Top 7 New Semiconductor Companies In Usa List and Guide: How To S…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for new semiconductor companies in usa
In an era defined by rapid technological advancement, sourcing reliable partners in the semiconductor industry is crucial for businesses aiming to innovate and stay competitive. The landscape of new semiconductor companies in the USA presents a unique opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to tap into cutting-edge technologies that enhance product offerings. However, navigating this complex market can be challenging due to the myriad of suppliers, technologies, and applications available.
This comprehensive guide serves as a valuable resource for B2B buyers, offering insights into the diverse types of new semiconductor companies, their specific applications, and the latest industry trends. From understanding the nuances of wide bandgap semiconductors to exploring innovations in chip design powered by artificial intelligence, this guide equips decision-makers with the knowledge necessary to vet suppliers effectively. Additionally, we delve into considerations regarding cost structures and the competitive advantages of various semiconductor technologies.
By providing actionable insights and practical advice, this guide empowers international buyers to make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they can confidently engage with the vibrant ecosystem of new semiconductor companies in the USA. Whether your focus is on enhancing manufacturing capabilities or developing state-of-the-art consumer electronics, the resources within this guide will help you navigate the global semiconductor market with ease.
Top 10 New Semiconductor Companies In Usa Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Z2Data – Semiconductor Fab Expansion
Domain: z2data.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
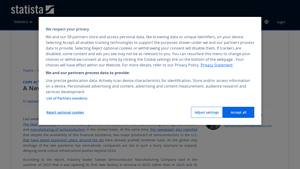
Introduction: The text discusses the construction and expansion of semiconductor fabrication plants (fabs) in North America in 2024. Key details include: 1. **Number of Fabs**: 19 new semiconductor fabs are currently being built. 2. **Key Companies Involved**: Major recipients of funding from the CHIPS & Science Act include GlobalFoundries, Intel, and TSMC. 3. **Funding**: The CHIPS Act allocated $53 billion fo…
2. TSMC & Samsung – Semiconductor Projects
3. Reddit – Semiconductor Insights
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
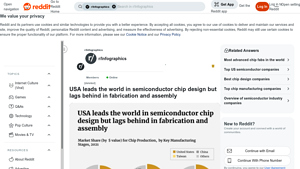
Introduction: USA leads the world in semiconductor chip design but lags behind in fabrication and assembly.
4. Semiconductor Giants – Daily Market Cap Rankings
5. Intel – Key Products
6. Micron – Memory and Storage Solutions
7. NVIDIA – Graphics Processing Units; TSMC – Semiconductors
Domain: builtin.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: NVIDIA: Graphics processing units (GPUs) for gaming, laptops, data centers, and applications in architecture, cybersecurity, robotics, and game development. TSMC: Semiconductors for high-performance computing, IoT, automotive, and consumer electronics; operates semiconductor foundries and offers engineering services. AMD: Internal processors, high-powered graphic systems, and specialized gaming pr…
Understanding new semiconductor companies in usa Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wide Bandgap Semiconductor | Utilizes materials like GaN and SiC for higher efficiency | Power electronics, electric vehicles | Pros: High efficiency, thermal performance; Cons: Higher initial costs |
| AI-Enhanced Chip Design | Leverages AI algorithms for optimized design processes | Consumer electronics, data centers | Pros: Faster development, improved performance; Cons: Requires skilled workforce |
| Silicon Photonics | Integrates optical components for data transmission | Telecommunications, data centers | Pros: High-speed data transfer, compact design; Cons: Complexity in integration |
| Advanced Fabrication Techniques | Focus on innovative manufacturing processes such as EUV | High-performance computing, consumer devices | Pros: Smaller, more powerful chips; Cons: High capital investment for fabs |
| Quantum Computing Semiconductors | Develops chips for quantum processing | Research institutions, advanced computing | Pros: Revolutionary performance, new capabilities; Cons: Still in experimental stages |
What are the Key Characteristics of Wide Bandgap Semiconductor Companies?
Wide bandgap semiconductor companies primarily utilize materials such as Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC). These materials enable devices to operate at higher voltages, temperatures, and frequencies compared to traditional silicon. This makes them particularly suitable for applications in power electronics and electric vehicles, where efficiency and performance are paramount. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the technology’s maturity, compatibility with existing systems, and the supplier’s ability to provide ongoing support and scalability.
How Do AI-Enhanced Chip Design Companies Operate?
Companies that focus on AI-enhanced chip design are at the forefront of integrating artificial intelligence into the semiconductor design process. This approach allows for rapid prototyping and optimization of chip architectures, significantly reducing time-to-market for new products. B2B buyers should consider the potential for performance improvements and cost savings in production, as well as the supplier’s expertise in AI technologies and their track record in delivering reliable, high-quality chips.
