material sourcing.
-
Quality and Certifications: Vehicles must meet various international standards and certifications, which can affect costs. Ensuring compliance can lead to additional investments in testing and quality assurance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability and reputation of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer better pricing due to their experience and efficiency.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is vital. Different Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can affect the total landed cost, impacting budgeting and pricing negotiations.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices?
To optimize sourcing costs, international buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Engage in open discussions about pricing structures and be transparent about your needs.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assess not just the upfront costs, but also long-term expenses related to maintenance, operation, and resale value. A more comprehensive view can lead to better purchasing decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of the factors that can lead to price fluctuations, such as seasonal demand and market trends. This understanding can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Conduct Market Research: Stay informed about the automotive market trends in both the U.S. and your home region. This knowledge can help in aligning your sourcing strategy with market realities.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices in the automotive manufacturing sector can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions, plant location, and specific buyer requirements. It is essential for international buyers to conduct thorough due diligence and consult with multiple suppliers to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing car manufacturing plants in usa With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Car Manufacturing Plants in the USA
As the automotive industry evolves, international B2B buyers must consider various manufacturing solutions to meet their needs effectively. While car manufacturing plants in the USA offer numerous advantages, alternative methods can provide different benefits depending on market demands, production scales, and logistical considerations. This section explores viable alternatives, allowing buyers to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Car Manufacturing Plants in USA | Contract Manufacturing | Advanced Robotics & Automation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High output; established quality control systems | Moderate to high; depends on the partner | Very high; consistent precision and speed |
| Cost | High initial investment; competitive labor costs | Variable; can be cost-effective based on volume | High upfront investment but lower long-term operational costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex; requires significant setup time and resources | Relatively easy; quick to onboard with existing partners | Challenging; requires specialized skills for setup and maintenance |
| Maintenance | Ongoing costs for facility upkeep and workforce training | Minimal; relies on partner for maintenance | High; requires regular updates and technical support |
| Best Use Case | Large-scale production of diverse vehicle types | Startups or small firms needing flexibility | High-volume production of standardized parts or vehicles |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Contract Manufacturing: Is It a Flexible Solution for Your Needs?
Contract manufacturing allows companies to partner with established manufacturers to produce vehicles or components. This approach can significantly reduce the time and capital required to enter the automotive market. Buyers can leverage the expertise and infrastructure of a contract manufacturer, allowing for rapid scaling in response to market demands. However, the quality control may vary based on the partner’s standards, and there may be less control over production processes compared to owning a manufacturing plant.
Advanced Robotics & Automation: Can This Technology Revolutionize Production?
Advanced robotics and automation systems are transforming the automotive manufacturing landscape. These technologies enhance production efficiency, reduce labor costs, and improve product consistency. They are particularly beneficial for high-volume, repetitive tasks, ensuring precision and reducing human error. However, the initial investment is significant, and companies must ensure they have the technical expertise to maintain and upgrade these systems. This solution is best suited for companies focused on mass production of standardized products where precision is paramount.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Manufacturing Solution?
Choosing the right automotive manufacturing solution depends on several factors, including production scale, budget constraints, and the desired level of control over manufacturing processes. For large enterprises with established market presence, car manufacturing plants in the USA may provide the reliability and output necessary to meet demand. Conversely, startups or firms looking for flexibility may find contract manufacturing an attractive option. Meanwhile, companies focused on high efficiency and precision might benefit from investing in advanced robotics and automation. Ultimately, a thorough assessment of specific business needs and operational capabilities will guide buyers to the most suitable solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for car manufacturing plants in usa
What Are the Key Technical Properties Essential for Car Manufacturing Plants in the USA?
In the competitive landscape of automotive manufacturing, understanding critical technical properties is vital for B2B buyers. Here are some essential specifications:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the specific classification of materials used in vehicle production, such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials. Each grade has distinct properties, including strength, weight, and corrosion resistance. For buyers, selecting the right material grade is crucial for ensuring vehicle safety, performance, and longevity. It also affects production costs, as higher-grade materials typically come with increased costs but can yield better performance and durability.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in parts manufacturing. In automotive production, precision is paramount, as even minor deviations can lead to assembly issues or safety concerns. Understanding tolerance levels helps B2B buyers ensure that components meet quality standards, which is essential for maintaining brand reputation and compliance with safety regulations.
3. Production Capacity
Production capacity indicates the maximum number of units that a manufacturing plant can produce within a specific timeframe. This metric is vital for buyers looking to assess whether a supplier can meet their demand forecasts. High production capacity can lead to economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs and improving supply chain efficiency.
