Top 9 Harmonized Code Usa List and Guide: How To Solve Scenario 1…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for harmonized code usa
In today’s interconnected world, navigating the complexities of international trade can be daunting, especially when it comes to understanding the harmonized code USA system. For international B2B buyers, such as those sourcing materials or products from Brazil to Nigeria, the challenge often lies in accurately classifying goods under the Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS). Misclassifications can lead to costly delays, unexpected tariffs, and compliance issues that disrupt supply chains.
This comprehensive guide is designed to demystify the harmonized code USA framework, providing insights into its various types, applications, and the nuances of the classification process. From understanding the difference between HTS and HS codes to exploring effective supplier vetting strategies, we cover the essential elements that every international buyer must consider. Additionally, we delve into the implications of recent legislative changes, including Chapter 99, and how these can impact your import strategy.
Empowering informed purchasing decisions is at the heart of this guide. By equipping B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe with the knowledge to navigate the HTS codes, we aim to enhance your ability to source products efficiently and cost-effectively. With actionable insights and expert recommendations, you will be better prepared to tackle the challenges of international trade and optimize your supply chain operations.
Top 10 Harmonized Code Usa Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. USPS – International Mail Services Codes
Domain: pe.usps.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Harmonized System Codes and Other Classification Codes related to international mail services, including descriptions, eligibility, prices, postage payment methods, and mail preparation for various international mailing options such as Global Express Guaranteed, Priority Mail Express International, Priority Mail International, First-Class Mail International, and First-Class Package International S…
2. Wise – HS Codes Explained
Domain: wise.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
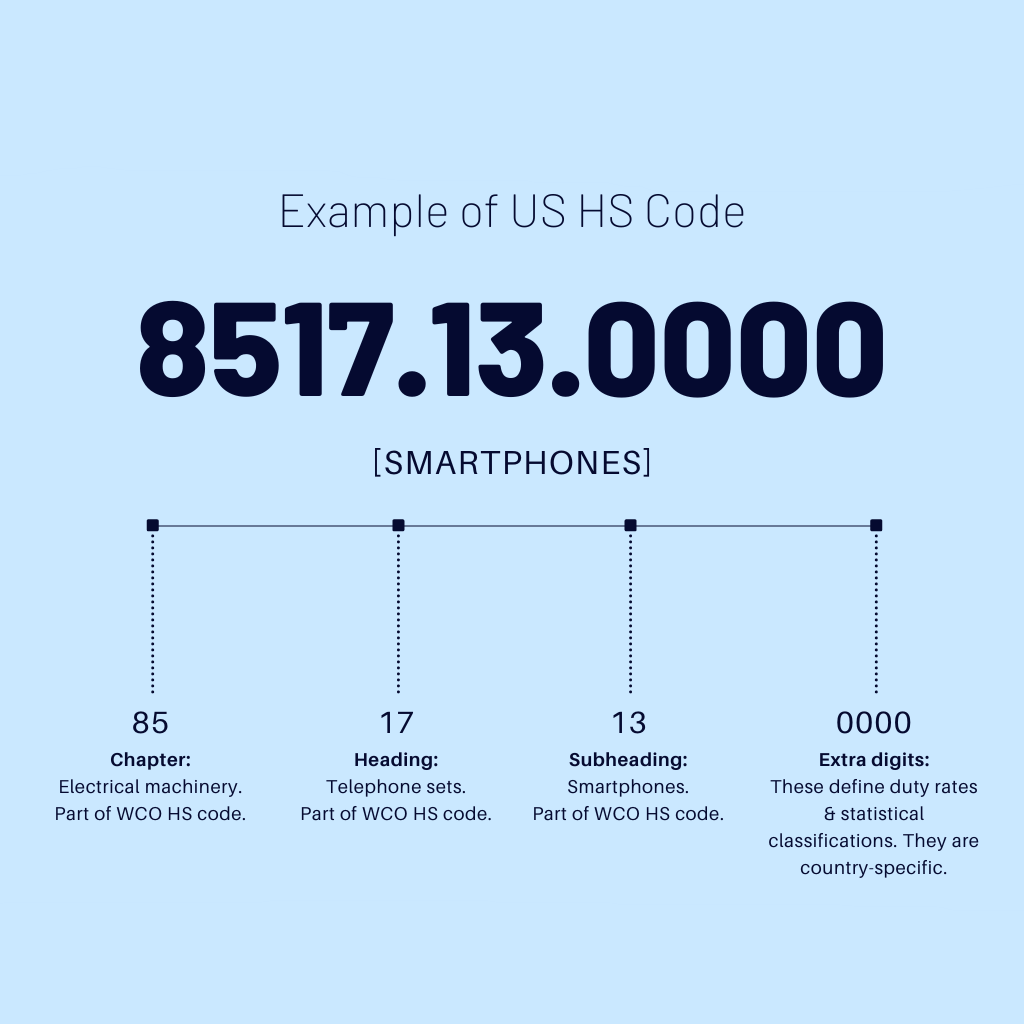
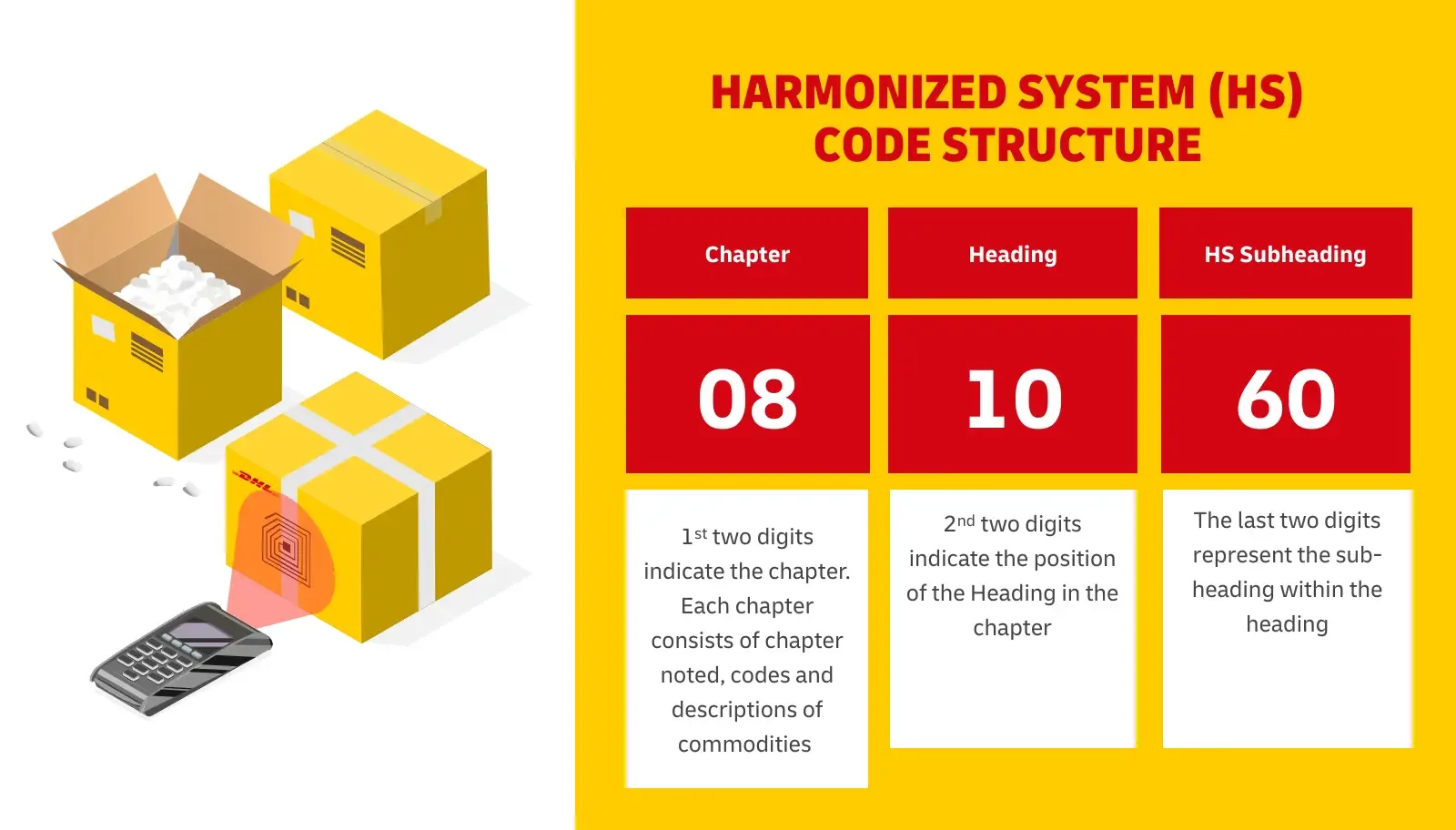
Introduction: HS codes are an international standard for calculating Import Duty tax, controlled by the World Customs Organisation (WCO). Each HS code describes a particular trade product, allowing governments to charge the right tariffs. HS codes consist of 4 parts, totaling 10 digits: the first 2 digits represent the chapter (industry), the next 2 digits represent the heading, the following 2 digits represent…
3. USA Customs Clearance – Harmonized Tariff Schedule Codes
Domain: usacustomsclearance.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) codes are required to accurately classify products and assess tariffs on goods imported into the U.S. Resources to find HTS codes include licensed customs brokers, HTS code lookup tools, and Customs and Border Protection (CBP). Licensed customs brokers provide expert assistance and can ensure accurate classification and duty rates. HTS code lookup tools are free bu…
4. DHL – Essential HS Codes for International Shipping
Domain: dhl.com
Registered: 1989 (36 years)