What Makes Silicon Photonics Companies Unique?
Silicon photonics companies specialize in the integration of optical components onto silicon chips, enabling high-speed data transmission with minimal loss. This technology is particularly beneficial for telecommunications and data centers, where bandwidth and speed are critical. Buyers should assess the compatibility of these solutions with their existing infrastructure, as well as the supplier’s experience in delivering scalable solutions that meet growing data demands.
What Innovations Are Found in Advanced Fabrication Techniques?
Companies focusing on advanced fabrication techniques, such as extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography, are revolutionizing semiconductor manufacturing. These innovations allow for the production of smaller, more powerful chips with greater efficiency. B2B buyers must weigh the benefits of enhanced performance against the higher capital investment required for advanced manufacturing facilities. Understanding the supplier’s capabilities in managing complex manufacturing processes is also crucial for successful partnerships.
How Are Quantum Computing Semiconductor Companies Pioneering New Technologies?
Quantum computing semiconductor companies are developing chips designed specifically for quantum processors, which promise to revolutionize computing capabilities. These firms are often engaged in cutting-edge research and may cater to niche markets such as advanced computing and scientific research. B2B buyers should be aware that while these technologies hold great potential, they are still largely experimental. Thus, considerations around supplier stability, ongoing research partnerships, and the potential for future scalability are essential when engaging with these companies.
Key Industrial Applications of new semiconductor companies in usa
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of new semiconductor companies in usa | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) | Enhances vehicle safety and automation capabilities. | Need for high reliability and compliance with automotive standards. |
| Telecommunications | 5G Infrastructure Components | Supports faster data transmission and connectivity. | Ensure compatibility with existing networks and scalability options. |
| Consumer Electronics | Smart Home Devices | Facilitates automation and energy efficiency in homes. | Focus on integration with IoT platforms and user-friendly interfaces. |
| Healthcare | Medical Imaging and Diagnostic Equipment | Improves diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes. | Compliance with medical regulations and high precision in components. |
| Industrial Automation | Robotics and Automation Systems | Increases efficiency and reduces operational costs. | Requirement for robust performance under industrial conditions. |
How Are New Semiconductor Companies Addressing Key Applications in Various Industries?
Automotive: New semiconductor companies in the U.S. are revolutionizing the automotive sector, particularly through the development of Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS). These semiconductors enable features such as adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automated emergency braking. By enhancing vehicle safety and automation capabilities, they help manufacturers meet increasing regulatory standards and consumer demands for safer, smarter vehicles. International buyers should consider the reliability and compliance of these components with automotive standards, ensuring they meet rigorous testing and performance benchmarks.
Telecommunications: The rise of 5G technology has prompted new semiconductor firms to create essential components for 5G infrastructure. These innovations facilitate faster data transmission, enabling improved connectivity for both consumers and businesses. For international B2B buyers, it’s crucial to ensure that the semiconductor solutions are compatible with existing telecommunications networks and possess scalability options to accommodate future growth. Understanding the supply chain dynamics and potential lead times for sourcing these components is also vital.
Consumer Electronics: In the consumer electronics sector, new semiconductor companies are at the forefront of developing smart home devices, which integrate seamlessly into IoT ecosystems. These semiconductors allow for automation, energy efficiency, and enhanced user experiences. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, focusing on the integration capabilities with existing platforms and ensuring user-friendly interfaces can significantly impact market adoption and customer satisfaction.
Healthcare: The healthcare industry benefits from advanced semiconductor technologies in medical imaging and diagnostic equipment. These innovations lead to improved diagnostic accuracy and better patient outcomes. Buyers in this sector must prioritize suppliers that comply with medical regulations and provide high-precision components, as the stakes in healthcare are exceptionally high. Understanding the regulatory landscape in different regions is essential for successful procurement and implementation.
Industrial Automation: New semiconductor companies are also pivotal in advancing robotics and automation systems in industrial settings. By enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs, these technologies enable businesses to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market. Buyers should seek suppliers that offer robust performance under varying industrial conditions and can provide support for integration with existing systems, ensuring a smooth transition to automated processes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘new semiconductor companies in usa’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Supply Chain Disruptions with New Semiconductor Companies
The Problem:
B2B buyers looking to partner with new semiconductor companies in the USA often face significant supply chain disruptions. These companies, while innovative and agile, may lack the robust infrastructure and established relationships with suppliers that larger firms have. This can lead to unpredictable lead times, shortages of critical components, and increased costs. Buyers may find themselves in a position where their production schedules are jeopardized due to delays in receiving essential semiconductor components, ultimately impacting their bottom line and customer satisfaction.