4. Lead Time
Lead time is the duration from order placement to delivery. In the automotive sector, reducing lead time is essential for maintaining competitive advantage and meeting market demands. Buyers must evaluate lead times when selecting suppliers, as shorter lead times can lead to better inventory management and responsiveness to market changes.
5. Quality Assurance Standards
Quality assurance (QA) standards are protocols established to ensure that products meet specific quality criteria. In the automotive industry, adhering to QA standards (like ISO/TS 16949) is crucial for minimizing defects and ensuring safety. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with robust QA processes, as this directly impacts the reliability and performance of the vehicles produced.
Which Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand in the Automotive Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother negotiations and better decision-making. Here are some common trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In automotive manufacturing, OEMs supply essential components that meet specific standards for vehicle assembly. Understanding OEM relationships is critical for buyers, as these partnerships can impact both quality and supply chain logistics.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and production planning. Understanding MOQs can help buyers negotiate better terms and optimize their purchasing strategies to align with production schedules.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process in which a buyer solicits price offers from suppliers for specific goods or services. For buyers, issuing an RFQ is a strategic way to gather competitive pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, enabling informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B buyers involved in cross-border trade, as they define who bears the costs and risks at various stages of shipping.
5. Tier 1, Tier 2, and Tier 3 Suppliers
These terms categorize suppliers based on their direct relationship with OEMs. Tier 1 suppliers provide parts directly to OEMs, while Tier 2 and Tier 3 suppliers supply components to Tier 1 suppliers. Understanding this hierarchy is essential for buyers as it helps in assessing the reliability and integration of their supply chains.
In summary, grasping the essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for B2B buyers in the automotive industry. This knowledge empowers buyers to make informed decisions, optimize supply chain management, and ensure the quality and reliability of their products.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the car manufacturing plants in usa Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the U.S. Car Manufacturing Sector?
The U.S. automotive industry, valued at approximately $863 billion in 2022, remains a vital component of the global supply chain, particularly for international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Major trends shaping the market include the increasing emphasis on electric vehicles (EVs) and advanced manufacturing technologies. The shift towards EVs is driven by consumer demand for sustainable options and regulatory pressures aimed at reducing carbon emissions. As a result, automotive manufacturers are investing heavily in electric and hybrid vehicle production, which presents opportunities for international buyers to source innovative technologies and components.
Moreover, automation and Industry 4.0 technologies are enhancing manufacturing efficiency and reducing operational costs. The integration of robotics, IoT, and data analytics in production processes is leading to increased precision and reduced waste. For international B2B buyers, understanding these technological advancements is crucial for aligning with suppliers who can meet the evolving demands of the automotive market.
Logistical considerations also play a significant role in sourcing strategies. The concentration of automotive plants in the Midwest and South of the U.S. offers a robust supply chain network, enabling quicker turnaround times for parts and finished vehicles. Buyers should leverage this geographical advantage to establish strong partnerships with local manufacturers and suppliers, ensuring reliability and responsiveness in their supply chains.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the U.S. Car Manufacturing Sector?
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of the automotive industry, prompting manufacturers to adopt environmentally responsible practices throughout their supply chains. The environmental impact of automotive production is significant, with efforts focused on reducing waste, conserving energy, and minimizing emissions. For international B2B buyers, engaging with manufacturers committed to sustainability not only aligns with global environmental goals but also enhances brand reputation and consumer trust.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers increasingly seek suppliers that adhere to fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 50001 for energy management are becoming essential indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with manufacturers that hold these certifications and utilize ‘green’ materials, such as recycled plastics and sustainably sourced metals, in their production processes.
Furthermore, the push for circular economy principles is gaining traction, encouraging manufacturers to design vehicles that can be easily disassembled and recycled. This trend presents opportunities for international buyers to invest in companies that prioritize sustainable design and manufacturing practices, ultimately leading to a more resilient and environmentally friendly supply chain.
What Is the Historical Context of Car Manufacturing in the U.S. and Its Relevance for B2B Buyers?
The history of automotive manufacturing in the U.S. dates back to the early 20th century, with Michigan emerging as the epicenter of the industry. The establishment of assembly line production methods by pioneers like Henry Ford revolutionized manufacturing efficiency, setting the stage for mass production. Over the decades, the U.S. automotive sector has evolved through various phases, including the rise of foreign manufacturers and the recent shift towards electrification and automation.
For international B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is crucial as it highlights the U.S. automotive industry’s adaptability and resilience. The established ecosystem of suppliers, skilled labor, and technological innovation continues to make the U.S. a competitive market for sourcing automotive components and vehicles. Buyers can leverage this rich history to identify reliable partners that are well-equipped to navigate current and future market dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of car manufacturing plants in usa
-
How do I solve challenges related to sourcing car manufacturing plants in the USA?