Introduction: HS codes (Harmonized System codes) are unique identifiers used to classify goods for international shipping. They consist of six digits, where the first two identify the chapter and the next four specify the heading and sub-heading within that chapter. HS codes are essential for customs clearance, helping to avoid delays and ensuring accurate representation of shipped products. While not mandatory…
5. Canada Post – HS Code Finder
6. FedEx – HTS Code Classification
Domain: fedex.com
Registered: 1991 (34 years)
Introduction: HTS Code (Harmonized Tariff Schedule) is a 10-digit classification system used in the United States to calculate customs duties on imported goods. The first six digits match the HS Code (Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System), which is a standardized 6-digit system used globally. HTS codes consist of 7 to 10 digits and are specific to a country, providing further classification releva…
7. Flexport – HS Code Classification
Domain: flexport.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: HS (Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System) codes are product classification codes used by U.S. Customs and all other members of the World Customs Organization (WCO) to classify goods for customs purposes. HS codes are six digits that can be broken down into three parts: the first two digits identify the chapter in the HS Nomenclature the goods are classified in, the next two digits id…
8. ALS – Harmonized System Codes
Domain: als-cs.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: HS (Harmonized System) and HTS (Harmonized Tariff System) Codes are internationally recognized reference numbers used to describe specific products during the import and export of goods. HS Codes consist of 6 to 10 digits and are used globally for product classification, while HTS Codes are specific to the US and extend HS Codes to a more detailed 10-digit level. The first 6 digits of an HTS code …
9. Ship4WD – HS/HTS Code Solutions
Domain: ship4wd.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: HS/HTS codes, also known as Harmonized System (HS) or Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) codes, are standardized international nomenclature used to classify goods for trade. HS codes consist of six-digit numbers for product identification, while HTS codes expand these into ten-digit codes for detailed classification, particularly for imports. Schedule B codes are specific to US exports, based on HS …
Understanding harmonized code usa Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| HTSUS Codes | Unique 10-digit codes specific to the U.S. | Importing goods into the U.S. | Pros: Clear classification, duty determination. Cons: Complexity in finding the correct code. |
| HS Codes | International 6-digit codes used globally for trade classification | Global shipping and customs clearance | Pros: Universally recognized, simplifies international trade. Cons: Less detailed than HTS codes. |
| Chapter 99 Codes | Temporary codes for specific legislative purposes | Compliance with U.S. trade regulations | Pros: Flexibility in classification. Cons: May be subject to rapid changes and updates. |
| Statistical Suffix Codes | Additional digits in HTS codes for statistical tracking | Market analysis and reporting | Pros: Enhanced data for trade analysis. Cons: Requires understanding of statistical reporting. |
| Duty Rate Lines | Subheadings in HTS codes indicating applicable duty rates | Cost estimation for imports | Pros: Helps in budgeting and pricing strategies. Cons: Variability in rates can complicate financial planning. |
What are HTSUS Codes and How Do They Benefit B2B Buyers?