The Solution:
To mitigate these risks, B2B buyers should conduct a thorough assessment of the supply chain capabilities of potential semiconductor partners. This involves not only evaluating their manufacturing capacity but also understanding their sourcing strategies and relationships with suppliers. Buyers can engage in direct discussions with these companies to inquire about their contingency plans for supply chain disruptions. Additionally, establishing a diversified sourcing strategy by partnering with multiple semiconductor firms can provide a buffer against unforeseen delays. It’s also beneficial to leverage technology and data analytics to monitor supply chain performance in real-time, enabling proactive adjustments before issues escalate.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Compatibility with Existing Systems
The Problem:
Another common pain point arises when B2B buyers need to ensure that the semiconductors from new companies are compatible with their existing technology stacks. Many new semiconductor firms introduce innovative products that may not seamlessly integrate with legacy systems. This can lead to increased costs for redesigning systems or reconfiguring processes, causing frustration and potential delays in product development.
The Solution:
Buyers should prioritize comprehensive compatibility assessments during the selection process for semiconductor partners. This includes detailed discussions about the specifications of the semiconductor products, potential integrations, and any required modifications to existing systems. It’s advisable to conduct pilot testing before full-scale implementation, allowing for adjustments without significant investment. Additionally, B2B buyers should request documentation and support for integration processes from the semiconductor companies. Engaging in collaborative workshops where technical teams from both sides work together can also enhance understanding and ensure smoother transitions.
Scenario 3: Navigating Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
The Problem:
International buyers often encounter regulatory hurdles when sourcing semiconductors from new companies in the USA. Compliance with local and international standards for quality, safety, and environmental impact is critical, yet new semiconductor firms may not always have the established protocols in place. This can create uncertainty and potential liability issues for buyers, who are responsible for ensuring that all components meet stringent regulatory requirements.
The Solution:
To effectively navigate these regulatory challenges, B2B buyers should conduct a thorough due diligence process that includes reviewing the compliance certifications and quality assurance protocols of potential semiconductor partners. Buyers can also seek partnerships with firms that have a proven track record in regulatory compliance and possess the necessary certifications such as ISO or IPC standards. Establishing clear communication channels regarding compliance expectations from the outset can help set the stage for mutual understanding. Additionally, considering the engagement of third-party consultants who specialize in semiconductor compliance can provide valuable insights and facilitate smoother transactions, ensuring adherence to both domestic and international regulations.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for new semiconductor companies in usa
What Are the Key Materials for New Semiconductor Companies in the USA?
The semiconductor industry relies heavily on specific materials that significantly influence product performance, manufacturing processes, and overall market competitiveness. Understanding these materials is crucial for new semiconductor companies aiming to establish themselves in the U.S. market, especially for international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Which Silicon-Based Materials Are Essential for Semiconductor Manufacturing?
Silicon is the cornerstone of the semiconductor industry. Its properties, including a moderate bandgap and excellent thermal conductivity, make it an ideal material for a wide range of electronic devices. Silicon wafers are used in the fabrication of integrated circuits, solar cells, and various electronic components.
Pros: Silicon is abundant and relatively inexpensive, which lowers production costs. It also has a well-established supply chain and manufacturing processes, making it easier for new companies to scale operations.
Cons: While silicon is versatile, it has limitations in high-temperature applications and does not perform well in high-frequency scenarios, leading to the exploration of alternative materials.
Impact on Application: Silicon’s compatibility with common electronic media makes it suitable for most consumer electronics, but its limitations in specific high-performance applications necessitate the use of advanced materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM and JIS for silicon quality. Understanding local sourcing capabilities and logistics is also crucial, especially for regions with less developed semiconductor ecosystems.
What Role Do Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) Play?
Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) are emerging materials that offer significant advantages over traditional silicon, particularly in power electronics and high-frequency applications.
Pros: GaN and SiC have higher thermal conductivity and can operate at higher voltages and temperatures, which makes them ideal for applications in electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and high-performance RF devices.
Cons: The manufacturing processes for GaN and SiC are more complex and costly compared to silicon, which can deter new entrants from adopting these materials initially.
Impact on Application: These materials enable more efficient power conversion and higher performance in demanding applications, making them increasingly popular among innovative semiconductor companies.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards is critical, particularly regarding the reliability of GaN and SiC devices in various environmental conditions. Buyers should also be aware of the evolving regulatory landscape surrounding these materials.
How Do Polymers and Composites Fit into Semiconductor Applications?
Polymers and composites are increasingly used in semiconductor packaging and insulation applications. These materials can provide excellent electrical insulation and thermal management properties.
Pros: They are lightweight, can be molded into complex shapes, and often have lower production costs compared to traditional materials.