Sourcing car manufacturing plants in the USA involves thorough market research and understanding the specific needs of your business. Start by identifying your production requirements, such as vehicle types and volumes. Engage with industry contacts and attend trade shows to gather insights. Utilize platforms like the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) to connect with suppliers and manufacturers. Finally, consider partnering with local consultants who can guide you through the regulatory landscape and facilitate connections with reputable manufacturers. -
What is the best approach for vetting automotive manufacturing suppliers in the USA?
To effectively vet automotive manufacturing suppliers, begin by assessing their certifications and compliance with industry standards such as ISO/TS 16949. Request case studies or references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and capacity. Conduct site visits to evaluate their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Additionally, consider their location and logistical capabilities to ensure they can meet your supply chain needs efficiently. Using a scorecard approach can help standardize your evaluation process across potential suppliers. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for car manufacturing plants in the USA?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for car manufacturing can vary significantly based on the manufacturer, type of vehicle, and production capabilities. Generally, established plants may have MOQs ranging from 500 to 1,000 units for standard models, while custom or specialty vehicles could have higher MOQs. It’s crucial to discuss your specific needs with the manufacturer to negotiate favorable terms. Additionally, consider the implications of MOQs on your inventory management and cash flow. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing from US car manufacturers?
Payment terms with US car manufacturers can vary widely, typically ranging from 30 to 90 days after delivery. Some manufacturers may require upfront payments or deposits, especially for custom orders. It’s essential to clarify payment schedules during negotiations to align with your financial planning. Additionally, consider using letters of credit to mitigate risks and ensure secure transactions, particularly when dealing with international suppliers. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing from US automotive plants?
To ensure quality assurance (QA) when sourcing from US automotive plants, implement a robust QA process that includes regular audits and compliance checks. Request detailed quality control documentation from manufacturers, including inspection reports and certifications. Establish clear communication channels for addressing quality issues and consider utilizing third-party inspection services to provide an unbiased assessment of product quality before shipment. Consistent monitoring of supplier performance is also critical to maintaining quality standards. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing vehicles from US manufacturers?
Logistics considerations for importing vehicles from US manufacturers include understanding shipping methods, costs, and timelines. Evaluate options such as container shipping or Roll-on/Roll-off (RoRo) for vehicle transport. Factor in customs duties, tariffs, and import regulations specific to your country. Collaborate with freight forwarders who specialize in automotive imports to streamline the process and ensure compliance with all legal requirements. Planning for potential delays in shipping or customs clearance is also essential. -
How does the location of a manufacturing plant impact my sourcing strategy?
The location of a manufacturing plant significantly impacts your sourcing strategy in terms of logistics, labor costs, and supplier access. Plants situated in the Midwest, particularly Michigan, have a rich automotive history and skilled labor force, making them ideal for certain production needs. Proximity to suppliers can reduce lead times and transportation costs. Additionally, consider the local infrastructure, such as transportation networks and availability of resources, which can influence the efficiency of your supply chain. -
What customization options are available when working with US car manufacturers?
Customization options when working with US car manufacturers can range from minor adjustments to complete vehicle redesigns. Most manufacturers offer a variety of trims, features, and finishes that can be tailored to meet specific market needs. For more extensive customizations, you may need to engage in discussions early in the design phase to align your vision with manufacturing capabilities. Be prepared for potential additional costs and longer lead times associated with customized production.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for car manufacturing plants in usa
In summary, the U.S. automotive manufacturing sector remains a vital player in the global marketplace, producing over 10 million vehicles in 2022 and contributing significantly to the economy. With a well-established infrastructure in key states like Michigan, Ohio, and Kentucky, international B2B buyers can leverage strategic sourcing opportunities that capitalize on the proximity to skilled labor and robust supply chains. The concentration of major manufacturers such as Ford, General Motors, and Toyota in these regions underscores the importance of these hubs for quality and innovation.
As you consider your sourcing strategies, remember that partnerships with U.S. manufacturers not only provide access to high-quality vehicles but also enhance your supply chain resilience. The ongoing shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles presents additional avenues for collaboration, particularly as the demand for sustainable transportation solutions grows globally.
Looking ahead, we encourage international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to engage with U.S. automotive manufacturers. Explore potential partnerships that can drive mutual growth and innovation in an evolving market. The future of automotive manufacturing is bright, and now is the time to position your business at the forefront of this dynamic industry.