HTSUS codes, or Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States codes, are unique 10-digit identifiers assigned to goods imported into the U.S. These codes are essential for determining the correct duties and taxes owed on imported items, making them critical for B2B transactions. Buyers must accurately classify their goods to avoid penalties and ensure compliance with U.S. regulations. However, the complexity of navigating over 21,000 classifications can be daunting, necessitating the expertise of customs brokers or trade compliance professionals.
How Do HS Codes Facilitate International Trade?
HS codes, or Harmonized System codes, are 6-digit international codes used for classifying traded products globally. They provide a standardized method for identifying goods, which streamlines the customs clearance process across different countries. For B2B buyers engaged in international trade, understanding HS codes is crucial as they facilitate smoother logistics and compliance with customs requirements. While HS codes simplify the trade process, they may lack the specificity needed for U.S. imports, highlighting the importance of HTSUS codes for detailed classification.
What are Chapter 99 Codes and Their Implications for Businesses?
Chapter 99 codes are temporary classifications introduced to accommodate specific legislative changes within the U.S. trade framework. These codes allow for modifications to existing HTS headings and may impose additional restrictions. For B2B buyers, staying informed about these codes is essential for compliance and avoiding potential disruptions in their import activities. While they provide flexibility, the rapid changes associated with Chapter 99 can create uncertainty, necessitating ongoing vigilance and consultation with trade experts.
Why are Statistical Suffix Codes Important for Market Analysis?
Statistical suffix codes are additional digits in HTS codes that help track and report trade statistics more effectively. These codes enhance data collection for market analysis, enabling businesses to make informed decisions based on trade patterns and trends. For B2B buyers, leveraging statistical suffix codes can provide valuable insights into market dynamics, aiding in strategic planning and competitive positioning. However, understanding these codes requires a level of expertise in trade data interpretation, which may be a barrier for some companies.
How Do Duty Rate Lines Affect Import Cost Management?
Duty rate lines are the subheadings in HTS codes that specify the duty rates applicable to imported goods. This information is vital for B2B buyers as it directly impacts the overall cost of importing products. By understanding duty rate lines, businesses can budget more accurately and develop pricing strategies that account for potential tariff fluctuations. However, the variability of duty rates can complicate financial planning, making it essential for buyers to stay informed about changes in tariff regulations and consult with customs experts to navigate these complexities effectively.
Key Industrial Applications of harmonized code usa
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of harmonized code usa | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Classification of agricultural machinery and equipment | Ensures compliance with import regulations and duty rates | Understanding HTS codes for specific equipment and materials |
| Textiles and Apparel | Importing and exporting fabrics and garments | Streamlines customs clearance and reduces delays | Awareness of tariff rates and trade agreements |
| Automotive | Sourcing auto parts and components from international markets | Accurate duty assessment and inventory management | Knowledge of HTS codes for specific parts and classifications |
| Pharmaceuticals | Importing drugs and medical devices | Helps in compliance with FDA regulations and tariffs | Ensuring correct classification to avoid penalties |
| Electronics | Importing electronic components and devices | Facilitates smooth customs processes and duty calculations | Identifying correct HTS codes to avoid customs issues |
How is Harmonized Code USA Applied in Agriculture?
In the agriculture sector, the Harmonized Code USA is essential for classifying agricultural machinery and equipment. This classification helps importers understand the applicable duty rates and comply with U.S. import regulations. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, knowledge of specific HTS codes can prevent costly customs delays and fines. Buyers must also consider the nuances of agricultural regulations in the U.S. to ensure smooth importation.
What Role Does Harmonized Code USA Play in Textiles and Apparel?
The textiles and apparel industry relies heavily on the Harmonized Code USA for importing and exporting fabrics and garments. Accurate classification of these items streamlines the customs clearance process, ensuring that goods are not held up at the border. For B2B buyers from Europe and the Middle East, understanding the specific HTS codes for different textiles is crucial for managing tariffs effectively. Additionally, buyers should be aware of any trade agreements that could affect duty rates.
How is Harmonized Code USA Used in Automotive Parts Sourcing?
In the automotive sector, the Harmonized Code USA is critical for sourcing auto parts and components from international markets. Correct classification ensures accurate duty assessments, which can significantly impact overall costs. For international buyers, especially those from Brazil and Nigeria, familiarity with HTS codes is vital for inventory management and financial forecasting. Buyers should also stay updated on any changes in tariff regulations that may affect their sourcing strategies.