Cons: Polymers may have lower thermal stability and mechanical strength than metals or ceramics, which can limit their use in high-performance applications.
Impact on Application: The use of polymers can enhance the overall efficiency and performance of semiconductor devices, particularly in consumer electronics where weight and size are critical factors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of specific polymer grades that meet industry standards, as well as the implications of sourcing materials from different regions.
Summary Table of Strategic Material Selection
| Material | Typical Use Case for new semiconductor companies in usa | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon | Integrated circuits, solar cells | Abundant and cost-effective | Limited performance at high frequencies | Low |
| Gallium Nitride | Power electronics, RF devices | High thermal conductivity and efficiency | Complex and costly manufacturing | High |
| Silicon Carbide | Electric vehicles, renewable energy systems | High voltage and temperature capabilities | Higher production costs | High |
| Polymers | Packaging and insulation | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower thermal stability | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide serves as a foundational resource for new semiconductor companies in the USA, particularly for international B2B buyers looking to navigate the complexities of material choices in this rapidly evolving industry.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for new semiconductor companies in usa
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for New Semiconductor Companies in the USA?
The manufacturing process of semiconductors is intricate and involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the performance and reliability of the final product. Here’s a breakdown of the typical stages:
1. Material Preparation
The first stage involves the preparation of raw materials, primarily silicon wafers, which serve as the substrate for semiconductor devices. Silicon is purified and crystallized into ingots, which are then sliced into thin wafers. The quality of these wafers is paramount, as any defects can affect the performance of the chips.
In addition to silicon, other materials such as gallium nitride (GaN) and indium phosphide (InP) are increasingly used for specialized applications. These materials undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet the necessary specifications before proceeding to the next stage.
2. Forming
Once the wafers are prepared, they enter the forming stage, which typically involves photolithography, etching, and doping. Photolithography uses light to transfer patterns onto the wafer, creating a blueprint for the circuit design. This is followed by etching, which removes unwanted material and defines the circuit pathways.
Doping introduces impurities into the silicon to alter its electrical properties, allowing it to conduct electricity in a controlled manner. Advanced techniques, such as extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography, are utilized for more precise patterning, essential for the latest generation of chips.
3. Assembly
After forming, the wafers are diced into individual chips, which are then assembled into packages. This stage may involve wire bonding or flip-chip technology, where the chips are directly attached to the substrate. The choice of assembly technique can affect the chip’s performance, thermal management, and overall reliability.
Moreover, encapsulation is crucial to protect the chips from environmental factors. This step ensures that the semiconductor devices can withstand operational stresses and maintain functionality over time.
4. Finishing
The final stage of the manufacturing process is finishing, which includes testing, inspection, and quality assurance. Chips undergo a series of electrical tests to verify their performance against specifications. This stage may also involve the application of protective coatings and final packaging for shipping.
How Do New Semiconductor Companies Ensure Quality Assurance During Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital component of semiconductor manufacturing, ensuring that each product meets international and industry-specific standards. Here are the key elements of quality assurance that new semiconductor companies in the USA typically implement:
Relevant International Standards and Certifications
New semiconductor companies often adopt several international standards to ensure quality and reliability. The most widely recognized is ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 demonstrates a commitment to maintaining consistent quality in products and services.
In addition to ISO, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in the European market and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas applications may also be relevant. These certifications help assure international buyers of the quality and safety of the semiconductor devices.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. The main QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage checks the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the manufacturing process. Rigorous inspections ensure that only high-quality materials are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing checks are conducted to monitor the production process. This includes testing at various stages, such as during photolithography and doping, to identify any deviations from the expected performance.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the chips are assembled, they undergo comprehensive testing to ensure they meet all specifications. This includes electrical testing and functional testing to verify that the chips operate as intended.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Semiconductor Manufacturing?
To ensure the reliability and performance of semiconductor devices, various testing methods are employed:
-
Electrical Testing: This involves measuring the electrical characteristics of the chips under different conditions to ensure they function correctly.
-
Thermal Testing: Chips are subjected to thermal cycling to assess their performance under varying temperature conditions, simulating real-world usage.
-
Visual Inspection: Automated optical inspection (AOI) systems are used to detect physical defects in the wafers and chips.
-
Reliability Testing: This includes stress tests that simulate long-term use, such as high-temperature operating life (HTOL) tests, to predict the lifespan of the chips.
How Can International B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
International buyers must ensure that their semiconductor suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures. Here are some strategies to verify supplier QC:
Conducting Audits and Inspections
Regular audits of manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the supplier’s quality management systems and processes. Buyers should request access to audit reports, certifications, and compliance documentation to verify adherence to international standards.