Why is Harmonized Code USA Important for Pharmaceuticals?
The pharmaceuticals industry utilizes the Harmonized Code USA to import drugs and medical devices efficiently. Proper classification under the HTS codes helps businesses comply with FDA regulations and accurately assess tariffs. For international buyers, particularly from the Middle East, understanding these codes is crucial to avoid penalties and ensure timely delivery of critical products. Buyers should ensure they are well-versed in the specific requirements for medical imports to facilitate smooth customs procedures.
How Does Harmonized Code USA Facilitate Electronics Imports?
In the electronics sector, the Harmonized Code USA aids in the importation of components and devices, helping businesses navigate customs processes effectively. Proper classification under HTS codes ensures that duty calculations are accurate, preventing unexpected costs. For B2B buyers from Africa and South America, identifying the correct HTS codes is essential to avoid customs issues that can lead to delays and increased operational costs. Understanding the specific regulations governing electronics imports is also critical for compliance and efficiency.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘harmonized code usa’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Complex HTS Code Classification
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the intricate task of classifying their products under the correct Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) codes. With over 21,000 codes available, misclassification can lead to significant delays in customs clearance, unexpected tariffs, and even legal penalties. For international buyers, especially those new to the US market, this complexity can create anxiety and uncertainty. Moreover, the nuances between HTS codes and HS codes can further complicate the classification process, leaving buyers feeling overwhelmed and hesitant to proceed with their shipments.
The Solution: To effectively navigate HTS code classification, buyers should invest time in understanding the specific characteristics of their products and how they fit into the HTS framework. A practical approach is to utilize online tools and resources provided by the US International Trade Commission (ITC) and other reputable sources. Creating a detailed product description that includes materials, uses, and manufacturing processes will aid in identifying the most appropriate code. Consulting with a customs broker or tariff expert can also provide invaluable insights and ensure compliance. By taking these steps, buyers can confidently classify their products, minimize the risk of delays, and ensure they meet all regulatory requirements.
Scenario 2: Staying Updated with Tariff Changes
The Problem: The dynamic nature of international trade means that tariffs and regulations are subject to frequent changes. For B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa or South America, keeping abreast of these changes can be a daunting task. The recent introduction of Chapter 99 by US Customs and Border Protection, which modifies existing HTS code headings and imposes stricter regulations, exemplifies this challenge. Buyers may find themselves facing unexpected costs or compliance issues if they are unaware of these updates.
The Solution: To stay informed about tariff changes, B2B buyers should establish a proactive communication channel with customs brokers and trade compliance specialists. Subscribing to trade newsletters, joining relevant industry associations, and participating in trade webinars can also provide timely updates on changes to HTS codes and tariffs. Additionally, leveraging technology, such as automated tracking systems, can help buyers monitor specific codes relevant to their products. By taking these proactive measures, buyers can mitigate the risks associated with tariff changes and better plan their import strategies.
Scenario 3: Understanding the Impact of Misclassification
The Problem: Misclassification of goods under the Harmonized Code can have severe consequences for international B2B buyers, including hefty fines, increased duties, and shipment delays. A common scenario involves a buyer mistakenly classifying a product as a lower-duty item, only to face a substantial post-clearance audit that reveals the error. This not only results in financial repercussions but can also damage the buyer’s reputation and disrupt supply chains.
The Solution: To prevent misclassification, buyers should conduct thorough research and due diligence on the HTS codes applicable to their products. Implementing a classification checklist that includes product specifications, intended use, and previous classifications can help ensure accuracy. Regular training sessions for staff involved in import processes can also be beneficial. Collaborating with a knowledgeable customs broker who can provide guidance and review classifications before submission can further safeguard against errors. By prioritizing accuracy in classification, buyers can protect their businesses from costly mistakes and maintain smooth operations in their import activities.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for harmonized code usa
When selecting materials for products classified under the Harmonized Code in the USA, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the properties of the materials, their suitability for specific applications, and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials, highlighting their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in Harmonized Code Applications?
Steel is a widely used material due to its high strength and versatility. It typically exhibits excellent tensile strength, making it suitable for structural applications. Steel’s temperature rating can vary significantly based on its alloy composition, with some grades capable of withstanding high temperatures and pressures. Additionally, corrosion resistance can be enhanced through treatments like galvanization.
Pros & Cons: Steel is durable and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for many applications. However, its weight can be a disadvantage in industries where lightweight materials are preferred. Manufacturing complexity can also increase with the need for specialized treatments.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various media, including water, oil, and gas, making it suitable for pipelines and construction materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM standards for steel quality. In regions like Brazil and Nigeria, understanding local regulations regarding material sourcing and environmental impact is crucial.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Harmonized Code Products?
Aluminum is known for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. It has a lower density than steel, which makes it ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical. Aluminum can withstand temperatures up to approximately 600°F (316°C) depending on the alloy, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion. However, it can be more expensive than steel and may have lower tensile strength, which limits its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including air and water, but may not be suitable for certain acidic environments without protective coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with DIN standards is essential for buyers in Europe. Additionally, understanding local market preferences for aluminum products can influence purchasing decisions.
What Are the Benefits of Using Plastic in Harmonized Code Applications?
Plastics, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, are increasingly popular due to their versatility and resistance to chemicals. They can be engineered to withstand a wide range of temperatures, with some types rated for use in extreme conditions.
Pros & Cons: Plastics are lightweight, cost-effective, and resistant to corrosion and chemicals. However, they may not provide the same level of durability as metals and can be affected by UV exposure unless treated.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for applications involving water, chemicals, and even food products, making them ideal for packaging and containers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with JIS standards in Japan and ASTM standards in the USA. Understanding the environmental impact of plastic use is also increasingly important in regions like Europe, where regulations are tightening.
Why Is Composite Material Gaining Popularity in Harmonized Code Products?
Composite materials, such as fiberglass and carbon fiber, combine the properties of different materials to achieve superior performance. They are lightweight and can be engineered for high strength and flexibility, making them suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: Composites offer excellent corrosion resistance and can be tailored for specific performance characteristics. However, they can be more expensive to manufacture and may require specialized processes.
Impact on Application: Composites are often used in aerospace, automotive, and marine applications, where weight and strength are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with international standards and certifications, particularly in industries like aerospace. Understanding the supply chain for composite materials is essential, especially in regions with less established manufacturing capabilities.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Harmonized Code USA
| Material | Typical Use Case for harmonized code usa | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components, pipelines | High strength and durability | Heavy weight, potential corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, lower tensile strength | High |
| Plastic | Packaging, containers | Cost-effective and versatile | Less durable, UV sensitivity | Low |
| Composite | Aerospace, automotive, marine applications | Tailored performance and lightweight | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection considerations for international B2B buyers navigating the Harmonized Code in the USA. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions that align with both performance requirements and regulatory compliance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for harmonized code usa
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Products Under Harmonized Codes in the USA?
The manufacturing process for products classified under Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) codes in the USA typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This initial stage involves sourcing raw materials that comply with relevant international standards. Depending on the product, materials may need to undergo processes such as cutting, sizing, and cleaning to ensure they are suitable for the next manufacturing steps.
-
Forming: In this stage, the prepared materials are shaped into specific forms. Techniques can include molding, casting, machining, or welding, depending on the nature of the product. For example, metal components may be stamped or forged, while plastic parts might be injection molded.
-
Assembly: This phase involves putting together various components to create the final product. Assembly can be manual or automated and often requires precise alignment and fitting of parts to ensure functionality and quality.
-
Finishing: The final stage focuses on enhancing the product’s appearance and performance. This can involve processes such as painting, coating, polishing, or applying protective finishes. The goal is to ensure that the product meets both aesthetic and functional standards.
Which Key Techniques Are Utilized in Manufacturing Processes Related to Harmonized Codes?
Several techniques are employed in manufacturing processes relevant to HTS codes, with an emphasis on efficiency and quality.
-
Lean Manufacturing: This approach aims to minimize waste while maximizing productivity. Techniques like value stream mapping and just-in-time (JIT) inventory help streamline operations.
-
Computer Numerical Control (CNC): CNC technology is pivotal in precision machining, allowing for high accuracy in cutting and shaping materials. This is particularly important for components with tight tolerances.
-
Additive Manufacturing: Often referred to as 3D printing, this technique is gaining traction in sectors such as aerospace and medical devices, allowing for the creation of complex shapes that are difficult to achieve with traditional methods.
-
Quality Control Integration: Incorporating quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process ensures that defects are identified and rectified early, reducing costs associated with rework or returns.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider for Quality Assurance?
Quality assurance is paramount in manufacturing, especially for international B2B transactions. The following standards are particularly relevant:
-
ISO 9001: This widely recognized quality management standard helps organizations ensure they meet customer and regulatory requirements consistently. Certification can enhance credibility with international buyers.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It is crucial for B2B buyers in Europe to verify that suppliers adhere to these standards.
-
API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides specifications for products in the oil and gas industry. Compliance with these standards is critical for buyers sourcing equipment and materials in this sector.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Implementing quality control (QC) checkpoints is essential for ensuring product quality. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection stage assesses the quality of raw materials before they enter the production process. Ensuring that materials meet specified standards can prevent defects in the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing process, IPQC involves monitoring production parameters and conducting tests to ensure that products meet quality standards at various stages.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection phase checks the completed products against established specifications. It often includes functional testing, visual inspections, and packaging assessments.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed for Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are utilized to ensure that products meet quality standards:
-
Mechanical Testing: This includes tensile tests, hardness tests, and impact tests to assess the material properties and ensure they meet required specifications.
-
Electrical Testing: For electronic components, testing for electrical conductivity, insulation resistance, and functional testing is critical.
-
Chemical Testing: Analysis of materials for chemical composition ensures compliance with safety and regulatory standards, particularly for products in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of their suppliers:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality management systems firsthand. This can help establish trust and ensure compliance with international standards.
-
Quality Control Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can provide insight into the supplier’s quality management practices, including defect rates and corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures and product compliance.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate several nuances related to quality control and certification:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulatory requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific standards applicable in their target markets to avoid legal complications.
-
Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and compliance can impact negotiations and supplier relationships. For instance, some regions may prioritize certifications more than others.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers maintain transparency in their supply chains, including the sourcing of materials and labor practices. This can help mitigate risks associated with unethical practices or substandard materials.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select reliable suppliers that meet their quality and compliance needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘harmonized code usa’
To successfully procure goods that require a Harmonized Code (HTSUS) in the United States, B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape of regulations and classifications. This guide provides a practical checklist to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring compliance and optimizing import operations.
Step 1: Understand the Importance of Harmonized Codes
Before diving into sourcing, it’s crucial to grasp the significance of Harmonized Codes. These codes are essential for accurately classifying goods for customs purposes, determining applicable duties, and ensuring compliance with U.S. import regulations. A misunderstanding of these codes can lead to costly delays and fines.
Step 2: Identify Your Product Categories
Start by categorizing the products you intend to import. Understanding the broad classification of your goods will help you narrow down the specific HTS codes applicable to them. This step is fundamental as it sets the groundwork for accurate coding, which directly affects duty rates and compliance.
- Conduct Market Research: Analyze similar products in your target market to see how they are classified.