Requesting Quality Reports
Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that outline the results of testing and inspections at various stages of the manufacturing process. These reports should include data on yield rates, defect rates, and any corrective actions taken in response to identified issues.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspection Services
Engaging third-party inspection services can further validate the supplier’s quality assurance processes. These independent entities can conduct unannounced inspections and provide unbiased assessments of the supplier’s operations.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is crucial. Each region may have specific regulatory requirements and standards that must be met. Buyers should be aware of:
-
Import Regulations: Different countries have varying import regulations that may affect the acceptance of semiconductor products. Familiarity with these regulations is essential for compliance.
-
Cultural Differences in Quality Standards: Different regions may emphasize different aspects of quality assurance. Understanding these cultural nuances can help buyers better communicate their expectations and requirements to suppliers.
-
Supply Chain Considerations: Global supply chains can introduce variability in quality. Buyers should consider the entire supply chain, from raw materials to final assembly, to ensure consistent quality throughout.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting new semiconductor companies in the USA as their suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘new semiconductor companies in usa’
The following guide serves as a practical checklist for international B2B buyers looking to procure from new semiconductor companies in the USA. By following these steps, buyers can ensure they make informed decisions that align with their technical requirements and business objectives.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, clearly outline your technical needs. This includes the types of semiconductors required, performance parameters, and any specific applications or industry standards.
– Considerations: Identify whether you need wide bandgap semiconductors for high-efficiency applications or specific materials for unique environments.
– Documentation: Prepare a detailed requirements document that can be shared with potential suppliers.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Understanding the landscape of new semiconductor companies is crucial. Utilize resources such as industry reports, trade publications, and semiconductor ecosystem maps to identify key players and innovations.
– Research Tools: Leverage platforms like StartUs Insights to discover emerging companies and their unique offerings.
– Trends: Stay informed about current trends in the semiconductor industry, such as advancements in EUV lithography and silicon photonics.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thorough vetting of suppliers is essential before commitment. Request comprehensive company profiles, technical documentation, and case studies to assess their capabilities.
– References: Seek testimonials or references from clients in similar industries or regions to gauge reliability and performance.
– Certifications: Verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications and adhere to industry standards, which can indicate their commitment to quality.
Step 4: Assess Manufacturing Capabilities
Investigate the manufacturing processes and technologies employed by potential suppliers. Understanding their production capabilities will help determine if they can meet your volume and quality requirements.
– Facilities: Visit manufacturing sites, if possible, or request virtual tours to assess their operational standards and technologies used.
– Flexibility: Evaluate their ability to scale production and adapt to changing market demands.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified potential suppliers, engage in negotiations to establish clear terms. This includes pricing, delivery schedules, payment terms, and warranty provisions.
– Transparency: Ensure all terms are documented to avoid misunderstandings later.
– Long-term Relationships: Consider discussing long-term partnerships, which can lead to better pricing and priority service.
Step 6: Test Samples and Prototypes
Before finalizing a large order, request samples or prototypes to validate performance against your specifications. This is a critical step to ensure compatibility with your applications.
– Testing Procedures: Develop a robust testing protocol to evaluate the semiconductors under real-world conditions.
– Feedback Loop: Provide feedback to the supplier to address any issues before full-scale production.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is vital throughout the procurement process. Set up regular check-ins with suppliers to discuss progress, address concerns, and make adjustments as necessary.
– Channels: Determine preferred communication channels and points of contact on both sides.
– Reporting: Implement a reporting structure for updates on production status, delivery timelines, and any potential disruptions.
By following this comprehensive checklist, international B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process and foster successful partnerships with new semiconductor companies in the USA.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for new semiconductor companies in usa Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for New Semiconductor Companies in the USA?
When sourcing from new semiconductor companies in the USA, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials such as silicon wafers, chemicals for etching, and metals for interconnections can vary significantly. Prices fluctuate based on market demand and availability, making it essential for buyers to monitor these trends.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is a significant expense in semiconductor manufacturing. The U.S. labor market demands competitive wages for engineers, technicians, and operators, which can impact pricing. Companies often invest in training to maintain high-quality standards, further influencing costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Given the capital-intensive nature of semiconductor fabs, overhead costs can be substantial.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in fabrication equipment is high. Tooling costs can be amortized over large production runs, but new companies may face higher per-unit costs until they reach optimal production volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product reliability necessitates rigorous testing and quality assurance processes, which add to the overall cost. Certifications for international standards can further increase expenses.
-
Logistics: Transporting semiconductor products, especially internationally, involves various costs related to shipping, customs duties, and insurance, which should be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: New companies often have tighter margins as they establish their market presence. Understanding their pricing strategies can provide insight into their long-term viability and competitiveness.