- Consult Industry Experts: Engage with customs brokers or trade consultants who can provide insights based on current regulations.
Step 3: Utilize the HTSUS Database
Access the Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States (HTSUS) to find the correct codes for your products. This database contains over 21,000 items, making it a comprehensive resource for import classifications.
- Search by Keywords: Use relevant keywords or phrases related to your product to find potential HTS codes.
- Review Code Descriptions: Ensure that the descriptions match your product specifications to avoid misclassification.
Step 4: Verify Compliance with Chapter 99 Updates
Stay informed about any recent changes, particularly regarding Chapter 99 of the HTSUS, which may introduce temporary modifications to existing codes. Understanding these changes is critical as they can impose stricter import regulations and affect your sourcing strategy.
- Check Regularly: Periodically review updates from the U.S. International Trade Commission (ITC) for the latest information.
- Consult Customs Experts: If uncertain, reach out to customs brokerage professionals who can assist in interpreting these updates.
Step 5: Engage a Customs Broker
Consider hiring a licensed customs broker to assist with the import process. Brokers possess expertise in navigating the complexities of HTS codes, ensuring accurate classifications and compliance with U.S. customs laws.
- Evaluate Broker Credentials: Ensure the broker has a strong track record and familiarity with your specific product category.
- Discuss Fees and Services: Understand the fee structure and what services are included, such as classification advice and documentation preparation.
Step 6: Document Everything
Maintain comprehensive documentation for every step of the sourcing and import process. This includes invoices, shipping documents, and any correspondence regarding HTS code classifications. Proper documentation is vital for audits and ensures smooth customs clearance.
- Create a Filing System: Organize documents electronically and physically for easy access.
- Regularly Update Records: Keep your records current, especially when changes in product specifications or HTS codes occur.
Step 7: Plan for Duty Payment and Compliance Checks
Budget for duties based on the HTS codes assigned to your products and prepare for potential compliance checks by U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP). Proper financial planning can prevent unexpected costs.
- Understand Duty Rates: Familiarize yourself with the duty rates associated with your HTS codes to avoid budget overruns.
- Prepare for Inspections: Be ready for potential inspections by maintaining accurate records and ensuring compliance with U.S. regulations.
By following these steps, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing products that require a Harmonized Code in the U.S., ensuring compliance and optimizing their import processes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for harmonized code usa Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Harmonized Code USA Sourcing?
When sourcing products classified under the Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) in the USA, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials can vary significantly based on quality and availability. For example, sourcing high-grade materials may incur higher upfront costs but can lead to better product durability and customer satisfaction.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the region where production occurs. In many countries, labor is less expensive than in the USA, which can provide a competitive edge. However, it’s essential to consider the implications of labor quality and skills.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient operations can reduce overhead costs, positively impacting the overall pricing strategy.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom products. Buyers should discuss these costs upfront, as they can affect the minimum order quantities (MOQs) and pricing structures.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that products meet specifications. While this may add to the cost, it is vital for maintaining standards and avoiding costly recalls or returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary greatly based on the mode of transport, distance, and any tariffs applicable to the HTS codes. Understanding Incoterms is essential to gauge who bears these costs during international transactions.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically incorporate a profit margin based on market conditions, competition, and perceived value. Negotiating margins can help buyers secure better pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sourcing Costs for HTS Codes?
Several factors can influence pricing in the context of HTS code sourcing. These include:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger order volumes often yield better pricing due to economies of scale. However, it’s crucial to balance volume with actual demand to avoid excess inventory.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom products generally incur higher costs due to additional design and production efforts. Clear communication about specifications can help mitigate unexpected price increases.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects costs. Sustainable or specialized materials may command premium pricing but can enhance brand reputation and product appeal.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet specific certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) can be more expensive due to compliance costs. However, these certifications can also open doors to new markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and location can impact pricing. Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is critical. Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) dictate who is responsible for shipping costs and risks, directly influencing total expenses.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International Buyers Sourcing Under HTS Codes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can significantly impact overall sourcing costs. Here are some strategies:
-
Research and Benchmarking: Understand market rates and benchmarks for the specific goods you are sourcing. This knowledge can strengthen your negotiating position.
-
Discuss Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Emphasize the importance of TCO in negotiations. Consider not only the purchase price but also ongoing costs such as maintenance, shipping, and potential tariffs.
-
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing trust and a long-term partnership with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time.
-
Be Transparent About Your Needs: Clearly communicate your requirements and constraints. This transparency can foster collaboration and lead to mutually beneficial solutions.
-
Stay Flexible: Be open to alternative solutions or compromises. Flexibility can lead to creative solutions that benefit both parties.
Conclusion
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing influences in HTS code sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers. By strategically navigating these aspects, buyers can optimize their procurement processes and achieve favorable outcomes in their sourcing endeavors. Always remember to consider indicative prices as a guideline, as actual costs may vary based on specific circumstances and negotiations.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing harmonized code usa With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions for Harmonized Codes
In the realm of international trade, the Harmonized Code USA (HTSUS) plays a critical role in categorizing goods for customs purposes. However, various alternative classification systems and methodologies exist that can offer different benefits to B2B buyers. Understanding these alternatives can help businesses streamline their import processes and ensure compliance with international regulations while maximizing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Comparison Table of Harmonized Code USA and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Harmonized Code USA (HTSUS) | Alternative 1: Global Harmonized System (HS) | Alternative 2: National Tariff Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy in duty determination; extensive item classification | Global standardization; widely recognized | Varies by country; less standardization |
| Cost | May incur higher brokerage fees | Generally lower costs; simpler structure | Costs vary; potential hidden fees for updates |
| Ease of Implementation | Complex; requires thorough understanding of codes | Easier to implement due to its simplicity | Moderate complexity; requires local knowledge |
| Maintenance | Regular updates; requires active monitoring | Less frequent updates; easier to maintain | Varies; may require local expertise for changes |
| Best Use Case | Best for detailed and specific U.S. imports | Ideal for global transactions and trade | Useful for specific national requirements |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Global Harmonized System (HS)
The HS code system is a standardized international classification that is six digits long. It is widely used across various countries, making it an ideal choice for businesses engaged in global trade. One of its primary advantages is its simplicity and widespread acceptance, which facilitates smoother customs processes in multiple jurisdictions. However, the HS system may lack the granularity needed for certain products, leading to potential misclassification and unforeseen tariffs.
National Tariff Codes
National tariff codes refer to country-specific classification systems that can vary widely in structure and complexity. These codes are beneficial for businesses that primarily operate within a single country or region. They offer specific details that may not be covered under the HS or HTSUS codes. However, the variability and lack of standardization can lead to confusion, particularly for companies looking to expand their markets internationally. Moreover, navigating these codes may require local expertise to ensure compliance and accurate classification.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Classification System
For B2B buyers, selecting the most suitable classification system depends on several factors, including the scope of their business operations, the complexity of their product lines, and their target markets. If a business primarily imports goods into the U.S. and requires detailed tariff classifications, the Harmonized Code USA may be the best fit. Conversely, companies with a global trading focus might benefit more from the Global Harmonized System due to its simplicity and universal acceptance. Finally, businesses operating in specific national markets should consider National Tariff Codes, keeping in mind the need for local expertise. Ultimately, understanding the nuances of each option will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for harmonized code usa
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Harmonized Codes in the USA?
Understanding the essential technical properties related to Harmonized Codes in the USA is crucial for international B2B buyers. These properties not only determine the classification of goods but also impact duty rates and compliance requirements. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
HTS Code Structure
The Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) code is a ten-digit numerical code used to classify imported goods. The first six digits align with the global Harmonized System (HS) code, while the last four digits are unique to the U.S. This structure allows for precise identification of products, ensuring accurate tariff assessments. For businesses, using the correct HTS code is vital to avoid penalties and ensure compliance with U.S. Customs and Border Protection regulations. -
Duty Rates
Each HTS code corresponds to a specific duty rate, which is the tax imposed on imported goods. Understanding these rates is crucial for B2B buyers as they directly influence the total landed cost of products. Accurate duty rate calculations can significantly affect pricing strategies and profit margins, making it essential for businesses to stay updated on any changes in tariff classifications. -
Statistical Suffix
The last two digits of the HTS code serve as a statistical suffix that helps the U.S. government track trade data. This information is vital for market analysis and economic forecasting. For international buyers, being aware of statistical suffixes can aid in understanding market trends and making informed purchasing decisions. -
Product Description Requirements
Each HTS code is accompanied by specific product descriptions that detail the characteristics of the goods. These descriptions must accurately reflect the items being imported to avoid classification errors. For B2B transactions, clear product descriptions enhance communication and reduce the risk of customs delays, which can impact supply chain efficiency. -
Trade Compliance and Regulations
Compliance with HTS codes is not just about classification; it also involves adhering to various trade regulations. Failure to comply can lead to fines, delays, and even confiscation of goods. International buyers must familiarize themselves with U.S. trade laws to ensure their shipments meet all requirements, thereby protecting their investments.
What Are Some Common Trade Terminology Related to Harmonized Codes?
Navigating the complexities of harmonized codes also requires understanding industry-specific jargon. Here are some key terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of harmonized codes, OEM products often have specific classifications that affect tariffs and regulations. Understanding OEM classifications can help buyers source products more efficiently and avoid unnecessary costs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory and cash flow effectively. It also impacts negotiations regarding pricing and shipping costs, making it a critical consideration in international trade. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing information for specific goods or services. This term is important in the context of harmonized codes, as accurate HTS classifications must accompany RFQs to ensure that suppliers provide correct pricing based on applicable duty rates. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to clarify shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation, particularly when dealing with complex customs processes related to harmonized codes. -
Customs Bond
A customs bond is a contract between a surety, the importer, and U.S. Customs that ensures compliance with customs regulations. For international buyers, securing a customs bond is essential for facilitating imports, as it provides a guarantee that duties and taxes will be paid.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the harmonized code system in the USA more effectively, ensuring compliance and optimizing their supply chain operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the harmonized code usa Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Affecting the Harmonized Code USA Sector?
The global trade landscape is continually evolving, influenced by various factors that shape market dynamics. For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial. Key drivers include the increasing complexity of international regulations, which necessitate a nuanced approach to harmonized tariff classifications. The U.S. Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTSUS) has recently seen modifications under Chapter 99, imposing stricter regulations on certain categories of imports. This shift emphasizes the need for companies to stay updated on compliance requirements to avoid costly penalties.
Emerging technologies are transforming sourcing strategies as well. Automation and artificial intelligence are making it easier to manage vast datasets, enabling businesses to classify products efficiently. Furthermore, digital platforms are streamlining communication between suppliers and customs brokers, facilitating smoother import processes. As a result, B2B buyers must leverage these technologies to enhance their operational efficiency and minimize delays in their supply chains.
Understanding regional market trends is equally important. For instance, countries like Nigeria and Brazil are experiencing growth in sectors such as agriculture and textiles, leading to increased import activities. Buyers must align their sourcing strategies with these trends to capitalize on emerging opportunities while navigating the complexities of HTS codes.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Harmonized Code USA Sector?
As global awareness of environmental issues rises, sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming imperative in the B2B landscape. The environmental impact of products and their supply chains is under scrutiny, prompting businesses to adopt more responsible sourcing practices. For international buyers, this means prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices and can provide certifications that verify their commitments to environmental stewardship.