What Factors Influence Pricing in Semiconductor Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing when sourcing from new semiconductor companies:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often come with bulk pricing advantages. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions typically incur higher costs due to the additional engineering and production processes involved. Clear specifications can help suppliers provide accurate quotes.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials affects both cost and quality. Suppliers offering certified materials may charge a premium, but this can ensure compliance with international standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established companies may command higher prices due to their proven track record, while new entrants may offer lower prices to attract business.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) affect pricing and responsibility for shipping costs.
How Can International B2B Buyers Optimize Costs When Sourcing Semiconductors?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can take several steps to optimize their sourcing costs:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers to negotiate better terms. Highlighting long-term partnership potential can lead to favorable pricing.
-
Cost Efficiency: Assess the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes not only purchase price but also shipping, tariffs, and potential maintenance costs. A lower initial price may not always be the best value.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations and market conditions. Buyers should also consider the impact of currency fluctuations on overall costs.
-
Building Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and priority service, especially during high-demand periods.
Disclaimer Regarding Indicative Prices
Prices for semiconductors can vary widely based on market conditions, technological advancements, and the specific requirements of each order. Therefore, it is essential for buyers to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are making informed decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing new semiconductor companies in usa With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in Semiconductor Solutions
When considering the rapidly evolving landscape of semiconductor solutions, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to evaluate various options available in the market. New semiconductor companies in the USA are at the forefront of innovation, but there are alternative technologies and methods that also address similar needs in the electronics sector. This analysis will compare new semiconductor companies with other viable solutions, helping businesses make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | New Semiconductor Companies In USA | Alternative 1: Established Semiconductor Manufacturers | Alternative 2: Semiconductor IP Providers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High performance with cutting-edge technologies like AI and EUV | Consistent performance with a proven track record | High efficiency in design, but dependent on manufacturing partners |
| Cost | Variable; often higher due to R&D investments | Generally lower due to economies of scale | Lower initial costs, but licensing fees can accumulate |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires integration with existing systems | High; established processes and supply chains | Moderate; requires expertise in IP integration |
| Maintenance | Ongoing support varies by company; generally good | Established support structures; reliable maintenance | Limited maintenance; focus on design rather than manufacturing |
| Best Use Case | Innovative applications in emerging technologies | Mass production of standard electronic components | Custom chip designs and specialized applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Alternative 1: Established Semiconductor Manufacturers
Established semiconductor manufacturers, such as Intel or Texas Instruments, have long-standing reputations and extensive experience in mass production. These companies benefit from economies of scale, allowing them to offer competitive pricing and reliable supply chains. However, their focus on high-volume production may result in slower adaptation to cutting-edge technologies compared to newer entrants. Buyers looking for consistent performance and lower costs for standard components may find established manufacturers to be a more suitable choice.
Alternative 2: Semiconductor IP Providers
Semiconductor intellectual property (IP) providers focus on delivering design solutions rather than manufacturing chips. Companies like ARM and Synopsys provide essential building blocks for chip design, enabling clients to develop customized solutions tailored to specific applications. This approach can significantly reduce time-to-market and development costs. However, the dependency on third-party manufacturers for production can lead to challenges in maintaining quality control and ensuring timely delivery. Buyers with specialized needs and in-house manufacturing capabilities may find this alternative advantageous.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Business Needs
For B2B buyers navigating the semiconductor landscape, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of new semiconductor companies in the USA compared to established manufacturers and semiconductor IP providers is essential. The choice between these options should be guided by factors such as performance requirements, budget constraints, implementation challenges, and specific use cases. By aligning the selected solution with their strategic goals, companies can optimize their procurement processes and drive innovation in their electronic offerings.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for new semiconductor companies in usa
What Are the Critical Technical Properties for New Semiconductor Companies in the USA?
Understanding the essential technical properties of semiconductors is crucial for new companies entering the market. These specifications not only influence product performance but also impact supply chain decisions and customer satisfaction. Below are some critical properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of semiconductor materials based on their purity and performance characteristics. Common materials include silicon, gallium nitride (GaN), and silicon carbide (SiC). Higher-grade materials typically offer improved efficiency, thermal conductivity, and longevity. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade is vital for ensuring that the semiconductor components meet specific performance requirements for their applications.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in semiconductor manufacturing. It is crucial in ensuring that components fit together correctly and function as intended. Tight tolerances are essential for high-performance applications, such as in aerospace or medical devices, where even minor deviations can lead to failure. B2B buyers should prioritize manufacturers who can consistently meet stringent tolerance requirements to minimize the risk of defects.