In the context of the Harmonized Code USA sector, the integration of ‘green’ certifications into product classifications can influence duty rates and compliance requirements. Products with eco-friendly certifications may benefit from reduced tariffs or expedited customs processing, making them more attractive in the U.S. market. B2B buyers should seek suppliers who can demonstrate adherence to recognized sustainability standards, as this not only enhances brand reputation but also meets the growing consumer demand for ethically sourced products.
Moreover, sourcing materials that have lower environmental impacts, such as recycled or sustainably sourced inputs, can help companies comply with stricter regulations while reducing their overall carbon footprint. As sustainability becomes a focal point for many organizations, aligning sourcing strategies with these values is not just a trend but a necessity for long-term success.
What Is the Historical Context of the Harmonized Code USA Sector?
The Harmonized System (HS) was established in 1988 by the World Customs Organization (WCO) to standardize the classification of traded goods globally. The United States adopted its version, the Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTSUS), which expanded the basic HS codes to a ten-digit format to accommodate specific U.S. trade laws and practices.
Over the years, the HTSUS has evolved to reflect changes in trade patterns, technological advancements, and international agreements. The introduction of Chapter 99 and other amendments signifies the U.S. government’s responsiveness to global market shifts and trade relations. Understanding this historical context allows international B2B buyers to appreciate the complexities and importance of proper classification when navigating U.S. customs regulations, ultimately facilitating smoother trade operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of harmonized code usa
-
How do I classify my products using the Harmonized Code in the USA?
To classify your products using the Harmonized Code (HTSUS), start by identifying the specific characteristics of your goods. Utilize the U.S. International Trade Commission’s HTSUS database, which categorizes over 21,000 items. You’ll need to determine the appropriate chapter, heading, and subheading for your product. If uncertain, consider consulting a customs broker or trade expert who can assist in ensuring accurate classification, as this affects duty rates and compliance with U.S. customs regulations. -
What are the consequences of misclassifying goods under the Harmonized Code?
Misclassifying goods can lead to significant consequences, including overpayment of duties, fines, and delays in customs clearance. It may also result in confiscation of goods if they are deemed illegal or hazardous under the wrong classification. Accurate classification is critical for compliance with U.S. Customs and Border Protection regulations, and it ensures that your business avoids unnecessary financial penalties and maintains a positive trade relationship with U.S. authorities. -
What is the difference between HTS and HS codes?
The HTS code is a specific classification system used in the United States, while the HS code (Harmonized System) is a global standard used by most countries. HTS codes are ten digits long and provide more detailed classifications compared to the six-digit HS codes. The first six digits of an HTS code correspond to the HS code, while the additional four digits represent U.S.-specific classifications, which can affect tariff rates and import regulations. -
How can I determine the duty rates for my imported goods?
To determine duty rates for your imported goods, you first need to classify your products using the HTSUS. Once you have the correct HTS code, refer to the Harmonized Tariff Schedule, which lists the applicable duty rates for each code. You can access this schedule online through the U.S. International Trade Commission’s website. Additionally, customs brokers can provide valuable insights and assist with calculations to ensure you are prepared for the associated costs of importing your goods. -
What are common payment terms for B2B transactions in international trade?
Common payment terms in international B2B transactions include letters of credit, advance payments, and open account terms. Letters of credit provide a secure method of payment, ensuring that funds are released only when the seller meets specific conditions. Advance payments offer security for the seller but can be risky for buyers. Open account terms allow buyers to pay after receiving goods, fostering trust but requiring strong relationships. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with your risk tolerance and business objectives. -
How do I vet suppliers when sourcing products under the Harmonized Code?
Vetting suppliers involves conducting thorough research and due diligence. Start by checking their business credentials, such as registration, certifications, and references. Request samples of products to assess quality and compliance with U.S. standards. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or ThomasNet to read reviews and ratings. Additionally, consider visiting suppliers in person or using third-party inspection services to verify capabilities and ensure they can meet your specific requirements under the Harmonized Code. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing goods?
When importing goods, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, transit times, and customs clearance processes. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with U.S. regulations to streamline the shipping process. Understand the costs involved, including freight charges, insurance, and duties. Additionally, maintain clear communication with your supplier regarding packaging and documentation to avoid delays at customs. Having a robust logistics strategy can minimize disruptions and enhance the efficiency of your supply chain. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for imported products?
To ensure quality assurance for imported products, establish clear specifications and standards with your suppliers. Conduct pre-shipment inspections to verify that goods meet your requirements before they leave the supplier’s facility. Implement a quality control process that includes regular audits and testing of products upon arrival. Collaborating with third-party inspection agencies can also enhance your quality assurance efforts, providing an objective assessment of product quality and compliance with U.S. regulations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for harmonized code usa
In navigating the complexities of the Harmonized Code system, international B2B buyers can unlock significant advantages in strategic sourcing. Understanding HTS codes not only facilitates compliance with U.S. customs regulations but also empowers businesses to optimize their supply chains and minimize costs. Accurate classification of goods ensures that importers pay the correct duties, avoiding potential fines and delays, while also enabling better negotiation with suppliers.
As we look to the future, the integration of updated codes and evolving regulations—such as those introduced under Chapter 99—will necessitate ongoing vigilance and adaptability. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must stay informed about these changes to maintain competitive advantages in the U.S. market.
By investing time in mastering the HTS code system, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and foster stronger relationships with customs brokers and suppliers. Now is the time to take proactive steps in understanding these classifications to drive growth and success in international trade. Engage with customs experts, invest in training, and leverage technology to streamline your sourcing processes for a more prosperous future.