3. Packaging Type
The packaging type of semiconductor devices affects their thermal management, electrical performance, and integration into electronic systems. Common packaging types include dual in-line packages (DIP), surface mount devices (SMD), and ball grid arrays (BGA). The choice of packaging can influence the size and heat dissipation capabilities of the final product. For buyers, understanding packaging types helps ensure compatibility with existing systems and can drive decisions on assembly processes.
4. Operating Temperature Range
The operating temperature range specifies the temperatures within which a semiconductor device can function reliably. This property is critical for applications in extreme environments, such as automotive or industrial sectors. B2B buyers must ensure that the semiconductor components they source can withstand the specific temperature conditions of their applications to avoid premature failure and ensure product reliability.
5. Power Dissipation
Power dissipation refers to the amount of power a semiconductor device can handle without overheating. This property is crucial for applications requiring high efficiency and performance, such as power electronics and high-frequency devices. B2B buyers should evaluate power dissipation ratings to ensure that the components can operate within the required parameters without risking damage or inefficiency.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Semiconductor Industry?
Navigating the semiconductor industry also requires familiarity with specific trade terminology. Understanding these terms can facilitate smoother transactions and clearer communication between buyers and suppliers.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the semiconductor industry, OEMs often source chips from semiconductor manufacturers to integrate them into their products. For B2B buyers, partnering with reputable OEMs ensures a reliable supply chain and consistent product quality.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. In semiconductor manufacturing, MOQs can vary significantly based on the complexity of the chip and production costs. Understanding MOQs helps B2B buyers manage inventory levels and production schedules effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services. In the semiconductor sector, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices, terms, and capabilities from multiple suppliers. This process is essential for securing the best deals and ensuring cost-effectiveness.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping, insurance, and liability responsibilities, reducing risks associated with international procurement.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered. In the semiconductor industry, lead times can be influenced by manufacturing capabilities, material availability, and logistics. B2B buyers should consider lead times when planning production schedules to avoid delays in their supply chain.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, new semiconductor companies can better position themselves in the market and enhance their relationships with international B2B buyers.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the new semiconductor companies in usa Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the New Semiconductor Sector in the USA?
The U.S. semiconductor industry is undergoing significant transformation, driven by a confluence of global factors. The demand for advanced electronics, from consumer gadgets to industrial automation, is rising sharply. This is largely fueled by the proliferation of IoT devices, AI applications, and the growing need for high-performance computing. Emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, such as Vietnam and Brazil, are increasingly becoming integral parts of this supply chain, seeking to leverage advanced semiconductor technology to boost their own tech ecosystems.
Key trends influencing the market include the shift towards wide bandgap semiconductors, which offer improved performance in power applications, and the adoption of advanced manufacturing techniques like extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUV). Furthermore, the integration of AI in chip design is revolutionizing how semiconductors are developed, allowing for more efficient and innovative solutions. International buyers must navigate these dynamics by focusing on partnerships with companies that not only offer cutting-edge technology but also demonstrate flexibility in meeting specific regional needs.
The U.S. semiconductor ecosystem is characterized by a diverse range of companies specializing in R&D, fabrication, and material supply, creating opportunities for international buyers to engage with a broad spectrum of innovative firms. Understanding the competitive landscape and identifying companies that align with specific technological requirements will be essential for effectively sourcing in this dynamic market.
How is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing in the New Semiconductor Industry?
As the semiconductor industry evolves, sustainability and ethical sourcing have emerged as critical considerations for B2B buyers. The environmental impact of semiconductor manufacturing—characterized by high energy consumption and waste generation—has prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices. New semiconductor companies in the USA are increasingly adopting environmentally friendly materials and processes, aiming to reduce their carbon footprint and comply with international sustainability standards.
Ethical supply chains are becoming a priority, with buyers seeking partners who prioritize transparency and responsibility in sourcing raw materials. This includes the use of certified “green” materials, such as those with low environmental impact or that are derived from sustainable sources. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and RoHS compliance for hazardous substances are becoming benchmarks for evaluating potential suppliers.
For international buyers, aligning with semiconductor companies that emphasize sustainability not only enhances their brand image but also meets the growing consumer demand for responsible sourcing. Investing in relationships with these forward-thinking companies can provide a competitive edge in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
What is the Evolution of the Semiconductor Sector in the USA and its Implications for B2B Buyers?
The semiconductor sector in the USA has evolved dramatically over the past few decades. Initially dominated by a few key players, the landscape has diversified with the emergence of over 2,000 new companies in the last five years. This growth is largely attributed to technological advancements and the increasing demand for semiconductors across various industries, including automotive, telecommunications, and consumer electronics.
The introduction of the CHIPS Act has further spurred investment in domestic manufacturing and R&D, aiming to reduce dependence on foreign supply chains. This legislative push not only enhances the U.S. position in the global semiconductor market but also offers international buyers more reliable sourcing options within the country.
As new semiconductor companies continue to innovate and expand, B2B buyers must stay informed about the latest developments and emerging technologies. By leveraging the U.S. semiconductor ecosystem, international businesses can access cutting-edge solutions that drive their own growth and competitiveness in the global market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of new semiconductor companies in usa
-
How do I identify reliable new semiconductor suppliers in the USA?
To identify reliable new semiconductor suppliers, start by researching their track record in innovation and quality. Utilize industry reports and databases to evaluate their market presence and client testimonials. Attend trade shows and industry conferences to network and gather insights. Additionally, consider leveraging platforms like LinkedIn for professional reviews and recommendations. It’s crucial to vet suppliers for certifications and compliance with international standards, ensuring they meet your specific requirements. -
What are the key factors to consider when sourcing semiconductors from new companies?
When sourcing semiconductors from new companies, consider factors such as technological capabilities, product reliability, and scalability. Investigate their R&D investments and the uniqueness of their technologies, such as wide bandgap materials or silicon photonics. Assess their production capacity and lead times, as well as their ability to customize products according to your specifications. Finally, review their financial stability to ensure they can meet your long-term needs without disruptions. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by new semiconductor manufacturers?
Payment terms can vary significantly among semiconductor manufacturers. Many new companies may offer flexible payment options, including net 30, net 60, or upfront deposits, especially for first-time orders. It’s essential to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring that the supplier’s terms are competitive and fair. Always clarify the implications of late payments and potential discounts for early payments. Establishing clear payment terms upfront can help build a strong partnership. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) typically required by new semiconductor firms?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary widely depending on the semiconductor type and the manufacturer’s production capabilities. New semiconductor companies may have lower MOQs to attract initial clients, while established firms might require larger orders to justify production costs. Always confirm the MOQ before proceeding, as it can impact your initial investment and inventory management. In some cases, you may negotiate MOQs based on your specific needs and long-term purchasing commitments. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in semiconductor products from new suppliers?
To ensure quality assurance in semiconductor products, request detailed documentation of the supplier’s quality control processes, including certifications like ISO 9001 or IATF 16949. Conduct audits or inspections at their facilities if possible, and ask for samples to evaluate product performance. Establish clear quality metrics and expectations in your contracts, including warranties and return policies. Regular communication and feedback loops with the supplier can also help maintain quality standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing semiconductors from the USA?
When importing semiconductors from the USA, consider logistics aspects such as shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with semiconductor importation to navigate potential challenges. Be aware of duties, tariffs, and compliance with international trade laws, which can affect overall costs. Finally, plan for potential delays in supply chains and establish contingency plans to mitigate risks associated with logistics. -
How do I assess the technological capabilities of new semiconductor companies?
Assessing the technological capabilities of new semiconductor companies involves examining their R&D focus and innovations. Review their product portfolio for advanced technologies like AI-driven chip design, through-silicon vias (TSVs), or extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUV). Look for published research papers, patents, and collaborations with research institutions to gauge their commitment to innovation. Engaging with their technical teams during discussions can also provide insight into their expertise and future direction. -
What are the common challenges faced when sourcing semiconductors internationally?
Common challenges when sourcing semiconductors internationally include navigating trade regulations, managing currency fluctuations, and addressing varying quality standards. Communication barriers may arise, complicating negotiations and technical discussions. Additionally, logistical issues, such as shipping delays and customs inspections, can impact delivery timelines. To mitigate these challenges, establish strong relationships with suppliers and logistics partners and stay informed about international trade policies affecting your supply chain.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for new semiconductor companies in usa
The semiconductor industry in the U.S. is witnessing a transformative era, marked by the emergence of over 2,000 new companies driving innovation in technologies such as wide bandgap semiconductors and silicon photonics. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, these advancements present unique sourcing opportunities. Strategic sourcing from these new players not only ensures access to cutting-edge technologies but also fosters competitive advantages in an increasingly digital world.
Engaging with new semiconductor companies allows buyers to leverage specialized products that address pressing challenges such as power consumption and data processing speed. The U.S. semiconductor ecosystem is robust, characterized by a diverse range of manufacturers, R&D facilities, and suppliers. By strategically partnering with these innovators, businesses can enhance their supply chains and adapt to the evolving demands of the electronics market.
Looking ahead, the semiconductor sector is poised for growth as global demand for smarter, faster electronics rises. International buyers are encouraged to explore these emerging companies to stay ahead of industry trends and secure the best solutions for their needs. Embrace the opportunity to collaborate with the next generation of semiconductor innovators and position your business for future success.